Special test for the neurodynamic tests of the cervical spine:
- During the neurodynamic tests, a positive test is considered present only when one or more of the following occurs :
- There is a reproduction of the patient’s symptoms.
- There is an asymmetric sensation between the right & left limbs.
- There is a significant deviation from normal sensation.
- Symptoms change with sensitizing movements.
- The test is applied in the clinic to check the neurological symptoms of the cervical spine & upper limb by the doctor.
Name of the special test for the neurodynamic tests of the cervical spine:
- Brachial plexus compression test
- Jackson’s compression test
- Scalene cramp test
- Shoulder abduction test
- Shoulder depression test
- Tinsel sign for brachial plexus lesions
- Valsalva test

Brachial plexus compression test:-
- Purpose = This brachial plexus compression test is used to check the mechanical cervical lesion.
- Technique = Starting position of the brachial plexus compression test is sitting position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] applies firm compression to the brachial plexus by squeezing the plexus under the thumb or fingers.
- Result = Pain at the site is not diagnostic.
- The test is positive only if the pain radiates into the shoulder or upper extremity.
- This test is positive for the mechanical cervical lesions having a mechanical component.
Jackson’s compression test:-
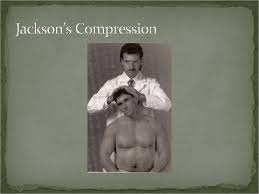
- This test is also a modification of the foraminal compression test.
- Purpose = This Jackson’s compression test is used to check the nerve root of the cervical spine.
- Technique = The patient is in a sitting position for the jackson’s compression test.
- First of all the patient rotates from the head to the one side.
- The examiner [ therapist ] then carefully presses straight down on the head.
- This Jackson’s compression test is repeated with the head rotated onto the other side.
- Result = The test is positive if the pain radiates into the arm, indicating pressure on a nerve root.
- When the pain distribution is given some indication of which the nerve root is affected.
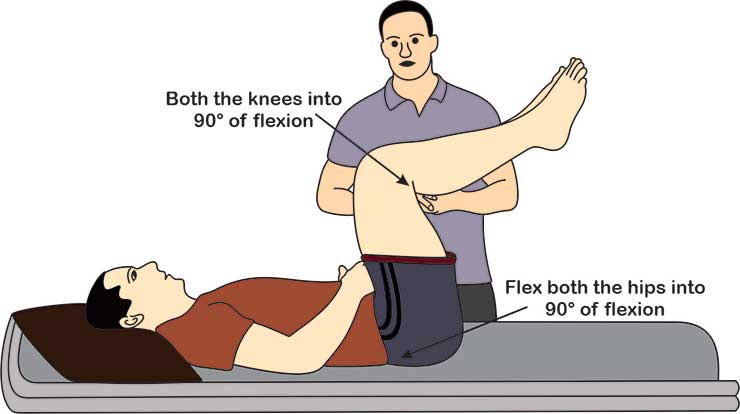
Scalene cramp test:-
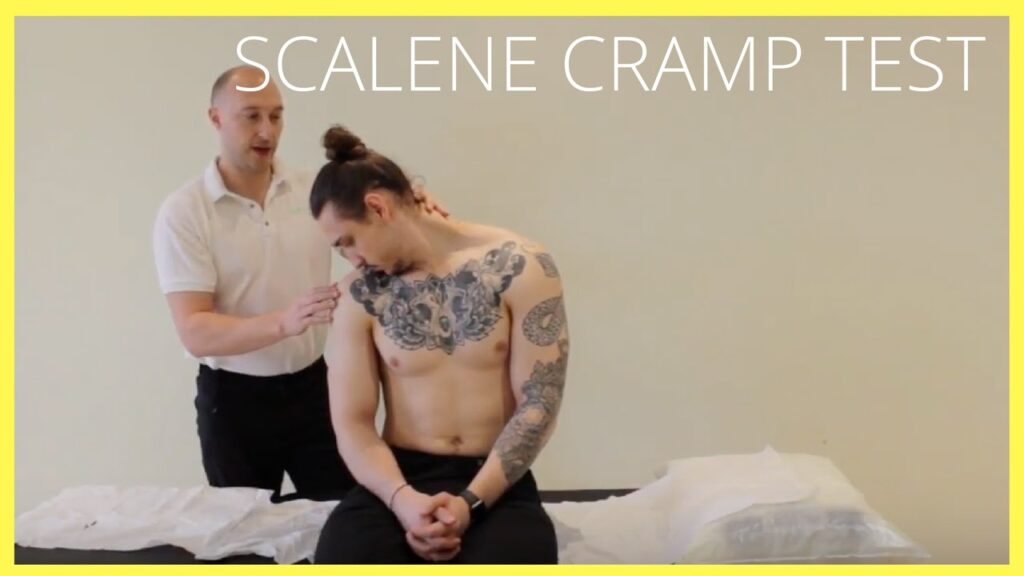
- Purpose = This scalene cramp test is used to check the plexopathy or thoracic outlet symptoms.
