What Causes Tight Gluteal Muscles?
Introduction of Gluteal Muscles:
The gluteal muscles mostly become tight after long sitting position seen in the office workers, overuse, or overactivity mainly in the sports person.
Tight gluteal muscles can lead to a number of other injuries, so it’s important to do regular stretching and strengthening exercise help to improve your fitness and reduced chances of Injury.
Tightness in gluteal muscles can cause mostly Hip pain and difficulty in performing day to day activity, However regualar stretches can help to overcome it.
If you sit at a desk all day, you should stand up and walk every 30 minutes or else you should change your position after few minues. This helps keep your glutes from becoming inactive or tight, and also prevent to become weak gluteal muscles.
Read on to learn more about tight glutes and what you can do to relieve gluteal muscles tightness.
Anatomy of the gluteal muscles:
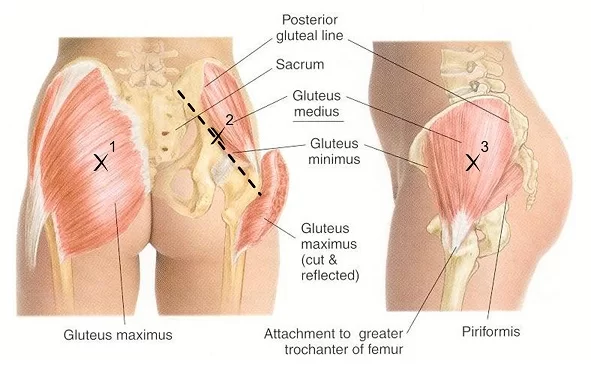
The gluteal muscle is known as glutes or buttock muscles, are a muscle group consist of gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae.
They are found in the buttock region, which is overlying the posterior aspect of the pelvic ring and the proximal part of the femur.
1) Gluteus maximus: Gluteus Maximus is the largest and heaviest muscle in the body. It is the most superficial of all gluteal muscles that are located at the posterior aspect of the hip joint.
2) Gluteus medius: The gluteus medius muscle is situated on the side of your hip. It resides underneath your gluteus maximus muscle (buttocks muscle).
this muscle is originates on the external surface of the outside of the ilium around your hip bone. It traverses downward—narrowing as it goes to insert on a rather large knob of bone located on the outside of the upper thigh bone which is called as greater trochanter.
3) gluteus minimus: gluteus minimus is the smallest muscle in all of this three gluteus muscles which is fan-shaped, arising from the outer surface of the ilium bone between the anterior and inferior gluteal line and passes behind, from the margin of the greater sciatic notch.
Function of the gluteus muscles :
- The functions of muscles include extension, abduction and internal as well as external rotation of the hip joint.
- The gluteus maximus also supports the extended knee through the iliotibial band.
Common causes of tight glutes include:
- sitting for long periods of time.
