Abductor pollicis brevis muscle
What is Abductor pollicis brevis muscle?
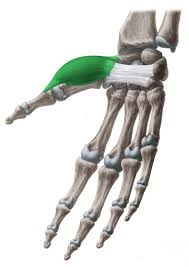
The abductor pollicis brevis muscle is a small, triangular muscle located in the hand. It is one of the intrinsic muscles of the hand, meaning that it originates and inserts within the hand itself.
As its name suggests, the primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis muscle is to abduct the thumb, meaning it moves the thumb away from the palm of the hand. It also helps in opposition & extension of the thumb.
This muscle is innervated by the median nerve, which is a nerve that originates from the brachial plexus and runs down the arm and into the hand. The abductor pollicis brevis muscle is an important muscle for fine motor control of the hand, and its proper function is crucial for performing many daily activities, such as grasping and manipulating objects.
There are four muscles in the thenar’s muscles group; abductor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis. The thenar eminence is the elevation they create on the palm’s radial (lateral) aspect.
Under the skin is the most lateral and superficial of the thenar muscles, the abductor pollicis brevis. It connects the thumb’s proximal phalanx to the scaphoid and trapezium carpal bones via the flexor retinaculum.
The abduction of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint is the primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis.
Origin of Abductor pollicis brevis muscle
It originates from the front of the transverse carpal ligament and extends into the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium, with the abductor pollicis longus tendon occasionally contributing.
Insertion
A short tendon connects the muscle to the base of the thumb’s proximal phalanx on the radial side.
Relations
The fusiform abductor pollicis brevis muscle is directly above the opponens pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis muscles at the surface of the thenar eminence. The thenar branch of the median nerve travels through a gap created by these three muscles. The abductor pollicis brevis’s superficial aspect is traversed by the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery.
Innervation
The median nerve’s recurrent (thenar) branch innervates the abductor pollicis brevis (root values C8 and T1).
Blood supply
The abductor pollicis brevis is vascularized by the superficial palmar branch that derives from the radial artery.
Function of Abductor pollicis brevis muscle
The abduction of the thumb at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints is the primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis muscle. The abductor pollicis longus muscle and this action work together. In addition, the abductor pollicis brevis makes it easier to move the thumb toward the fingertips in the opposition to the carpometacarpal joint and to flex the metacarpophalangeal joint. All of the previously mentioned elements of this muscle are of incredible importance for the appropriate working of the hand, like getting a handle on round objects or completing errands that request accuracy (for example composing and sewing).
Clinical relevance
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Median and ulnar nerve lesions
- Syringomyelia
- Motor neuron disease
- Peripheral neuropathy
Assessment
By providing resistance to abduction upward and away from the palm’s plane, the function can be evaluated.
Abductor pollicis brevis muscle stretching
With adduction and flexion of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint and radial deviation of the hand at the wrist joint, the abductor pollicis longus is stretched.
Abductor pollicis brevis muscle strengthening exercise
With your palm facing you, wrap a rubber band around your thumb and grab one end with your free hand.
Holding the band taut, pull it across your palm.
Against the band’s resistance, move your thumb away from your palm.
Go into the subsequent repetition by controlling your thumb back until it is resting against the side of your hand.
By pulling harder on the rubber band, you can make your abductor pollicis brevis work harder.
Perform 15 repetitions for each thumb.

FAQ
How is abductor pollicis brevis tested?
The strength of the abductor pollicis brevis is measured by placing the patient’s thumb in an abduction position and applying force to the proximal phalanx in the direction of adduction. If strength is significantly or significantly reduced in comparison to the opposite extremity, this test is positive.
What is the pen-pencil test for abductor pollicis brevis?
The patient lies down on a table with his palm facing up and his hand flat. The patient is approached to steal his thumb to contact the inspector’s pen which is held above it. The abductor pollicis brevis, one of the LOAF muscles in the hand that is supplied by the median nerve, is the subject of this test.
What causes the abductor pollicis brevis to feel pain?
A sudden increase in the strain placed on the tendons and muscles of the thumb is to blame. This over-burden is normally brought about by the monotonous lifting of your new pal out of the bunk and taking care of positions with the wrist in a flexed position.
How is the abductor pollicis brevis massaged?
Place the middle joint of your index finger on the opponens or adductor pollicis muscle by bending it. After that, roll your painful hand over the areas that are tender and lightly press both hands together.
How can pain in the adductor pollicis brevis be treated?
The thumb can be immobilized with a splint for the majority of these injuries to allow the injured ligament to heal. To restore thumb stability and repair an extensive or complete ligament tear, surgery, and rehabilitation are required.


One Comment