Paralysis Type, Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, and Exercise
What paralysis mean?
Paralysis is a loss of muscle function in part of the body. It can be localized or generalized, partial or complete, and temporary or permanent. Paralysis can affect any part of the body at any time in human life. If you experience it, you probably won’t feel pain in the affected areas.In the body that may be accompanied by sensory loss, also referred to as loss of feeling.
The term is derived from the Greek word that means disabling of the nerves. This is because it is usually due to damage to the nervous system that there is loss of motor function or sensory information.
- The nervous system has two parts:
- The central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord.
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS), which contains the nerves outside of the CNS
- The nerve cells, or neurons, in the PNS serve several functions.
- Paralysis occurs when nerve signals are interrupted as a result of damage to the nerves, spinal cord, or brain.
Definition :
Paralysis occurs when unable to make voluntary muscles movements and the nervous system problem causes by paralysis.
An injured nerves send signals to muscles.and those signals make muscles to move. when you are paralyzed, or have paralysis, you can’t move certain parts of body.
There are some degrees of severity of paralysis :
- Patient may experience temporary paralysis and regain partial or full movement over time.
- Paralysis can affect any part of the body. It can be
- Partial(paresis): patient can control some muscles ,but not all.
- Complete: patient have no control over any muscles.
- Paralysis also divided into two types based on the site of injury in the nervous system;
- Flaccid : muscles get flabby and shrink.
- Spastic : muscles tighten,causing uncontrollable jerks and spasm(spasticity).
Common causes of Paralysis :
Paralysis occurs mainly due to strokes,spinal cord injuries and nerves disorders like multiple sclerosis.
Other Causes :
- traumatic brain injury
- birth defects like spina bifida
- post polio syndrome
- muscular dystropy
- Guillain-Barre” syndrome (GBS)
Motor neuron disease that damage the upper and lower motor neuron cells
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- cerebral palsy (CP)
- Todd’s paralysis
- Myopathy include DMD
- brain injury
- spinal tumor
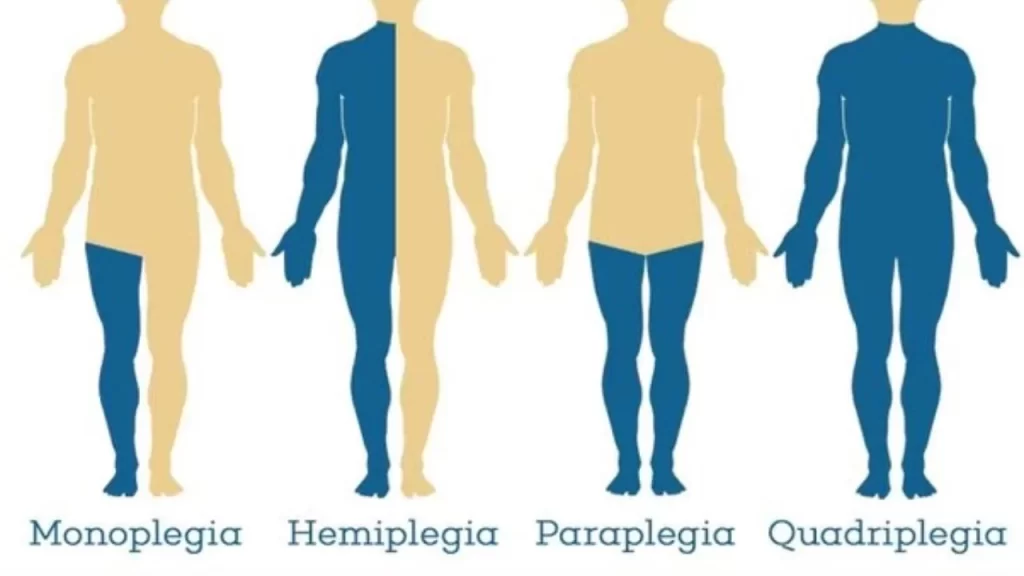
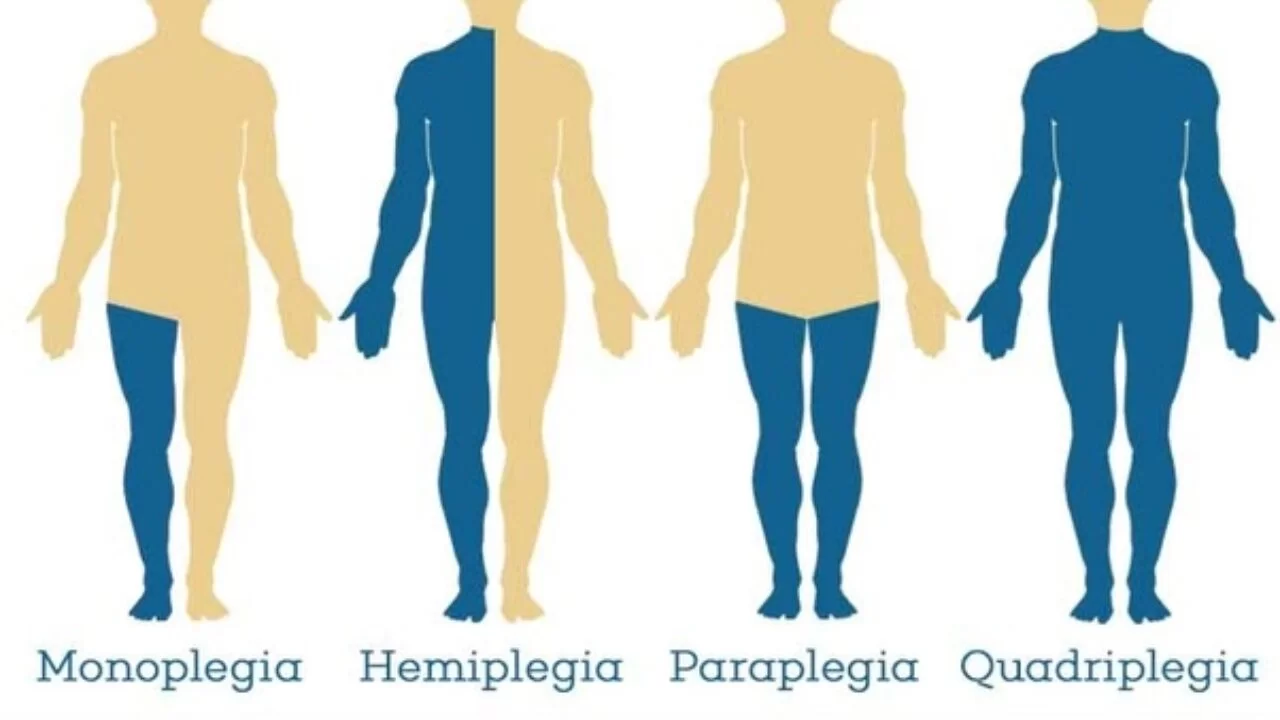
Types of paralysis :
Monoplegia- it is a paralysis of a single area of the body,most typically one limb.people with monoplegia typically retain control over the rest of their body.not move or feel sensations in the affected limb.
It is the temporary condition,and is especially common in the stroke or brain injury and the nerves affecting the paralyzed area are not fully severed.