- delayed muscle soreness after exercising.
- poor posture.
- stress on the muscle from striding, jumping, or running
- no warming up before exercising
- not stretching after exercising
- gluteal muscle soreness or tightness in the buttocks
- pain or soreness in the hips
- tight hip flexors
- chronic low-back pain
- tight hamstrings muscles
- knee pain
- pelvic pain or instability
- Herniated disk
- piriformis syndrome,
- muscle strain, and shingles
- arthritis of the sacroiliac joints
- bursities
Signs and symptoms :
The gluteal muscles help support important functions like: hip rotation
walking
running
going down steps
They’re connected to several other muscles. For that reason, you might experience tightness in the glute itself or you may feel tightness or
pain in parts of your:
- leg
- back
- hip
- pelvis
You may be able to identify tight glutes by the following symptoms:
- pain in the pelvis or experiencing muscle soreness after or before exercise
- not stretching or warming up before exercise
- exercising with poor form
- having poor posture
- sitting for long periods
- having muscle imbalances
- pain or tightness in the lower back and knees
- sore or tight hips or hamstrings, which sit at the backs of the upper legs
- Running, squatting, and other movements that work the legs and lower back can increase any pain or tenderness. Also, the muscles may feel particularly tight first thing in the morning.
- you may felt pain in lower back and radiates up to your thigh muscles.
- pain after walking.
- Stretching and strengthening the glutes can prevent tightness, help relieve pain and other symptoms, and reduce the risk of injury.
- Tenderness or aching in the buttock.
- Tingling or numbness that extends down the back of your leg.
- Having a hard time sitting.
- Feeling pain that gets worse the longer you sit.
- Pain that gets worse with activity like walking or exercise.
- Severe pain in the lower body.
Why do glute stretches?
Stretching regularly is another way to prevent inactive and tight glutes. Glute stretches can improve hip rotation, and help with walking, running and descending stairs also prevent the risk of injury and fall.
If you have soreness or tightness in the buttocks, pain or soreness in the hips tight hip flexors, low-back pain, tight hamstrings, knee pain or pelvic discomfort than stretching your glutes muscles can help.
How to loosen tight gluteal muscles :
1) Knee to opposite shoulder :
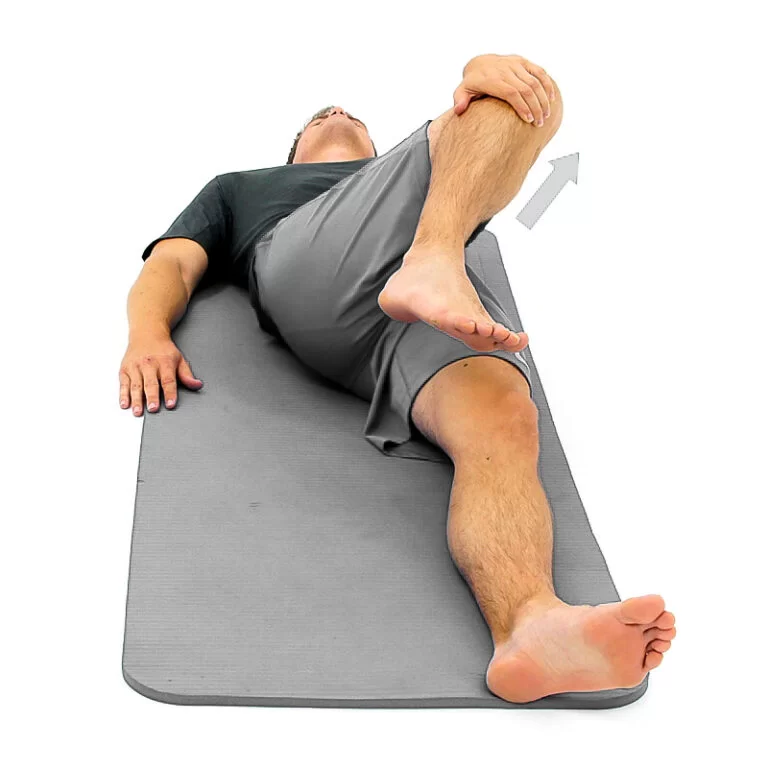

