Tibialis Anterior Muscle Pain
What is the Tibialis Anterior Muscle Pain?
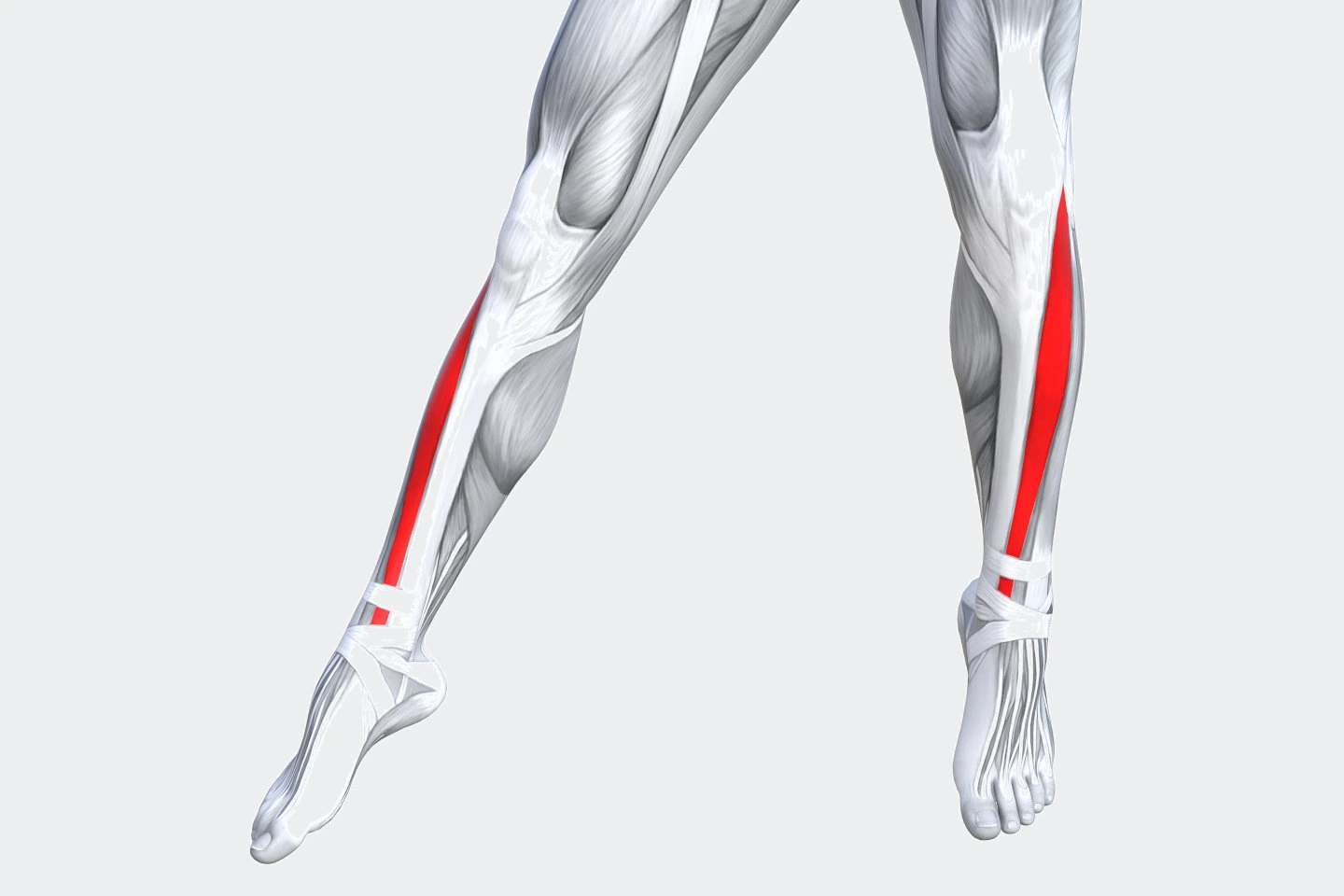
This tibialis anterior muscle pain produces by the muscle, which is situated at the front of the lower leg and is connected to the top of the foot.
The patient feels the pain in this region is complicated by the shin splints, which produce pain on the inside of the lower leg and shin.
This pain is produced at the front of the lower leg which lies outside of the tibia bone and at the tendon on the top of the foot.
This muscle tendon is the large tendon that is visually crossing the front of the ankle joint.
Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The Tibialis anterior muscle is situated on the lateral side of the tibia.
This muscle is thick or fleshy above and tendinous below.
