Static vertebral artery tests:
- These Static vertebral artery tests are used to check the pathology of the vertebral artery.
- This clinical test is applied by to therapist when the patient is complaining about neurological symptoms in the upper limb.
- This Static vertebral artery test is applied to the examination part of the assessment.
- This Static vertebral artery test is passive.
What is the purpose of the Static vertebral artery tests?
This Static vertebral artery test is used to check the pathology of the vertebral artery.
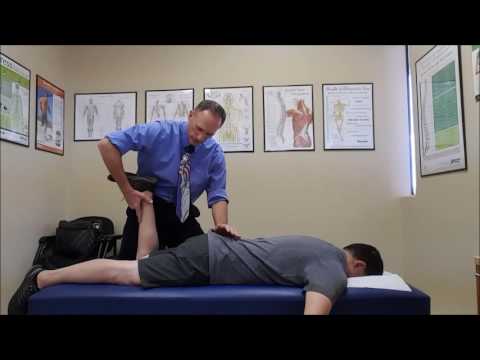
How do you perform the Static vertebral artery tests?
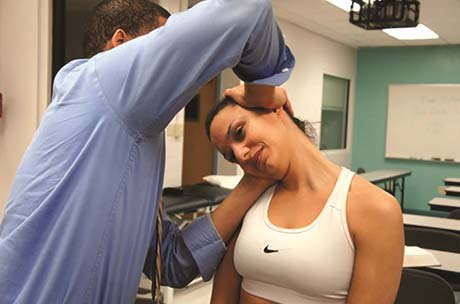
- The examiner [ therapist ] may test the following passive movements with the patient supine or sitting, as advocated by grant, watching for eye nystagmus & complaint by the patient of dizziness, lightheadedness, or visual disturbances.
- Each of these tests is increasingly provocative.
- If symptoms occur with the first test, there is no need to progress to the next test.
In the sitting position :
- Sustained full neck & head extension.
- Sustained full neck & head rotation, right & left [ if this movement causes symptoms, it is sometimes called a positive Barre – Lieou sign.]
- Sustained full neck & head rotation with extension movement right & left [ DeKleyn’s test].
- Provocative movement position.
- Quick head movement into provocative position.
- Quick repeated head movement into provocative position.
- Patient’s head is put still, then sustained do the trunk movement left & right.
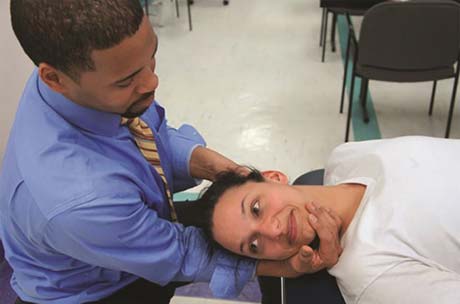
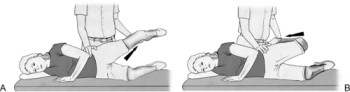
In supine position:
- Sustained full neck & head extension movement.
- Sustained full neck & head rotation left & right.
- Sustained full neck & head rotation with extension left-right [ if combined with side flexion, it is called Hallpike maneuver ]extension combined with rotation is the position most likely to occlude the vertebral artery.
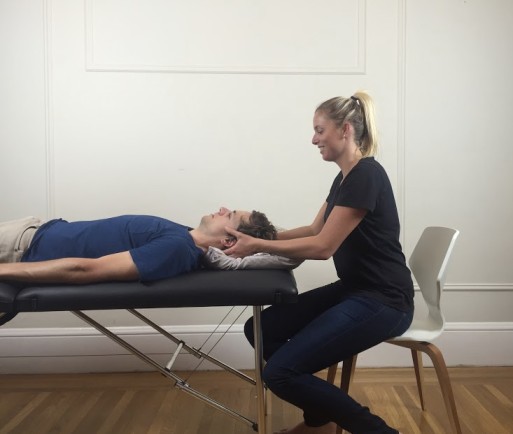
- Unilateral posteroanterior oscillation [ Maitland’s grade – IV ] of C1 to C2 facet joints [ prone lying ] with the head rotated left & right.
- Simulated mobilization & manipulation position.
- Each position of the test is must be held for at least 10 to 30 seconds till the symptoms are evoked.
- Extension in isolation is more likely to test the patency of the inter vertebral forearm, wheres rotation & side flexion or mostly rotation & extension are more likely to test the vertebral artery.
- If the symptoms are evoked so that care must be taken concerning for any treatment to follow.
- Aspinall advocated the use of a progressive series of clinical tests are evaluated the artery.
- With these tests, the examiner [ therapist ] progressively moves from the lower cervical spine & lower vertebral artery to the upper cervical spine & upper vertebral artery where it is more vulnerable to pathology.



we are sorry, we do not have video tutorials.