Special test for the sacroiliac joint involvement:
- This test is reported that active mobility tests should not be used to test the passive mobility of the sacroiliac joints.
- Patient felt passive movements used to look for asymmetry were more effective.
- These tests are applied to the clinic for checking the involvement of the SI joint.
- These clinical tests are applied by to therapist or doctor when the patient is complaining about pelvic pain.
Name of the special test of the sacroiliac joint involvement:
- Flamingo test or maneuver
- Goldthwait’s test
- Ipsilateral anterior rotation test
- Laguere’s sign
- Mazion’s pelvic maneuver
- Piedallu’s sign
- Supine to sit the test
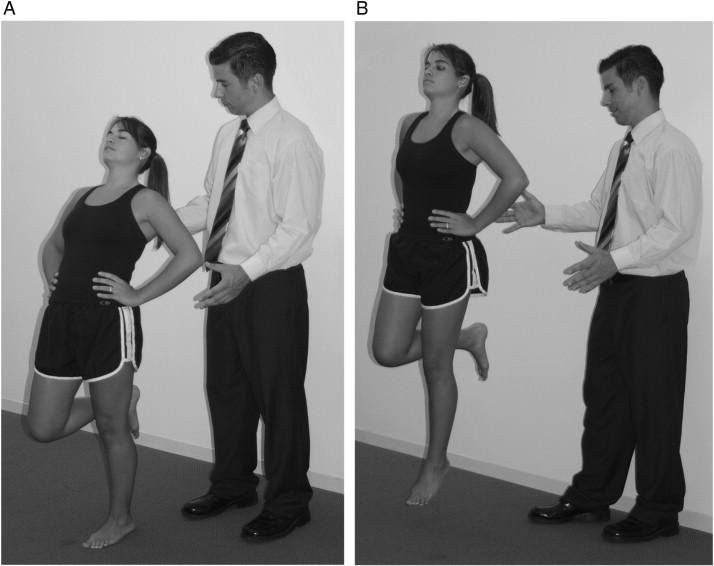
Flamingo test or maneuver:-
- Purpose = This flamingo test or maneuver is used to check the pain on the symphysis pubic.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient is standing position.
- Then the examiner instructs the patient to stand on one leg.
- When the patient is standing on one leg, the weight of the trunk causes the sacrum to shift forward & distally with forwarding rotation.
- The ilium moves in the opposite occur, but the stress is greatest on the stance side.
- Result = Pain in the symphysis pubic or sacroiliac joint indicates a positive test for lesions in whichever structure is painful.
- The stress is increased in the patient’s hip of one leg.
- This test position is also used in the stress x-ray of the symphysis pubis.
Goldthwait’s test:-
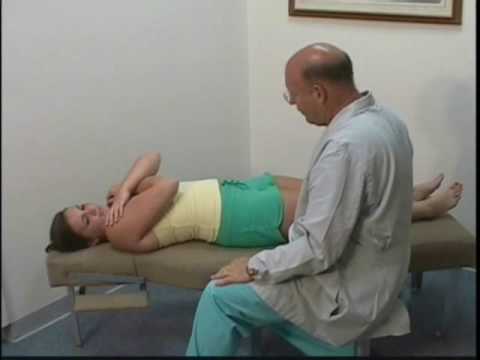
- Purpose = This Goldthwait’s test is used to check the neurological involvement of the sciatic nerve.
- Technique = The patient is in the supine position for the Goldthwait’s test in starting position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] places one hand under the lumbar spine so that each finger is an interspinous space.
- The examiner [ therapist ] uses the other hand to perform SLR.
- Result = If the pain is elicited before movement occurs at the inter spaces, the problem is in the sacroiliac joint.
- If the patient feels pain during the inter space movement, it is indicated to be a lumbar spine dysfunction.
- As with the SLR test, pain may be referred to along the course of the sciatic nerve if there is neurological involvement.
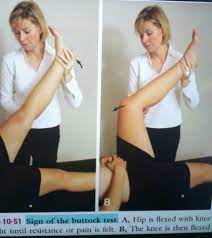
Laguere’s sign:-
- Purpose = This laguere’s sign is used to check the hip pathology.
- Technique = In the starting position the patient is in the supine position for the laguere’s sign test.
- To test the left sacroiliac joint, the examiner [ therapist ] flexes, abducts & laterally rotates the patient’s left hip joint, applying an over pressure at the end of the ROM.
- The examiner [ therapist ] must stabilize the pelvis on the opposite side by holding the opposite ASIS down.
- Result = Pain in the left sacroiliac joint constitutes a positive test.
- The other side is tested for comparison.
- This test should be performed with caution for patients with hip pathology, because hip pain may ensure.
