Yergasons Test of the shoulder
- Yergasons test is applied in the clinic to check the pathology of the biceps tendon.
- This clinical test is applied by to doctor or therapist when the patient is complaining about the front of the arm.
- This test is applied to examine part of the assessment of the shoulder.
- This test is primarily designed to check the ability of the transverse humeral ligament to hold the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove.
What is the Purpose of the shoulder?
- This Test is used to check the biceps tendon pathology, like unstable superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) lesion & bicipital tendonitis.
- This test also checks the transverse humeral ligament which holds the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove.
How to perform the Yergasons Test of the shoulder?
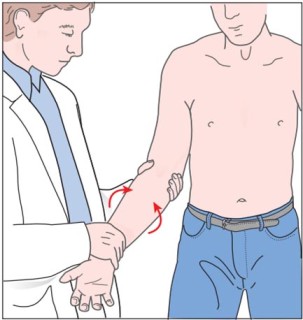
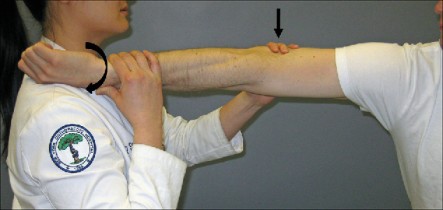
- Starting position is a standing or sitting position.
- With the patient’s elbow flexed to 90′ & stabilized against the thorax & with the forearm pronated, the examiner resists supination while the patient also laterally rotates means externally rotates the arm against resistance.
- If the examiner palpates the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove during the movement of supination & lateral rotation means external rotation of the biceps tendon will be felt to pop – out of the groove, it indicates the torn transverse humeral ligament.
- Tenderness in the bicipital groove alone without the dislocation may indicate bicipital paratenonitis/tendinosis.
- This test is not as effective as Speed’s test when testing the biceps tendon, because the bicipital groove moves only slightly over the tendon Affecting only a small part of the tendon during the test & because biceps tendon pain tends to occur with motion/palpation rather than with tension.
- Sensitivity of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder = 0.43
- Specificity of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder = 0.79
- Positive Likelihood Ratio of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder = 2.05
- Negative Likelihood Ratio of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder = 0.72
- This result is depending on the Diagnostic Properties which is mostly detected for the biceps pathology.
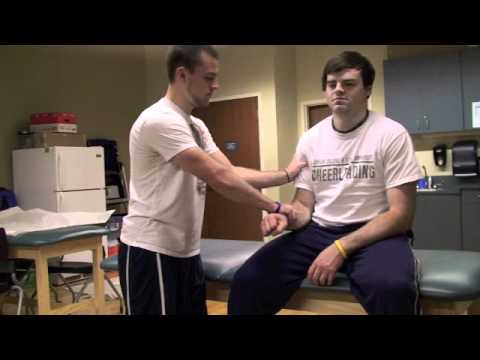
Yergasons Test of the shoulder Video
Clinical Context of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder :
- The Yergasons Test was devised in 1931 mostly for detecting bicipital tendonitis.
- This Yergasons Test is now clear that the pains arise from the SLAP lesion, tendinopathy & tenosynovitis,
- This test also accesses the ability of the transverse humeral ligament which holds the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove.
- The tendon of the biceps is associated with an isolated overuse injury in the youths & rotator cuff disease in the elderly.
- This Yergasons Test is more useful for diagnosing the SLAP lesions than biceps diseases.
Variations of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder :
- A common variation of the Yergasons Test is described as when the patient moves the shoulder into external rotation means lateral rotation while simultaneously moving the forearm into the supine position against resistance.
- But this movement is complex so the patient is encouraged to perform it without the resistance first so elicit an effective response when the resistance is added.
Clinical Tip of the Yergasons Test of the shoulder :
- After the elbow is stabilized between the waists of the therapist & the patient has used the freehand which is palpated over the inter tubercular sulcus in the bicipital groove which detects the snapping’ & clicking sound or any unusual subluxation during this test.

One Comment