Adductor hallucis muscle
What is Adductor hallucis muscle?
The adductor hallucis muscle is an intrinsic muscle, which has two heads. The adductor hallucis muscle is functionally a member of the medial group of plantar foot muscles, which are divided into three vertical groups: lateral, central, and medial. Nevertheless, it is anatomically situated within the foot’s central compartment.
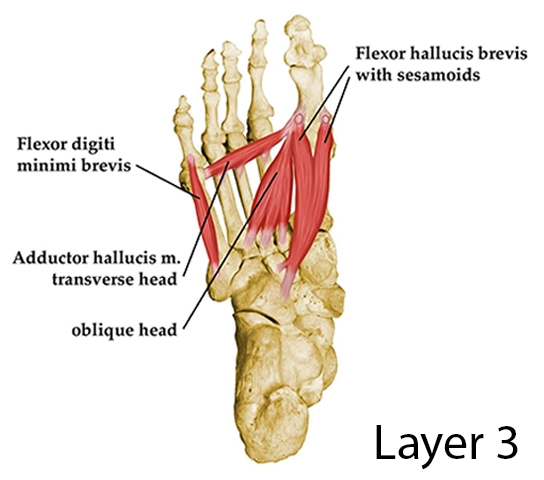
Additionally, the muscles of the foot are divided horizontally into four layers, varying from superficial to deep. Adductor hallucis, along with flexor hallucis brevis and flexor digiti minimi brevis, make up the third layer of plantar foot muscles in that classification.
Adductor hallucis can work walking by adducting and flexing the first toe (hallux). Additionally, it helps to maintain the foot’s transverse and longitudinal arches.
Origin
The transverse and oblique heads of this muscle are the two muscular heads. The bases of the metatarsals 2 to 4 create the oblique head; the bone of the cuboid; the lateral cuneiform bone and the fibularis longus tendon.
The plantar ligaments and deep transverse metatarsal ligaments of metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints 3 to 5 are the sources of the transverse head.
Insertion
Before inserting distally on the lateral side of the base of the first digit’s proximal phalanx, the adductor hallucis’ two heads join together. The flexor hallucis brevis tendon on the fibular sesamoid is also connected at the distal attachment point.
Relations
This muscle is located in the central compartment of the sole. It is plantar (inferior) to the tendons of the plantar interossei muscles, flexor digitorum brevis, and flexor digitorum longus. The flexor hallucis brevis attaches to the muscle mediolaterally and proximally.
The dorsal (superior) surface of the oblique head of the adductor hallucis is covered by the deep plantar arterial arch and deep branches of the lateral plantar nerve. The transverse head’s dorsal surface is then crossed by the plantar metatarsal arteries. The proper plantar digital nerves of the plantar area run across the plantar surfaces of both heads.
Innervation
The deep branch of a lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) that originates from the tibial nerve innervates the adductor hallucis.
Blood supply
The posterior tibial artery and its branches provide this muscle with the majority of its vascular supply;
Deep branches of the medial plantar artery
Lateral plantar artery and its branches
deep plantar arch and plantar metatarsal arteries 1-4
Function
At the first metatarsophalangeal joint, the adductor hallucis muscle performs the following two actions:
It pulls the great toe toward the midline of the foot or adducts it.
It flexes the great toe with the flexor hallucis longus.
In the terminal stance phase of the gait cycle, these actions are necessary. The adductor hallucis strengthens the forefoot as the center of gravity for the body before the heel lifts by flexing and adducting the big toe. It also fixes the forefoot and stabilizes the foot arches because its transverse head is horizontal.
Clinical relevance
The foot’s transverse and longitudinal arches are supported by it. It is an essential intrinsic muscle of the foot.
The adductor hallucis may play a role in hallux valgus deformities because it pulls on the first digit’s lateral aspect. A full surgical release of the adductor hallucis distal tendon during bunionectomy has been linked to hallux varus, according to surgeons.
Assessment
By resisting flexion and adduction of the first digit, the adductor hallucis muscle can be tested.
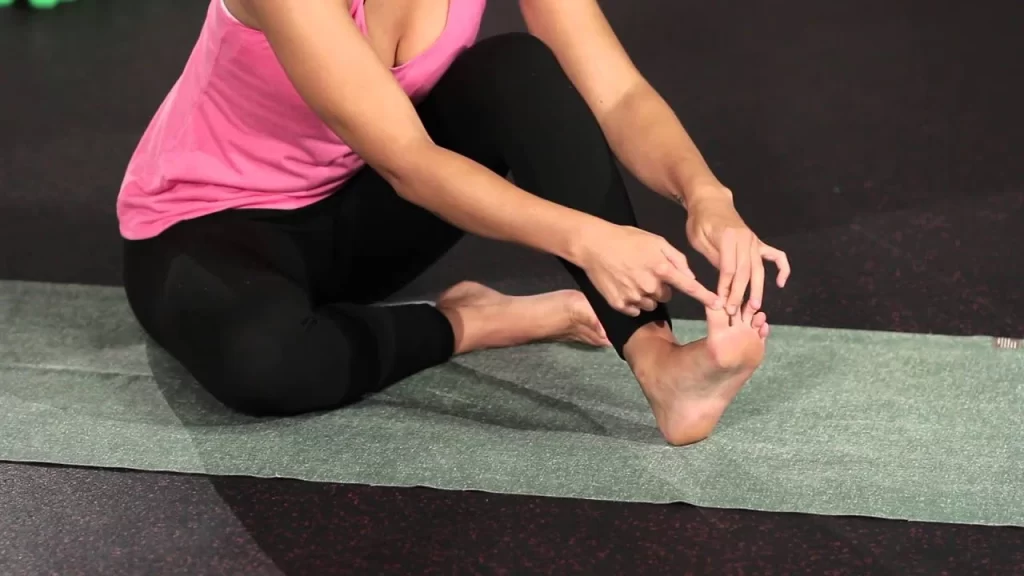
Adductor hallucis muscle stretching
Abducting the big toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint stretches the adductor hallucis, the foot’s internal muscle.

Adductor hallucis muscle strengthening exercise
Toe adduction squeeze
Squeeze inward with some cotton buds or wedges between your toes. Your intrinsic foot muscles and toe strength will benefit from this exercise.
Toe spread out
Open the toes of your feet outward with a band. Your intrinsic foot muscles and toe strength will benefit from this exercise.
FAQ
What is the adductor hallucis supplied by?
The adductor pollicis receives most of its blood from the deep palmar arterial arch. An important anatomical landmark for the radial artery is the adductor pollicis.
What nerve is adductor hallucis?
The Adductor hallucis (Adductor obliquus hallucis) is the muscle that adducts the big toe and is produced by two head oblique and transverse muscles. The lateral plantar nerve innervates each of its two heads.
How do you massage adductor hallucis?
Place your foot on a tennis ball while sitting up straight. To gently massage the foot, gently rotate the ball across the sole. After two minutes, stop for ten seconds, and then continue.
What is the function of the adductor hallucis?
Function. It supports the transverse and longitudinal arches while adducting and flexing the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint. By stabilizing the metatarsal heads and transverse arch of the foot, it may be most active during the push-off phase of the gait cycle.
How do you treat adductor hallucis?
As soon as possible, apply ice. Ice can be applied for 10 minutes every hour for the first few hours, decreasing to 2 or 3 times per day as pain and swelling decrease. A progressive rehabilitation program that includes stretching and strengthening exercises is essential once the pain has subsided.