Brachialis Muscle Pain
When you feel pain in the arm and limit the movement or use of the arm, it is indicated to be brachialis muscle pain. This pain arises due to forceful or repetitive strain on the brachialis muscle. This pain is relieved by the RICE technique and physiotherapy treatment.
What is brachialis muscle pain?
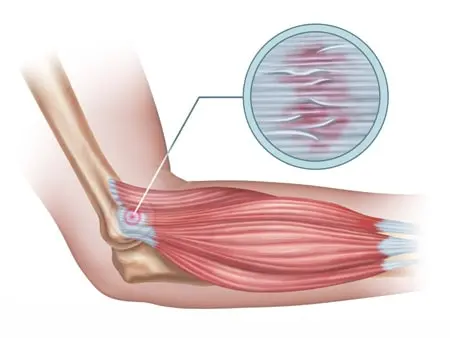
- The brachialis muscle is situated in the arm near the crook of the elbow joint.
- This muscle is flex and bends the elbow joint when the hand and forearm are in a pronated position with the palm facing down.
- This muscle is working as closely with the biceps brachii and brachioradialis muscles which ensures that the elbow joint bends properly.
- When the damage occurs in the brachialis muscle it produces pain and limits the movement of the arm normally.
- The patient feels weakness in the arm and also presents swellings in the muscle due to injury.
- The home treatment used RICE therapy to relieve the pain and also used physiotherapy treatment for reducing the swellings and spasms.
Anatomy of the brachialis muscle
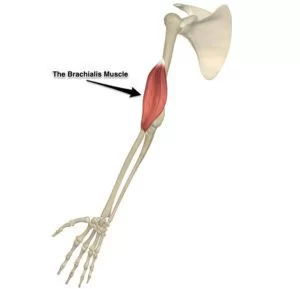
- This brachialis muscle arises from the front of the humerus bone or upper arm bone.
- This brachialis muscle is inserted into the coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna bone.
- This brachialis muscle is along with the supinator muscle, which is created up the floor of the cubital fossa of the elbow joint.
- The brachialis muscle is inverted by the musculocutaneous nerve and some regions of the radial nerve.
- The function of the brachialis muscle is to bend the elbow joint mostly when the forearm is pronated means palm down position.
Cause of the brachialis pain
- This brachialis muscle is injured by a forceful or repetitive strain placed on the muscle.
- Especially this force is applied when the elbow joint is in a pronated position.
- Climbers or throwing athletes and people who have participated in racquet sports are mostly suffering from a brachialis injury due to overuse and repetitive strain.
- This muscle is mostly damaged by overuse of this muscle.
Symptoms of the brachialis muscle pain
- The patient feels pain in the front of the elbow joint.
- Swelling is present in the front of the elbow joint.
- The patient feels a problem extending the elbow joint because it places stress on the injured brachialis muscle.
- The patient feels Weakness in the muscle and also feels the movement of flexing the elbow joint.
- In the patient, trigger points are present in the muscle pain.
- The patient is also experiencing brachialis muscle weakness when the patient is suffering from neck pain with cervical radiculopathy.
Diagnosis of brachialis pain
When the patient feels any symptoms and causes of pain of this muscle so that as soon as visit and contact the healthcare provider.
So that the healthcare provider is assessing the condition and conducts the correct treatment on the patient.
In the diagnosis of a brachialis injury healthcare providers follow the examination of the brachialis muscle.
The first healthcare provider is to study the history of the injury and try to know about the cause of the pain.
In the observation observe the swelling and skin redness in the patient.
In the palpation palpate the swelling and check the temperature.
In the examination examine the ROM ( range of motion ) and strength of the elbow joint.
A healthcare provider also suggested an X-ray which is help to assess the possible fracture and also magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which evaluates the soft tissues in the anterior elbow joint.
Treatment of brachialis pain
RICE Principle
In the initial phase of the muscle pain used to RICE principle is to relieve the muscle pain.
[R] rest – When the pain occurs someday rest is suggested to the patient. During the rest, time patient is also used to a splint to release the pain.
[I] ice – Ice is used on the area of pain for 15 to 20 minutes, the patient is also used to an ice pack and frozen peas which are used to reduce the swelling.
[C] compression – In the compression used to bandage the muscle pain area for reducing the pain, swelling, and spasms.
[E] elevation – The patient is elevated to the foot with the help of the pillow to relieve the swelling.

Massage:
Massage is also an adequate treatment for brachialis muscle injury.
So massage helps them reduce the pain or improve the blood flow and improve tissue extensibility to the muscle.
This massage is applied with the help of oil to release the swelling.
This massage is applied in a circular movement.
Trigger Point Release:
Trigger point release therapy involves the application of firm pressure to a hyperirritable spot and taut band, which is known as a trigger point.
This pressure is work to reduce the tension in the muscle, by reducing the blood flow to the area decreasing the pressure felt.