This Tibialis Anterior muscle fiber is run vertically downward and ends in a muscle tendon, which is apparent at the anterior surface of the muscle at the lower third of the leg.
This Tibialis Anterior Muscle is overlap the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve in the upper part of the leg.
This Tibialis Anterior Muscle originates from the :
The lateral condyle and upper half or 2/3 of the lateral surface of the body of the tibia.
This muscle is the deep surface of the fascia.
This Tibialis Anterior Muscle is inserted at the medial and under the surface of the first cuneiform bone and the base of the 1st metatarsal bone.
One of the main functions of this tibialis anterior muscle is to pull the foot up means ankle joint flexion and ankle joint dorsiflexion and it assists in keeping the arch from collapsing.
Causes of Tibialis Anterior Muscle Pain
- Overuse of the tibialis anterior muscle and injury in the muscle produces pain in the muscle.
- The collapse of the medial means inside arch with an inwards ankle shift, because the anterior tibialis muscle assists in the keep medial arch up, and a collapse of the arch cause overwork of the muscle.
- Very rare to occur a tear or injury to the tibialis anterior muscle from a sudden injury.
- Sometimes due to injury muscle strain in the tibialis anterior muscle also occur.
- If the patient does the repetitive use of the tibialis anterior muscle, it is produced minute rips inside the tibialis anterior tendon.
- It occurs in microscopic injuries and occurs to an inflammatory reaction in the muscle.
- When the patient is worn to strapping or shoelaces too high, it does injury in the tibialis anterior tendon, which is present in the front of the ankle joint.
Symptoms of Tibialis Anterior Pain
- The patient feels pain or tightness in the front of the lower leg.
- This pain is felt while walking or while applying pressure to the affected site.
- While the patient walking, the pain is become more severe while lowering the foot to the ground, directly after the heel strike.
- The patient feels the spasms in the muscle due to the overuse of the muscle.
- Also, presents tenderness at the point of the muscle.
- Patients feel the ankle joint stiff when they occur tendinopathy in the anterior tibialis muscle.
- The patient also feels pain during walking.
- The patient feels the high temperature over the pain site.
- The patient also presents an abnormal gait.
- When they occur to anterior tibialis muscle rupture or injury, it is lead to foot drop, the diminished power of dorsiflexor muscles, and also decreases the strength of ankle flexor muscles and reduced the ability of the foot motion.
When does the patient require to contact the doctor?
- When the muscle pain is not healed and relieved by after the home treatment of RICE principle and medicine as soon as possible contact the doctor.
- If the patient and the patient’s relatives observe the abnormal gait in the patient.
- Also, observe to foot drop in the patient.
Treatment of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle Pain
RICE principle:
In the first starting stage of the exercise used to RICE principle at the home.
R rest – The patient is doing the rest when the patient is feeling the pain means not doing long walking and overuse of work.
I ice -The patient applied ice on the site of the pain for 20 minutes, the patient is also used to ice packs and frozen peas.
C compression -Warp to bandage for the compression around the place of pain the reduce the swelling.
E elevation – elevate the foot for reducing the swelling.
Orthotics:
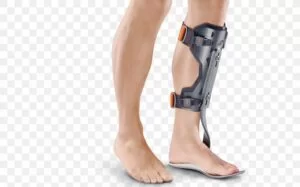
Orthotics help to support the foot and reduce strain on the anterior tibialis muscle.
When this muscle strain happens due to a collapsed arch, the orthotic device helps to push the foot and release the muscle strain at the anterior tibialis muscle.
It also occurs due to compensation from pain so these orthotics prevent this compensation, this pain must first be dealt with.
If the pain is produced by the sudden injury these orthotics is played a significant factor in the healing.
Footwear:
Using the right footwear is helpful to reduce strain on the anterior tibialis muscle by assisting with the proper support.
The proper footwear is beneficial to the patient for complimenting an orthotic device.
The appropriate shoe depends on the specific foot mechanics.
In most cases, a neutral running shoe and walking shoe are worn with any orthotic device.
In some cases, with the advice from the orthotic professional, a stable running shoe is worn to be required in combination with the orthotic device.
Another characteristic to consider with the anterior tibialis muscle is the weight of the shoe.
If the tibialis anterior muscle is weak or healing is slow use of the lighter shoe is recommended.
The patient is also used to kinesiology tape to relieve the stress on the inflamed tibialis anterior tendon.
The patient is using anti-inflammatory medicines means NSAIDs help to minimize pain and inflammation.
A runner holding their tibialis anterior pain.
The patient present to reduce foot motion.
Physiotherapy Treatment for the tibias anterior muscle pain
The physiotherapy treatment includes Electrotherapy modalities and exercise which is used to relieve pain relief of the muscle.
