FABER test
- This test is also known as Patrik’s test or the Figure – 4 test.
- This test is described by Dr. Donald Corenman which is MD – Colorado Spine Doctor.
- This test stands for Flexion, Abduction & External Rotation [lateral rotation].
- These three movements are combined & given to result in clinical pain which is a provocation test to assist in the diagnosis of pathologies at to hip, lumbar& sacroiliac regions.
Purpose of FABER test:
- This test is used to identify the presence of hip pathology
- Which is attempting to reproduce pain in the hip, sacroiliac region, or lumbar spine.
- This test is a passive screening tool for identifying the many musculoskeletal pathological like hip, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, lumbar spine/an iliopsoas spasm.
- This test also assesses to hip due to the forces are being transferred through to the joint.
- Position of flexion, abduction &external rotation means lateral rotation does combine & applied over pressure & apply to stresses on the femoral-acetabular joint which is produced pain if the patient feels too irritated.
- Combine with other tests like ROM [ range of movement ]&hip quadrant test, this FABER test is a useful tool to guide practitioners when the patient is referred for further imaging with persistent hip/groin pain.
- When this test is clustered, it is provided with highly useful information for identifying suffering from sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
- In This test of the sacroiliac joint, as the horizontal abduction force is going through the femur& the soft tissues are under tension which is transfer the forces to the sacroiliac joint.
- This test is indicated to pathology located in the hip/sacroiliac joint.
How to perform of FABER test?
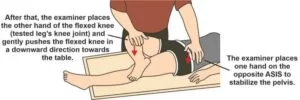
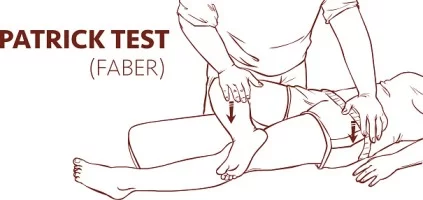
- Starting position of the test for the patient is supine.
- The leg is placed into figure-4 position means hip flexed &abducted with to lateral ankle is resting on to contra lateral thigh proximal side of the knee.
- After that stabilizing to the opposite side of the pelvis at anterior superior iliac spine, then applied to external rotation, posterior or abduction force is lightly applied on the ipsilateral knee till the end range of motion [ ROM] is achieved.
- Then further few small-amplitude oscillations are applied for checking the pain provocation at to end range of motion[ROM].
Result of FABER test?
- The positive test is indicated the leg’s knee is remaining above the opposite straight leg.
- If test positive, the test indicates that the hip joint may be affected, that there may be illiospasm, or that the sacroiliac joint may be affected.
- The negative test is indicated to leg’s knee is falling to the table /at least being parallel with to opposite leg.
Interpretation of FABER test?
- When this test is positive it helps to guide many clinical diagnoses:
- Sacroiliitis
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain on external hip rotation
- Intraarticular Hip Disorder
- Iliopsoas Strain or Iliopsoas Bursitis
- Groin Pain on external hip rotation
- Hip Osteoarthritis
- Hip chondral lesion
- Hip loose bodies
- Hip Impingement includes a femoral acetabular impingement
- Hip Labral Tear
- Posterior Hip Impingement
- Posterior Hip Pain on external hip rotation
Evidence of FABER test?
Reliability :
- This test is measured with a ruler or normalized FABER range of movement [ROM] & inclinometer in all three resulting in excellent for intra-rater reliability, with to highest ICC which is being demonstrated for to inclinometer so that ICC value is 0.86, 0.86 & 0.91).
- With The use of an inclinometer which is increased reliability when this test is performed by an experienced clinician for comparison with height measurements.
- Sensitivity of this test for identification of hip pathology & with the arthroscopy =0.89
- For Correlation with a positive test for OA on radio graphs – r = 0.54
- Kappa of this test = 95%
- Confidence interval = 0.63 [0.43-0.83]
- Kappa Maximum of this test = 0.83
- Percent agreement of this test =84%,
- Prevalence of this test =0.37
- Bias of this test =0.07
The diagnostic value of this test is compared with MR arthrography in labral tear:
Result of this test :
- Sensitivity of this comparing =41%
- Specificity of this comparing =100%
- Positive predictive value of this comparing = 100%
- Negative predictive value of this comparing = 9%
- Validity&reliability of this test is very contradictory;
- Some people say this test is an invalid &unreliable test; while some people disagree about this outcome & feel the physical diagnostic tests do not have enough quality for evidence which is doing the support for diagnosis purposes.
Clinical Relevance of FABER test?
- This test is used in assessment of the hip, sacroiliac joint & lumbar spine pain is provocation test which is alongside quality for subject assessment & basic objective assessment.
- This test is performed quick & give a measure of ROM [range of movement ]as well as being to pain provocation test, although it does not give a clear diagnosis.
- It assists the user in clinically reasoning which is performed in further tests /exercises.




2 Comments