When the pressure is removed, blood flows back to the place and flushes to any toxins which are released by the muscle.
These points are also guided as to pain in other regions of the body, lasting into a few seconds.
Dry Needling:
Dry needling is a procedure that is used to reduce muscle restriction by releasing the trigger points with acupuncture needles.
A soft tissue Occupational Therapist is used to individually packed of sterilized acupuncture needles which are direct to needle the trigger point and produce a local response within the muscle, which is fast dissipating to allow the muscle of relaxing.
Myofascial Release:
Myofascial release is the too manipulative treatment that is trying to release the tension in the fascia due to trauma, posture, or inflammation.
Connective tissues are called fascia which surrounds the muscles, bones, nerves, and organs of the body.
Points of the restriction in the fascia which is placed a great deal of pressure on nerves and muscles causing chronic pain.
A soft tissue occupational therapist is used to long stretching strokes means to balance this tissue and muscle mechanics which is improved joint ROM ( range of motion ) to relieve pain.
Heat:
Using heat on the painful brachialis muscles through the use of the heat pack which is help to alleviate the pain.
Heat is an affordable, effective form the pain relief which is works by increasing the blood flow to the site, relaxing the muscles, and increasing ROM ( range of motion ) and flexibility.
Physiotherapy treatment of the brachialis pain
The physiotherapy treatment includes electrotherapy, stretching, and exercise to relieve the pain and swelling of the muscle.
Electrotherapy for the brachialis muscle pain :
The electrotherapy treatment includes SWD ( Short wave diathermy ), TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), IFT ( Interferential therapy ), and the US ( Ultrasound ) which is used to reduce pain and swelling.
Ultrasound therapy is used on tender points and trigger points to reduce swelling.
Short-wave diathermy is applied to a site of pain to reduce the pain.
TENS and IFT machine is used in the place of pain to release the pain and swelling.
Strengthening exercise for brachialis muscle pain:
- Hammer Curl
- Cross Arm Landmine Curl
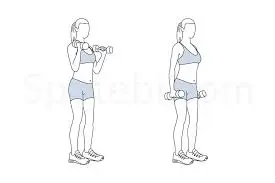
Hammer Curl :
The patient’s position is holding one dumbbell in both hands, relaxing the knee joint, and standing with the feet shoulder-width apart.
Starting with the arms at the sides and palms facing inwards, flex the elbow and raise the dumbbell to the shoulder.
Back to the starting position and repeat with the alternate arm.
For optimal results, perform 2 to 3 sets of the 10 to 15 repetitions 3 times per week.
In the modified version of the hammer, curl is used to incline the bench to provide a larger ROM ( range of motion ) for the brachialis.
The patient’s position is seated on an incline bench and leaning back with the headrest, and maintaining a dumbbell in each hand.
Starting with the arms at to sides and palms facing inwards, flex the elbow and raise the dumbbells to the shoulder, then back to the starting position and repeat this exercise.
Do this exercise in 2 to 3 sets of 15 to 20 repetitions 3 times every week.
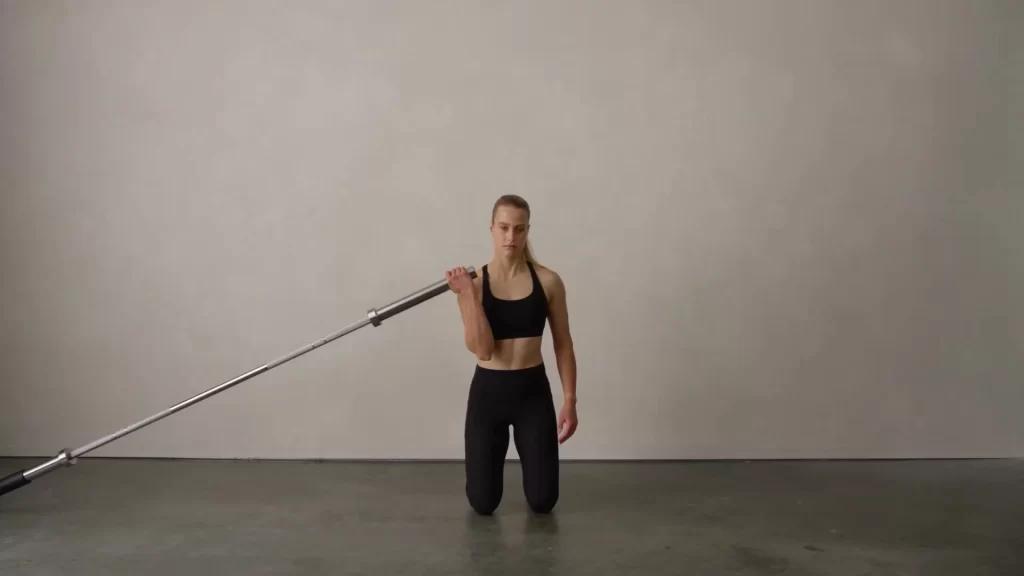
Cross Arm Landmine Curl:
The patient’s position is secure the barbell in a landmine attachment, a corner, or however the stabilize the end of one side of the bar on the floor in front of the body.