Electrotherapy modalities such as Interferential therapy(IFT), Ultrasound therapy(US), Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) are useful to relieve muscle pain.
Stretching exercise for tibialis anterior muscle pain
- Standing Tibialis Anterior Shin Stretch
- Kneeling Shin Stretch:
- Seated Shin Stretch
- Lying Shin Stretch
- Stair Stretch
- Standing Stretch
- Tennis Ball Massage
- Band foot drop
- Seated toe raise
- Wall to raise
- Heel walk
- Tibialis Anterior press and flex

Standing Tibialis Anterior Shin Stretch:
The patient’s position is in the standing position.
The patient is used to a hand on a wall or other support for balance, then both knees are flexed slightly.
The patient’s foot remains squarely on the floor.
The other foot of the patient to be stretched is placed just behind this stable foot, with the toe of the stretching foot touching the floor.
Keep the toe firmly on the floor and pull the stretching leg forward so that feel a stretch from the top of the stretching foot through the shins.
Once the patient feels stretched, then maintain this stretching position for 15-30 seconds.
Repeat this stretch exercise with the other foot.
Then use this stretch as part of a warm-up stretching routine or as part of a cool-down.
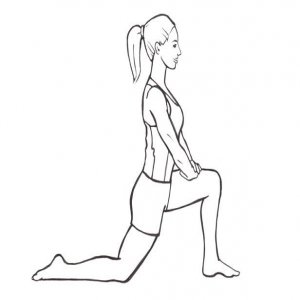
Kneeling Shin Stretch:
The patient’s position is kneeling to gently stretch the shins.
The patient’s right knee flexion provides the stretch as the sitting position on the heels.
If it leads to pain in the knees, skip it.
Kneel on a mat with the tops of the feet flat on the ground and buttocks over the heels.
Maintain this exercise for 15-20 seconds.
Seated Shin Stretch:
The patient’s position is to drop the knee joint towards the floor so that the toe of the foot is extended into the floor as in the standing stretch.
After then gently pull the forward while the toe is planted in the ground, similar to the standing stretch but seated.
Maintain this stretching position for 15-20 seconds.
Then repeat this exercise on both sides.
Lying Shin Stretch:
The patient’s position is lying on the side with the knee flexed on the upper leg so that the foot is now behind the back.
Reach back and grab the forefoot, pulling it to the back.
Maintain this stretching position for 15 -20 seconds.
Then repeat this exercise on both sides.
Stair Stretch:
The patient’s position is to stand with the back toward a step, curb, and stool of similar height.
Then raise the leg for the want to stretch and place the top of the foot on the step behind you.
Then slowly squat down and lower the body weight through the leg to the standing position to apply pressure through the top of the foot on the step till they feel a stretch in the facade of the shin.
Maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds, and then relax.
Then repeat this stretching exercise 3 times on both legs every day.
Standing Stretch :
The patient’s position is in standing on one foot.
To stretch another tibialis anterior, flex the right knee and bring the heel up toward to buttock, then grab the top of the right foot with the right hand.
Pull the right foot in closer to the buttock, and the toes are pointed up toward the roof.
Then gently pull the foot in till the patient feel a stretch along the front of the right shin, maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds, and then relax from stretching.
Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times on both legs every day.
Tennis Ball Massage:
The patient’s position is in a sitting position comfortably with the knee joint bent and standing with the foot resting on an elevated surface in front of you.
Feel the tibialis anterior muscle running along with the externals of the shin bone.
Place the tennis ball against the muscle and maintain the ball in place with the palm.
With firm pressure, slowly roll the tennis ball up and down the tibialis anterior muscle for 30-60 seconds.
This exercise is discomfiting for the patient but helpful for the patient.
Repeat this exercise 3 times on both sides every day.

Band foot drop:
The patient’s position is holding a resistance band around an anchor close to the ground, sitting down then looping the band over your foot.
Bend the ankle up towards the body then briefly hold it at the top
After then slowly back to starting position, and repeat this exercise for 10 to 15 repetitions.
After that repeat with the opposite side.
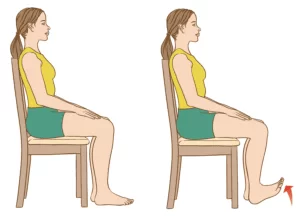
Seated toe raise:
The patient’s position is sitting on a chair with the feet in front of you, then slowly raising the toes off of the ground.
Maintain for this position 1 to 2 seconds at the top, and repeat this stretching exercise for 3 sets of 10 to 15 repetitions every day.