If you have sciatica pain, try this glute stretch. Pulling your knee toward your opposite shoulder can help loosen your glutes and release tension around your sciatic nerve.
- To do this stretching :
- Start on your back with your legs extended and your feet flexed upward.
- Bend and lift your right knee and place your hands around your knee.
- Pull your right knee up toward your left shoulder.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds. Return your leg to the starting position.
- Straighten your right leg and repeat with the left leg.
2)Pigeon stretch :

- To do this stretching :
- Start on all fours. Lay your right knee toward your right wrist, placing your shin on the floor.
- Move your right ankle toward your left wrist.
- Slide your left leg back, point your toes, and face your hips forward. Extend your spine.
- Gently walk your hands forward. Hold for 5 to 10 breaths.
- Return to the starting position. Switch your legs and repeat this stretch.
3)Seated glute stretch :

- To do this stretch:
- Sit on the floor and extend your legs out in front of you.
- Keeping your back straight, lift your left leg and place your left ankle on your right knee.
- Lean slightly forward to deepen the stretch.
- Hold for 10 to 20 seconds then repeat on the opposite side.
4) Standing glute stretch :

This stretch targets the largest gluteus muscle to release tension.
- 1. Plant both feet on the floor, shoulder-width apart.
- 2. Lift and turn out your left leg. Rest the outside of your left ankle just above your right knee.
- 3. Bend your right knee so that you are in a single leg squat position and gently push down on your left knee using your left elbow.
- 4. Hold this position for 30 seconds.
Yoga Poses for Tight gluteal muscles :
If you’re trying to get rid of gluteal tightness, Yoga is a great option.
1) Happy Baby/Ananda Balasana :
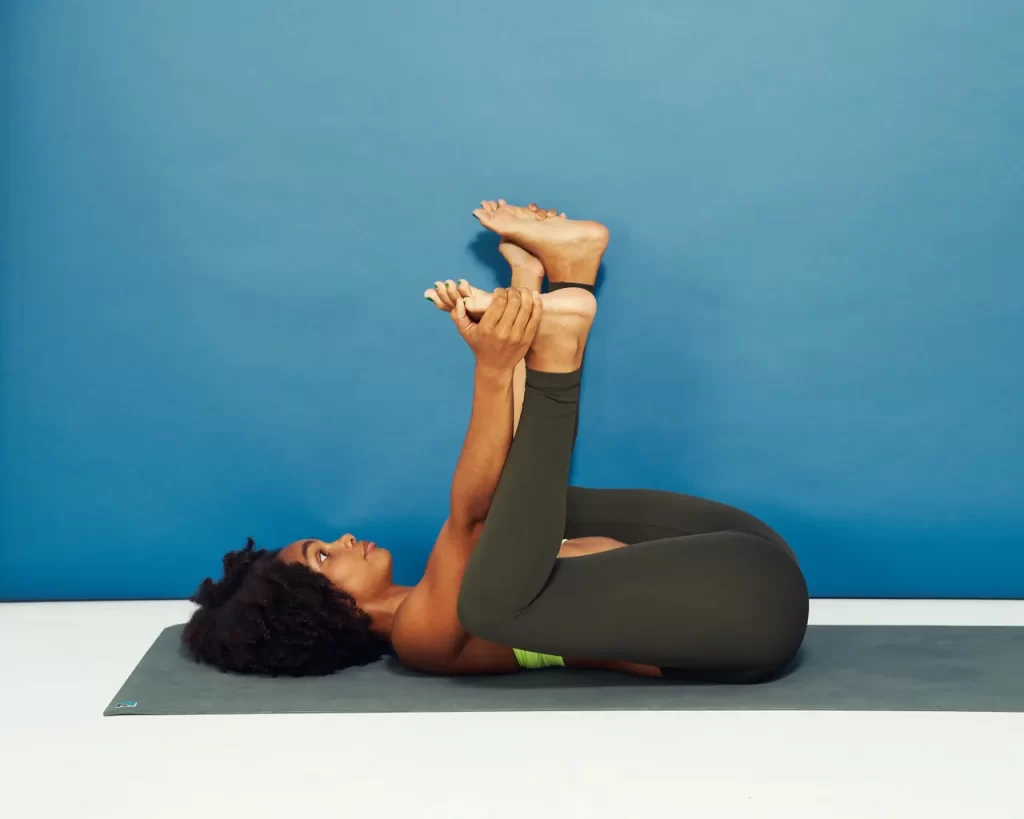

