Special test for the vascular signs:
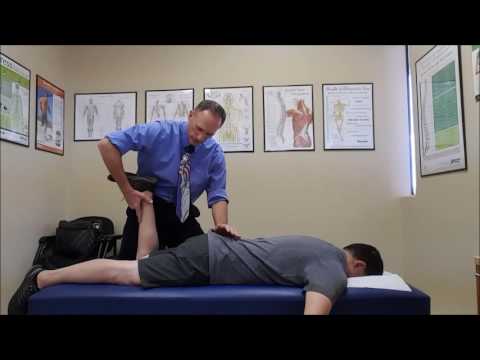
- Vertebral & internal carotid artery testing is an important component of the cervical spine assessment in cases where end range mobilization & manipulation treatment techniques are contemplated, especially if the techniques involve a rotary component& the upper cervical spine.
- The vertebral artery is most vulnerable to injury as it transitions from its protective area in the forearm transversarium within the cervical spine transverse processes, then looping before it enters the cranial vault behind the first vertebra.
- Vertebrobasilar artery insufficiency leads to ischemic symptoms from the pons, medulla & cerebellum of the brain.
- Several authors have reported that the vertebral artery tests have not been conclusively proven to be effective in indicating stretching & occlusion of the vertebral artery or internal carotid artery but do say that the tests should be performed to decrease the risk of potentially catastrophic complications when doing end – range mobilization or manipulation, most of the upper cervical spine.
- Although the following text discusses many vertebral artery tests, not all of them have to be performed.
- However, the patient must be tested in the position in which the treatment will be given & held in that position for at least 10 to 30 seconds, mostly if the technique is an end-range technique or involve the upper cervical spine.
- Any of the signs & symptoms that indicate vertebral – basilar artery problems would indicate the treatment should not be given.
- When doing all the test more than one test,10 seconds is elapsed between every test to ensure there are no latent symptoms from the previous test.
- These tests are often more effective if performed with the patient sitting because the blood must flow against gravity & there is a restriction caused by the passive movement.
- However, the supine position allows a greater passive range of movement.
- Movements to the right tend to have more effect on the left vertebral artery,& movements to the left tend to have more effect on the right artery.
Name of the Special test for the vascular signs:
- Barre’s test
- Hautant’s test
- Naffziger test
- Underburg’s test
Barre’s test:-
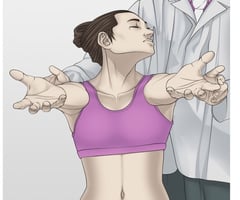
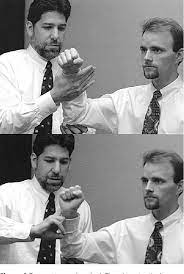
- Purpose = This barre’s test is used to check the blood flow in the brainstem.
- Technique = The patient is in a standing position for the test.
- The patient stands with the shoulder forward flexed to 90′, elbows straight & forearms supinated, palms up & eyes closed, holding the position for 10 to 20 seconds.
- Result = The test is considered positive if one arm slowly falls with simultaneous forearm pronation.
- The cause of the test is thought to be diminished blood flow to the brainstem of the brain.
- This barre’s test is identical to the first part of Hautant’s test.
Hautant’s test:-
- This test has two parts & is used to differentiate dizziness or vertigo caused by articular problems from that caused by vascular problems.
- Purpose = This hautant’s test is used to check the vascular impairment to the brain.
- Technique = The patient sits & Forward flexes both arm to 90′.
- The eyes are then closed.
- The examiner [ therapist ] watches for any loss of arm position.
- If the patient arms move, the cause is non vascular.
- The patient is then asked to rotate or extended & rotated the neck.
- This position is held while the eyes are again closed.
- Result = If waving of the arms occurs, the dysfunction is caused by vascular impairment to the brain.
- Each position of test held for 10 to 30 seconds.
Naffziger test:-
- Purpose = This Naffziger test is used to check the compression of the jugular veins.
- Technique = The patient is seated,& the examiner [ therapist ] stands behind the patient with his or her fingers over the patient’s jugular veins.
- The examiner [ therapist ] compresses the veins for 30 seconds [ Naffziger ]recommended 10 minutes] & then asks the patient to cough.
- Result = Pain may indicate nerve root problems or space-occupying lesions.
- If similar symptoms or lightheadedness occur with the compression of the jugular veins, the test should be terminated.
Underberg’s test:-
- Purpose = This underburg’s test is used to check the blood supply of the brain
- Technique = The patient stands with the shoulders forward flexed to 90′, elbow joint straight & forearms supinated.
- The patient then closes the eyes & marches in place while holding the extended & rotated head to one side.
- The test is repeated with head movement to the opposite side.
- Result = The test is considered positive if there is dropping of the arms, loss of balance, or pronation of the hands.
- A positive test result is indicated to the decreased blood supply to the brain.