Wall toes raise:
The patient’s position is to stand 12 inches away with the back towards the wall with the feet hip-width apart, then keep the knees slightly bent then lean back into the wall.
Raise the toes off the floor and maintain at the top for 1 to 2 seconds then lower the toes back to the ground.
Then repeat this stretching exercise in 3 sets of 10 to 20 repetitions every day.
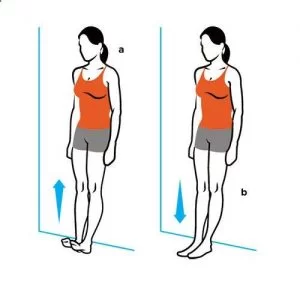
Heel walk
The patient’s position is to stand on both feet hip-width apart with no shoes on, then raise the toes off the floor so that the heels are in contact with the floor.
The patient is walk forward while leaning back placing the weight on the heels.
Repeat this exercise for 30 to 45 seconds and repeat this exercise 3 times every day.

Tibialis Anterior press & flex:
The patient’s position is sitting position on the ground with the leg extended out in front of them.
Then apply pressure to the trigger points on the muscle using a roller stick or massage ball.
While applying the pressure flex the ankles up and down, and do this exercise for 30 to 60 seconds. Then repeat this exercise with the opposite leg.
Strengthening exercise for the tibialis anterior muscle:
The patient’s position is sitting position on the floor or a bench.
Then secure an exercise band around to something sturdy and loop the band around the top of the foot.
With the toes facing up, bend the ankle toward the count of two, and back the ankle joints down to the count of four.
Do this exercise 10 – 20 repetitions in 2- 3 sets daily.
When the foot drop appears in the patient do some exercises:
- Seated Elastic Band Exercise for Foot Drop
- Cuff Weight Exercise for Foot Drop
- Isometric Exercise for Foot Drop
Seated Elastic Band Exercise for Foot Drop
The patient’s position is sitting position on the floor with the leg extended in front of his/her.
Alternatively, the patient is sitting on a chair with their foot propped up on another chair.
Tie a loop in the band, and pull the toes and foot up while keeping the knee straight.
Only the ankle joint move as they bend the foot up.
Pull the foot up as far as possible, and the patient is kept in the end position for a second or two.
Then slowly relax back into the starting position.
perform this exercise for 10 to 15 repetitions every day.
Till the anterior tibialis muscle tries and no longer bends the ankle joint up.

Cuff Weight Exercise for Foot Drop:
The patient’s starting position is sitting position with the cuff weight on the foot and then flexing the ankle joint so the foot and toes move up towards the knee joint.
When the foot is flexed up and maintain the position for a couple of seconds.
After then slowly back to the starting position.
Repeat this exercise for 10-15 repetitions.
Isometric Exercise for Foot Drop:
The patient’s position is in a sitting position in a chair or lying down.
Cross one leg over the other with the impacted leg on the bottom.
Put the foot on top of the ankle joint and wish to exercise.
Press the top of the weak foot into the sole of the other foot, and then Press down with the stronger foot to resist the foot.
Must be taken care no movement occur at the ankle joint.
Maintain this position for 5 to 10 seconds and then slowly release.
Do this exercise in 10 -15 repetitions and 2 to 3 times every day.
FAQ
How do you relieve tibialis anterior muscle pain?
When analyzed early, anterior tibialis tendonitis can be treated conservatively. If have these symptoms, start with the RICE protocol. Bracing, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can also help reduce pain and inflammation.
What does tibialis anterior muscle pain feel like?
When the anterior tibialis muscle is overworked, you may experience pain /tightness at the front of the lower leg. This can be while walking or while using pressure on the affected region. While walking, the pain would be more severe while lowering your foot to the floor, immediately after the heel strike.
How long does it take for the tibialis anterior to recover?
The restoring time for anterior tibialis tendon repair will take up to 8 to 12 weeks but restoration of function and ability to accept full activity, load, and stress can take up to 1 year.
Can you massage the tibialis anterior?
The tibialis anterior is an essential muscle in the anterior compartment of the lower leg. Active trigger points in this muscle can lead to pain in the big toe and the ankle joint. Especially affected are runners and indoor athletes. However, you can treat these points and pain with a self-massage.
What causes tibialis anterior weakness?
Because the prior function of the tibialis anterior is dorsiflexion, paralysis of this muscle results in “foot drop,” or an inability to dorsiflex, this immobility can be caused by nerve injury, like direct injury to the deep peroneal nerve, or a muscle disorder, like ALS.



One Comment