Mazion’s pelvic maneuver:-
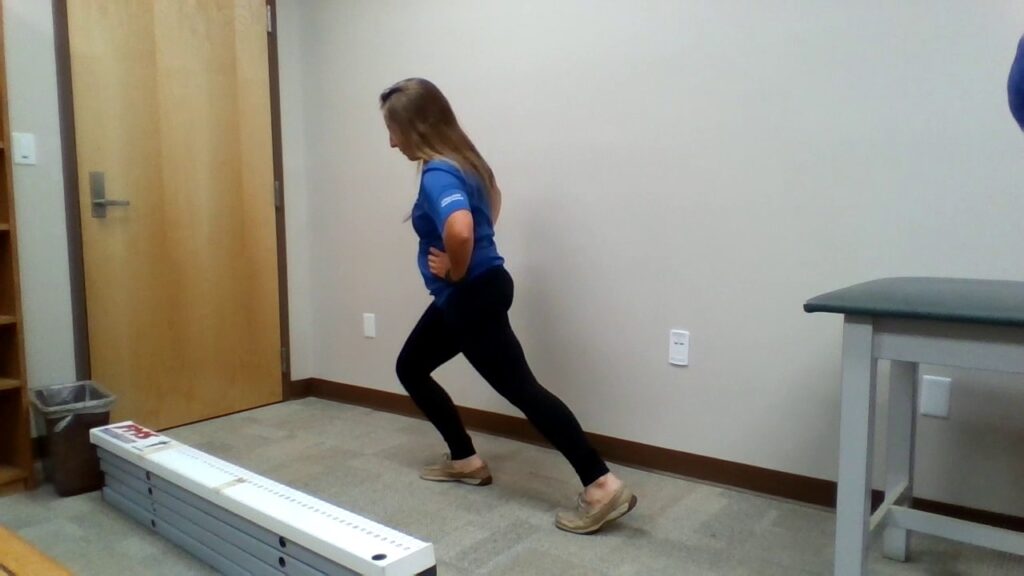

- This test is also known as the standing lunge test.
- Purpose = This mazion’s pelvic maneuver is used to check the forward displacement of the ilium.
- Technique = The patient is in a standing position for the test.
- The patient stands in a straddle position with the limb on the unaffected side forward so that the feet are 0.5 to 1 meter [ 2 to 3 feet ] apart.
- The patient bends forward, trying to touch the floor until the heel of the back leg lifts off the floor.
- Result = If the pain is produced in the lower trunk on the affected side, it is considered a positive test for the unilateral forward displacement of the ilium relative to the sacrum.
Piedallu’s sign:
- Purpose = This piedallu’s sign is used to check the torsion movement of the SI joint.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient is sitting position for the piedallu’s sign test.
- Then the examiner asked the to patient sit on a hard, flat surface.
- The position keeps the muscles from affecting the pelvic flexion symmetry & increases the stability of the ilia.
- This test is given to effect, it is a test of the sacrum on the ilia.
- The examiner [ therapist ] palpates the PSIS & compares their heights.
- If one PSIS, usually the painful one, is lower than the other, the patient is asked to forward flex while remaining seated.
- Result = If the lower PSIS becomes the higher one on forwarding flexion, the test is positive.
- It is that side that is affected.
- Because the affected joint is not moved properly & so that it is hypo mobile, it goes from a low to a high position.
- This test is believed to indicate an abnormality in the torsion movement at the sacroiliac joint = SI joint.
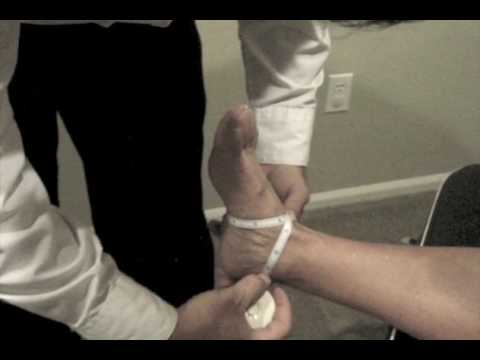
Supine to sit the test:
- This supine to sitting test is used to check the long sitting test.
- Purpose = This supine to sit test is used to check the lumbar pathology.
- Technique = The patient lies supine with the leg straight.
- The examiner [ therapist ] ensures that the medial malleoli are level.
- The examiner is asked to the patient to sit up,& the examiner observes whether one leg moves up farther than the other.
- If so, it is believed that there is a functional leg length difference resulting from a pelvic dysfunction caused by pelvic torsion or rotation,
- Result =It may also be caused by spasm of the lumbar muscled in the presence of lumbar pathology.