BERA Test (Brain Stem Evoked Response Audiometry)
What is a BERA Test?
The BERA (Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response) test is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the auditory function of an individual’s nervous system, specifically the brainstem and the auditory pathways.
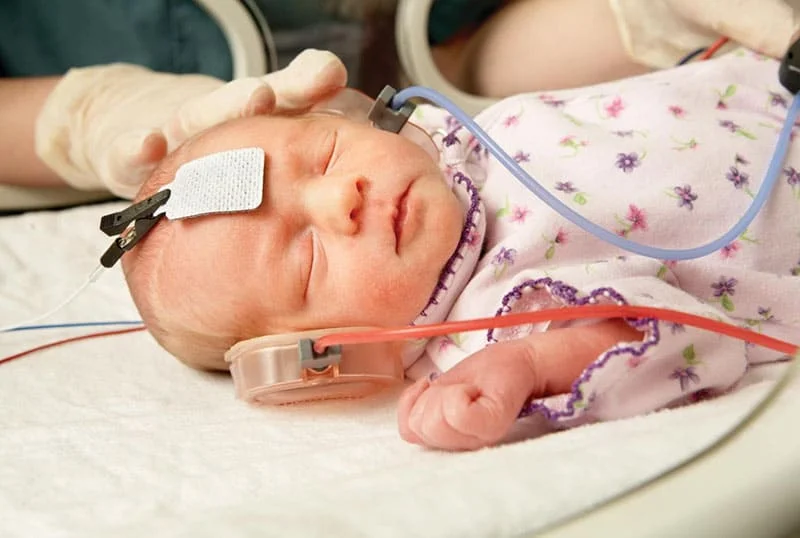
This non-invasive test is commonly employed to evaluate hearing disorders, especially in infants, young children, and individuals who cannot provide reliable responses during traditional hearing assessments.
During the BERA test, electrodes are placed on the scalp to detect electrical responses generated by the auditory system in response to sound stimuli, typically in the form of clicks or tone bursts presented through earphones. These electrodes record the electrical activity generated by the auditory nerve, brainstem, and other associated structures as they respond to the sound stimuli.
Related Anatomy
Sound goes via the outer ear canal and stimulates it before reaching the eardrum. Three microscopic bone fragments in the eardrum, the malleus, incus, and stapes, are responsible for transmitting vibrations to the inner ear. The inner ear houses the vestibular portion, which is responsible for maintaining balance, and the cochlear region, which is involved in hearing.
The brainstem, a crucial area of the brain, receives hearing and balance impulses from the inner ear via the 8th cranial nerve, also referred to as the vestibulocochlear nerve.
For newborns who are at high risk of hearing loss and cannot undergo a standard audiometric exam, the test is indicated.
BERA Test Price In India
Depending on where you take the BERA test, the price starts at INR 1440 and can go as high as INR 3000. The BERA test evaluates how a child’s hearing is influenced or affected by various nervous system components. The ABR test gauges how the auditory nerve reacts to sounds.
It is carried out if a newborn or infant fails the auditory screening test administered immediately after birth in the hospital or if an older kid exhibits hearing loss that is suspected but not proven by more conventional hearing tests.
What Is The BERA Test All About?
- The BERA exam is risk-free and painless.
- The BERA test can only be performed on a child who is asleep or lying comfortably, immobile, and with their eyes closed.
- If your child is under six months old, the ABR test can typically be performed while they are both asleep.
- The BERA test can typically be administered while your child is awake if they are older than seven and can relax and lay still. The test will be conducted in a room with soundproofing in the Department of audiology.
- Your child will need medication to assist him or her in relaxing throughout the operation since the ABR test is administered under anaesthetic to youngsters between the ages of 6 months and 7 years.
- ABR testing are done in centres while people are asleep. There are certain eating and drinking restrictions that must be followed in the hours before the surgery if anaesthetic is required. If these rules are not fulfilled, the test won’t be finished that day.
- After the tests are completed under anaesthetic, your child’s primary care physician will need to see your child for a medical and sign a health history form.
- The test lasts between an hour and an hour and a half, but due to recovery time, the entire appointment will last between two and four hours if your child needs an aesthetic.
Why Is BERA Tests Done?
It can be challenging to determine a child’s hearing loss right away. Hearing loss can make speech, language, cognitive, social, and emotional problems worse. Therefore, it is ideal to test a child’s hearing when they are still very young.
