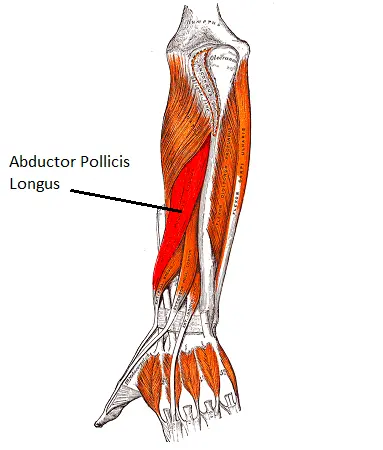
Abductor pollicis longus muscle
What is Abductor pollicis longus muscle?
The muscle known as the abductor pollicis longus can be found in the forearm’s posterior compartment. Along with the supinator, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, and extensor indicis, it is one of the forearm’s five deep extensors.
All of the deep extensor muscles, except for the supinator, cross the wrist joints and can act on them from the forearm to the hand. The three pollicis muscles move the thumb’s joints in a variety of ways because they attach to the bones.
The abductor pollicis longus muscle not only extends the hand at the radiocarpal joint, but it also abducts and extends the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint.
Origin of Abductor pollicis longus muscle
It comes from the hand’s flexor retinaculum, the scaphoid bone’s tubercle, and occasionally the trapezium’s tubercle as well.
Insertion
It is inserted into the capsule of the metacarpophalangeal joint as a thin, flat tendon on the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the thumb.
Relations
The abductor pollicis longus muscle belly is located in the posterior forearm’s distal half. Its tendon is lateral to the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis, and it is located deep to the extensor digitorum and lateral to the extensor pollicis longus muscle. The superficial surface of the abductor pollicis longus is traversed by the posterior interosseous nerve and artery, which run between the extensor digitorum and abductor pollicis longus.
The lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox is formed by the tendon of the abductor pollicis longus. The styloid process of the radius is located distally and posterior to this triangular space at the base of the thumb. The neurovascular structures of the hand traverse the anatomical snuffbox; the cephalic vein, the radial artery, and the superficial branch of the radial nerve. The extensor pollicis longus (medial) and brevis (lateral) bones complete this space’s margins, while the scaphoid and trapezium bones from the floor.
Innervation
The posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8), which is a continuation of the deep radial nerve, innervates the abductor pollicis longus. A branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus is the radial nerve.
Blood supply
The interosseous branches of the ulnar artery supply the abductor pollicis longus muscle with blood;
The lateral branch of the posterior interosseous artery supplies the muscle’s proximal portion.
The distal part is vascularised by a puncturing part of the front interosseous corridor.
Function of Abductor pollicis longus muscle
The abductor pollicis longus pulls the thumb away from the palm either on its own or in conjunction with the abductor pollicis brevis. More specifically, at the first metacarpophalangeal joint, it causes (mid-) extension and abduction of the thumb. This activity is found in exercises like bowling and scooping.
The muscle also helps the thumb fully extend at the metacarpophalangeal joint, working with the long and short extensors. When letting go of previously held objects, for instance, this action is crucial for releasing the hand grip. Additionally, the abductor pollicis longus aids in the radial deviation of the hand at the radiocarpal joint.
Clinical Relevance
DeQuervain’s Syndrome is the most significant clinical condition that affects the APL, usually in conjunction with the Extensor pollicis brevis. The first extensor compartment of the wrist experiences pain and swelling as a result of thickening and inflammation of the APL and EPB tendons. The tendons are more susceptible to degeneration and lesions because pain is worse when the thumb is moved.
Assessment
The subject is asked to abduct the thumb while holding the forearm in a neutral position to measure the strength of APL. In the direction of the thumb’s adduction, resistance is applied against the lateral aspect of the first metacarpal’s distal end.
Finklestein’s test is the one that was used to make a clinical diagnosis for DeQuervains. The patient is instructed to form a fist by inserting the thumb between the fingers. The therapist or examiner moves the wrist passively to the ulnar side. Pain over the radial styloid process at the junction of the APL and EPB tendons is a sign of a positive test.
Abductor pollicis longus muscle stretching
To stretch the Abductor pollicis longus muscle, perform adduction and flexion of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint and radial deviation of the hand at the wrist joint.
Abductor pollicis longus muscle strengthening exercise
Thumb isometrics
The thumb muscles can be reinforced in different headings with this activity. Make a fist with your thumb and use your other hand to apply pressure in both directions to get started. To resist the pressure, hold for 5 to 7 seconds with an upright thumb.

FAQ
What is the adductor pollicis longest primary function?
Adductor pollicis is contained two heads; slanted and cross-over. From the capitate and third metacarpal bones to the base of the first proximal phalanx, this muscle stretches. The adduction of the thumb in the carpometacarpal joint is this muscle’s primary function.
How can abductor pollicis longus pain be treated?
Heat or cold packs Stretching and myofascial release of the tendons are two components of manual therapy. Strength training for chronic ailments. In extremely painful or acute cases, thumb splinting (thumb spica), medication, and taping can be used.
How is the abductor pollicis longus detected?
Abductor pollicis brevis strength is tried by putting the patient’s thumb in a place of kidnapping and applying power in course of adduction at the proximal phalanx. This test is positive assuming strength is decreased or uniquely diminished contrasted and the contralateral furthest point.
How long does pain from the adductor longus last?
Recovery can be significantly slowed and take anywhere from 12 to 16 weeks if the tear is high on the adductor tendon. Depending on the severity of the tear, the mid-belly muscle will typically heal in four to twelve weeks.
How is the adductor pollicis massaged?
The Adductor Pollicis self-releases easily. Find the muscle and support it with your other fingers on the back of your hand while placing the thumb’s pads over it. Apply pressure now.


2 Comments