Hemiplegia-this are affects one side of the body,it may be referred to as either ”left hemiplegia”or ”right hemiplegia”. most common causes is cerebral palsy. and other conditions, as incomplete spinal cord injuries, brain injuries,and nervous system disorders can also results in hemiplegia.
Quadriplegia – referred to as tetraplegia ,is paralysis below the neck and the all four limbs, as well as torso, are typically affected. As with paraplegia, though, the degree of disability and loss of function may vary from person to person, and even from moment to moment.
Sign and symptoms-
In Paralysis following most common symptoms are seen it can be vary according to type of paralysis.
- Muscle weakness
- Stiffness
- Numbness or pain[affected muscles]
- Involuntary spasm or twitched
- Visible signs of muscle loss
- Increased spasticity
- Restlessness
- Hypertension
- Headache ( severe headache )
- Vasodilation ( above the level of the lesion)
- Vasoconstriction(below the level of lesion)
- Autonomic dysreflexia
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction
- Pressure sores
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Blurred vision
- Poor balance
- Difficulty grasping or holding on to objects
Diagnosis
Diagnosing paralysis is often easy, especially when your loss of muscle function is obvious. For internal body parts where paralysis is more difficult to identify, your doctor may use X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or other imaging studies.
If you experience a spinal cord injury, your doctor may use myelography to assess your condition. In this procedure, they’ll insert a special dye into the nerves in your spinal cord. This will help them see your nerves more clearly on X-rays. They may also perform an electromyography. In this procedure, they’ll use sensors to measure electrical activity in your muscles.
Treatment of Paralysis :
What are the treatment options for paralysis?
In most cases, paralysis can only be managed, and not completely cured through medical interventions as there is no cure for paralysis. At times, patients have reported complete recovery from paralysis over a period of time or after the underlying disease which was causing paralysis has been cured. Certain rehabilitative therapies have enabled some patients to regain their muscle function partially after paralysis. But such rehabilitative therapies focus on helping the patient live on their own and improve the quality of life.
Rehabilitative therapies for paralysis include the following:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Mobility aids
- Supportive devices
- Assistive technology
- Adaptive equipment
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatment are mostly depends on symptoms, diagnosis and cause of disease and is vary patient to patient.