- Lie faceup with both knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your feet off the floor and grab the outside edges of your feet with your hands.
- Gently pull your feet toward your chest and let your knees lower toward the floor on either side of your body. Keep your back flat on the floor.
- Hold for at least 10 seconds.
2) Low Lunge/Anjaneyasana :
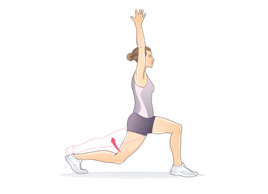
- From high lunge, simply drop your back knee to the floor, keeping the leg extended long and the shin flat on the mat.
- Hold for at least 10 seconds and then repeat it on the other side.
3) Garland Pose/Malasana (Yoga Squat)
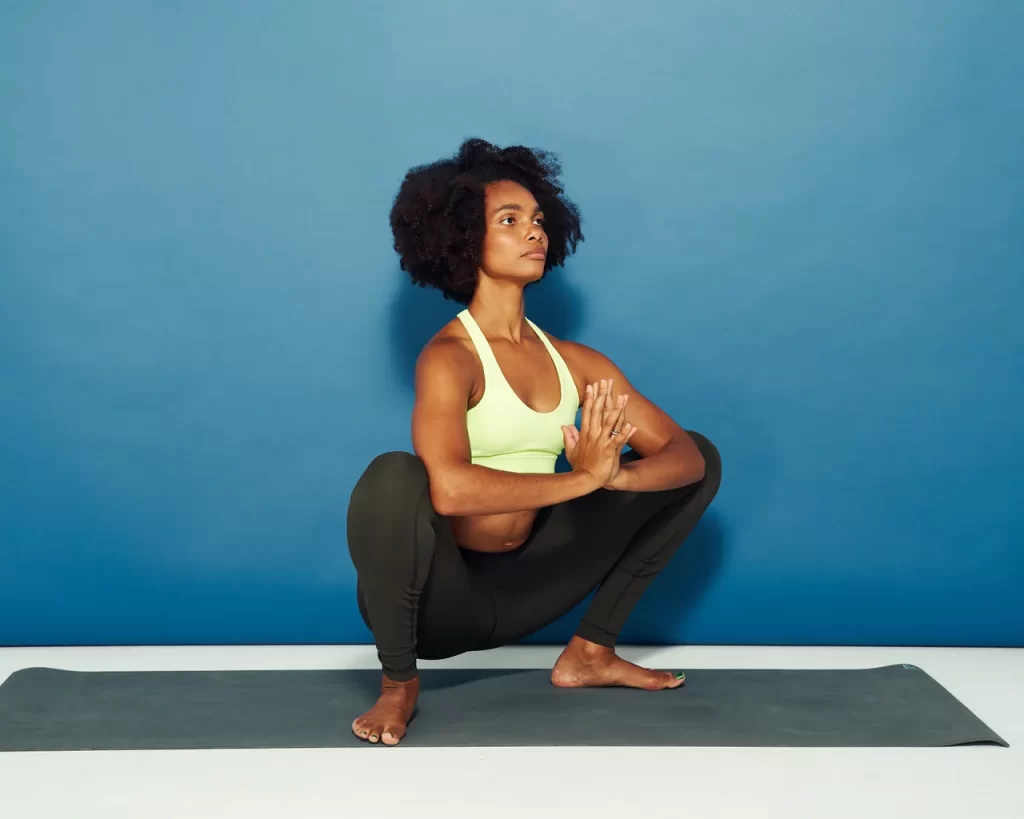

- From a seated position, place your feet wider than shoulder apart, feet flat on the floor, toes facing out. Your torso should be upright.
- Place your hands in prayer position in front of your chest, elbows pointed out to the sides.
- Use your elbows to press your knees open.
- Hold for at least 10 second and than relax.
4) Bridge Pose/Setu Bandha Sarvangasana :

- Lie face upright position, arms resting by your sides, knees bent so that your feet are flat on the floor.
- Press through your heels to lift your back up and walk your feet in a few steps toward your body, keeping your feet and knees hip-width apart.
- Interlace your fingers underneath your body and press your fist into the mat.
- Hold for at least 10sec and than relax.
Why you need to strengthen your gluteal muscles?
1) Without strong glutes, especially gluteus maximus, your hamstrings may become overactive and tighten up leading to chronic hamstrings muscle injury like tendinopathies or tears. When a muscle isn’t working effectively your body relegates the task to the next muscle in line.
2) like in number 2 without strong glutes your lower back muscles such as the erector spinae and quadratus lumborum (QL’s) will become overactive. This can lead to lower back pain.
3 )The opposing muscles to the glutes are the hip flexors and adductors. When a the glutes are weak, this can create an imbalance in the pelvis known as lower crossed syndrome. This is occurs when the glutes and abdominals are weak and the hip flexors and lower back muscles are tight.
4 ) As a rule of thumb weak glutes = tight glutes. When your muscles is weak the nervous system will try to find stability by tightening up or slamming the brakes on so to speak. If you have tight glutes then a simple rule of thumb is that they are possibly also weak.
So what can you do to strengthen your glutes?
Home exercise :
gluteal bridge :

- Keep one leg off the ground the whole time., feeling the deep abdominals contracted Hold this on while pressing down with the heel and lifting off with the single leg. Hold for 10 seconds at the top whiles squeezing the gluteal muscles.
lunges in variation:

- Standing up tall, back straight, step the right leg forward so that when you drop the hips and lunge the knee comes into alignment with the ankle.
- Drop the hips down and bend the back knee so that the back upper leg is almost in alignment with the spine. hold it for 10 sec and repeat it daily

One Comment