- Technique = The patient is sitting & rotates the head to the affected side & pulls the chin down into the hollow above the clavicle by flexing the cervical spine.
- If the pain is increasing, it is usually in the trigger points of the scalenes muscle toward which the head is rotated.
- Result = Radicular signs may indicate plexopathy or thoracic outlet symptoms.
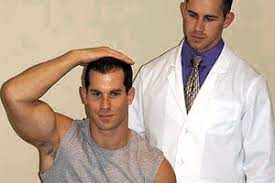
Shoulder abduction test:-
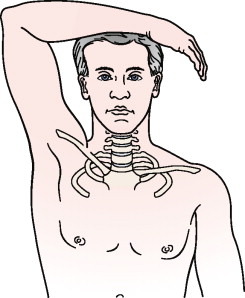
- This shoulder abduction test is used to test for the radicular symptoms, mostly involving the C4 or C5 nerve roots.
- Purpose = This shoulder abduction test is used to check the herniated disc, epidural vein compression or nerve root compression.
- Technique = The patient is sitting or lying down, the examiner [ therapist ] passively or the patient actively elevates the arm through abduction so that the hand or forearm rests on top of the head.
- Result = A decrease in or relief of symptoms indicates a cervical extradural compression problem, like herniated disc, epidural vein compression or the nerve root compression, usually in the C4 – C5 or C5 – C6 area.
- Differentiation is by the dermatomes distribution of the symptoms.
- This finding is called Bakody’s sign.
- Abduction of the arm decreases the length of the neurological pathway & decrease the pressure on the lower nerve roots.
- If the patient feels the pain increases with the positioning of the arm, it is implied that pressure for increase in the inter scalene triangle.
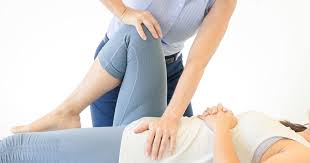
Shoulder depression test:-
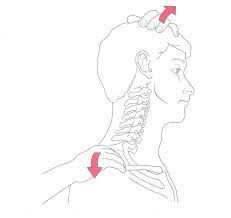
- The test may be used to evaluate for brachial plexus lesions since the test position is the mechanism of injury for these lesions, plexopathies & radiculopathies.
- With brachial plexus lesions, more than one nerve root is commonly affected.
- Purpose = This shoulder depression test is used to check the irritation /compression of the nerve root.
- Technique = The examiner [ therapist ] side flexes the patient’s head to one side while applying downward pressure on the opposite shoulder.
- Result = If the pain is increased, it indicates irritation or compression of the nerve roots or foraminal encroachments, like as osteophytes in the area on the side being compressed, or adhesions around the dural sleeves of the nerve & adjacent joint capsule or a hyper mobile joint capsule on the side being stretched.
- Differentiation is by the dermatomes distribution of symptoms.
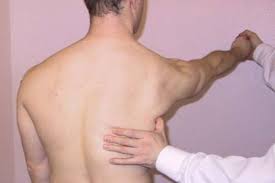
Tinel sign for brachial plexus lesions:-
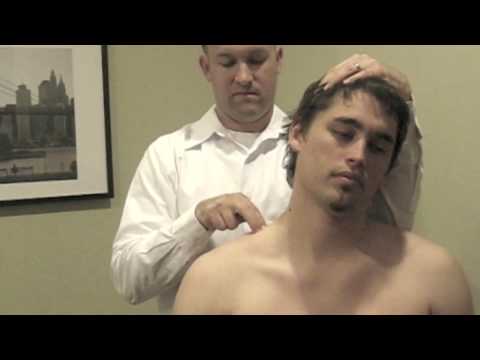
- Purpose = This tinel sign for brachial plexus lesions is used to check the neuroma.
- Technique = The patient sits with the neck slightly side flexed.
- The examiner [ therapist ] taps the area of the brachial plexus with a finger along the nerve trunks in such a way that the different nerve roots are tested.
- Pure local pain implies that there is an underlying cervical plexus lesion.
- Result = A positive tinel sign means the lesion is anatomically intact & some recovery is occurring.
- If the pain is elicited in the distribution of a peripheral nerve, the sign is a positive for a neuroma & indicates a disruption of the continuity of the nerve.
Valsalva test:-
- This test is used to determine the effect of increased pressure on the spinal cord.
- Purpose = This Valsalva test is used to check the herniated disc, tumors, stenosis or osteophytes.
- Technique = The examiner instruct the patient to take a deep breath & hold it while bearing down as if moving the bowels.
- Result = A positive test is indicated by increasing pain, which may be caused by increased intrathecal pressure.
- This increased pressure within the spinal cord usually results from space-occupying lesions like a herniated disc, a tumour, stenosis, or osteophytes.
- Test results are very subjective.
- The test should be performed with care & caution because the patient may become dizzy & pass out during the test or shortly afterwards if the procedure blocks the blood supply to the brain.