Following are the most common goal of treatment and accordingly treatment are carried out :
- Improve motor learning
- Improve flexibility & joint integrity
- Improve strength and Manage spasticity
- Improve movement control
- Improve postural and balance control
- Improve gait and locomotion
- Improve aerobic capacity and endurance.
Treatment protocol :
Physiotherapy Treatment protocol are vary according to symptoms and diagnosis. Physiotherapist used to heating therapy, massage and and exercise, and also functional electrical stimulation is used in paralysis.
Mobility aids like wheelchair-supportive devices like cane, brace and walkers and adaptive equipment wherever necessary, like grips, special eating utensils and bath and washroom equipment.
Improve motor learning :
For the motor learning, therapist can use the strategy that are develop,feedback and practice.
In the strategy development,
The therapist assist the patient in learning the desired task.
Verbal instruction are used to direct the patients attention to task.
The desired task is demonstrated at the ideal speed,then patient is begin to practice.
Clear verbal instructions are given and active participation is essential for learning.
In the feedback,
Feedback can be intrinsic or extrinsic.
During early intervention visual inputs are critical for motor learning but after by having the patient look at the movement it is very useful for the patient.
In the practice,
it is essential for motor learning and recovery.
With constant repetition of a single task and with adequate rest periods.
Improve joint flexibility and Reduce spasticity:
With the active and passive movements of all the affected joints performed to patient.
Stretching- most commonly useful to the wrist extensions compartments and the lower limb useful to the calf muscles( quadriceps and hamstring muscles) and prevent contracture.
For joint integrity:
To teach the patient safe self ROM activities.
Arm cradling
Sitting position , lean forward and reaches hand to floor
Supine position ,hands clasped behind the hand
For improve strength :
progressive resistive strength training after the check of MMT of all the joints.
Core stability exercise – bridging ex.
Respiratory technique :
Deep breathing ex : – this technique are used for the movement of the increase vital capacity, and the therapist can apply light pressure during both inspiration and the expiration. and the manual contacts can be made just below the sternum and the this will assist the patient to concentrate on deep breathing patterns due to absence of abdominal and thoracic sensation. And the expiration manual contacts are made over the thorax with the hands spread wide. -inflation hold and incentive spirometry are also useful to the adjuncts to deep breathing exercise.
Glossopharyngeal breathing :- This technique are used for patients with high-level cervical lesions. Also used for the accessory muscles of respiration to improve vital capacity. And gives instruction to the patient for inspire small amount of air repeatedly, using a “gulping” patterns and utilizing available facial and the neck muscles. And gradually inspired to improve chest expansion despite paralysis of the primary muscles of respiration.
Air shift maneuver :- This technique are provide to the patient with an independent method of chest expansion. With closing the glottis after a maximum inhalation, and the relaxing the diaphragm and allowed to air to shift from the lower to upper thorax.
Assisted coughing: This technique are mostly used by movement of secretions, manual are placed over the epigastric area. and the therapist pushes quickly in an inward and upward direction as the patient attempts to cough.
Mat exercise :
- Rolling
- Prone on elbows position
- Prone on hands position
- Supine on elbows position
- pull-ups
- Sitting position
- Quadruped position
- Kneeling position
Transfer :
Transfer training is generally initiated once the patient has achieved to sitting balance and other functional activities, and such as tub transfers, ambulations, and driving. Training is usually initiated on the mat surface and progresses to alternate surface to the bed, toilet, bathtub, carto chair to floor and etc.
Transfer to the patients such as a bed-to-wheelchair,and any scoot transfer and etc.
Gait training and locomotor :
Gait training, strengthening, and balance exercises were the most common physiotherapy activities in individuals with an AIS D spinal cord injury. Overall strengthening was the most common group therapy activity across all levels and types of spinal cord injury.
loco motor training :
Gait training has contributed to enhanced overall health and wellness.
Potential benefits may include :
1 Improved cardiovascular and pulmonary function
2 Heightened bowel and bladder function
3 Increased blood flow to the upper and lower extremities
4 Enhanced strength and healing potential of skin to reduce pressure sores and other complications
5 Increased bone density
6 Overall improvements in sense of well-being (emotional and psychological)
Gait training may include ;
- Although the majority of persons with the paralysis regain the ability to walk, and do not achieved the ambulation endurance, speed, or security required to perform their daily activities independently and safely.
- Support of body mass by lower limb.
- The production to the basic loco motor rhythm.
- Dynamic balance control of the moving body.
- The increasing to the muscle strength and coordination.
- The increasing walking velocity and endurance with walking forward,backward,side stepping and crossed stepping
- Maximizing skills and increasing flexibility.
- Increase cardiovascular fitness.
- Increase safety awareness.
- Education on the proper use of assistive devices.
- Step up and step down training.
- Single leg stance with stable balance and control.
- Locomotor training using body weight support and motorized treadmill training.

2 Comments