The patient is in a standing position perpendicular to the barbell with the feet in a relaxed stance.
Grasp the barbell with the left hand and palm facing upwards, and then contract the left brachialis muscle which curls the barbell upwards and across the body.
Squeeze the brachialis muscle hard at the top of the repetition and slowly back to the starting position.
Repeat this exercise in 2 to 3 sets of the 15 to 20 repetitions 3 times every week.

Stretching for the brachialis muscle pain
Stretching helps to reduce the tightness of the muscle pain.
- Stretching with a Block
- Stretching on the Floor
- Stretching with the Table
- Stretching with the Wall
- Standing Stretch
- Seated Stretch
Stretching with a Block:
The brachialis muscle pain is removed by doing a simple stretch at the table with a block.
The patient’s position is to sit at the table and place a solid object like a yoga block and a thick book in front of his/her.
Rest the elbow joint over the thing and stretch the forearm out straight ahead.
For the stretch, the patient is done with the palm facing upward, and again with the palm facing down, and this stretching position is to hold up to 15 to 30 seconds and repeat 3 times in 1 session every day.
Stretching on the Floor:
The brachialis muscle is also stretched by lying down on the back on the ground and in bed.
Keep the legs straight in front of the body and anchor the elbow firmly onto the ground, must keep the elbow joint connected to the floor.
Use the other hand to push the hand to the side, another floor stretch patient can do involves lying on the back and using the other hand to form a circle around the wrist and pulling the arm up over the head.
This stretching position is to hold up to 15 to 30 seconds and repeat 3 times in 1 session every day.
Stretching with the Table:
The easy stretch at the table includes relaxing the elbows on the table and using the opposite hand to rotate the palm facing upward.
Turn the palm up as far as possible which is going without hurting, then turn the palm facing downward in the same fashion, must keep the elbow joint firmly connected to the table.
The patient is also using the table for the stretch by sitting in the chair and placing the forearm parallel to the edge of the table.
With the feet planted on the floor, lean forward to stretch.
This stretching position is to hold up to 15 to 30 seconds and repeat 3 times in 1 session every day.
Stretching with the Wall:
The patient’s position standing position at arm’s distance from the wall and extending the arm toward the wall.
The hand must be held lower than the shoulder, with the arm slightly in front of the body.
Put the hand and the fingers, against the wall and carefully turn the head away from the wall.
Standing Stretch:
The patient’s position is standing near to doorway with the shoulder joint parallel to the doorway’s opening.
The patient reached straight to the side and slightly back to grasp the doorjamb at shoulder level with the right hand. Back also away from the doorjamb, if necessary must fully straighten the right arm.
Turn the body slowly toward the left till feel a stretch in the upper right arm, and maintain this stretch for 15 to 30 seconds breathing normally, then repeat the opposite side.
Do this stretching exercise 3-5 times on both sides.
Seated Stretch:
The patient’s position is sitting down on the floor, then straightening both arms and planting the hands on the floor behind the body slightly wider than the hip joint.
Turn the hands so that fingers are pointed straight back, and scoot the hip joint slowly forward, holding the weight evenly distributed, till the feel mild tension in the brachialis muscle
Maintain this stretching position for holding 15-30 seconds, breathing normally, and then scoot the hips back toward the hands to release the stretch.
Repeat this stretching exercise 3 to 5 times every day.
FAQ
Why does my brachialis muscle hurt?
Injury or strain to the brachialis can cause pain in the upper arm, numbness in the back forearm, and thumb, or problem with elbow flexion. Pain is usually caused by heavy lifting using improper methods (bent elbows) such as picking up children or working with heavy tools.
How long does a brachialis strain take to recover?
The time required to recover from a bicep tear or strain will depend on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, as well as the severity of the injury. Mild damages take ten weeks or more, while more painful injuries that need surgery can take months to fully recover function.
What causes brachialis tendonitis?
A tendinopathy injury is due to overuse or constant loading of the brachialis tendon without sufficient rest times to allow for tissue regeneration and healing. The repetitive nature of flexing your elbow needed in rock climbing can lead to deterioration of the brachialis tendon that inserts into a bone in your elbow.
Why does my brachialis hurt when I curl?
Tight and tense muscles are a big contributing aspect to pain in our forearms when curling. The muscles in our forearms can become more tense and even tighter when we curl. This tightness then refers to a pain sensation in our brain.
How do you know if you strained your brachialis?
The clinical characteristics of a brachialis muscle injury are pain and swelling in the anterior mid-arm. Unlike a biceps muscle injury, in which a palpable gap may be felt on physical assessment, injury to the brachialis muscle would be tricky to palpate due to its position deep in the overlying biceps brachii


One Comment