Healthy hearing is defined as the ability of the sensory neuron to transmit audio information from the eardrum to the cerebral at a specified rate. The BERA test can reveal whether or not sound impulses are being delivered to your brain by your nerves and whether their speed is within permissible limits.
During this hearing test, it is possible to identify the child’s hearing impairment type (conducting or input from sensors), degree (hearing threshold), and location (inner ear or other regions).
BERA is used to diagnose otoneurology in addition to testing hearing threshold. This will help people who have a single or asymmetrical hearing impairment.
How Is BERA Tests Performed?
The following electrodes are inserted into the head at various sites to record these waveforms:
A non-inverting electrode is positioned over the top of the skull, which is the most noticeable location at the rear of the head.
Reverse electrodes are supported by a robust bony elevation on each ear lobe or submandibular protrusion.
An earthing electrode is positioned above the brow.
The generated waveforms are amplified by a variety of electrical techniques, making waveform recording simple.
Wave I through Wave VII are the waveform’s peaks.
The following electrodes are inserted into the head at various sites to record these waveforms:
A non-inverting electrode is positioned over the top of the skull, which is the most noticeable location at the rear of the head.
Reverse electrodes are supported by a robust bony increase behind each ear on each lobe or submandibular protrusion.
An earthing electrode is positioned above the brow. Wave I through Wave VII are the waveform’s peaks.
The time interval between the wavelength and the click stimulation is typically less than 10 milliseconds.
In various locations and polarities, various readings are obtained and annotated.
The waves are captured and sent for interpretation.
Waveform recording is made simple by the electrical methods used to amplify the generated waves.
How to Prepare For The BERA Test?
The cost of the BERA test is not extremely high, but extreme caution must be used in the preparation process. The following are some tips:
Hair must be oil-free. The subject of the test is advised to take a shampoo bath before the examination.
The BERA method still necessitates extensive deception. In order to put the patient or newborn to sleep throughout the procedure, a little sedative may be administered.
What Are The BERA Test’s Indications?
The BERA Test Indications are:
- To find where the hearing loss is coming from. The examination finds anomalies from the cranial nerve to the brainstem.
- As an auditory diagnostic examination in children who may not respond to conventional audiometry, such as those who are hyperactive, mentally ill, or other children.
- Asymmetric hearing loss is defined as hearing loss that is more obvious in one ear than the other.
- For newborns who are at a high risk of hearing loss, such as those who have a family history of congenital hearing loss.
- Hyperbilirubinemia (excess bilirubin)
- Head deformities or abnormalities
- Head injuries
- Head deformities or abnormalities
- Acoustic neuroma, a mammary tumour of the eighth cranial nerve, and abnormalities of the nervous system are suspected.
Results of BERA Test Interpretation
Audio-evoked potential signals are waves with peaks and troughs that come from the brainstem. Wave I, Wave II, and so forth are positive potentials that are labelled as wave I, wave II, and so forth till wave VII and are recorded from the sensor at the vertex.
Summary
By analyzing the recorded brainwave patterns, audiologists, and healthcare professionals can identify potential hearing issues, assess the severity of hearing loss, pinpoint the location of auditory pathway abnormalities, and help determine appropriate treatment or intervention strategies.
The BERA test is a valuable tool in diagnosing hearing impairments, particularly in individuals who may not be able to participate in standard hearing assessments due to age, developmental stage, or cognitive limitations.
FAQs
What is the Bera hearing test used for?
An objective method of provoking brain stem potentials in response to click-heavy audiological stimuli is the BERA hearing test. However, it is typically utilized to detect any abnormalities in the brainstem or vestibulocochlear nerve.
What is the normal range of the BERA test?
It tests hearing sensitivity in the 1000–4000 Hz frequency range. Seven waves are created in the first 10 ms in a healthy person.
What age is the BERA test for?
If your child is under 6 months old, the ABR test can typically be completed while he or she is napping. If your child is older than 7 years old and is able to relax and lie still, the BERA test can typically be performed while your child is awake. The test will be conducted in a unique, sound-treated room in the Department of Audiology.
How long is Bera hearing test?
The test itself lasts between an hour and an hour and a half, but owing to recovery time, the full consultation will last between two and four hours if your child requires anaesthesia.