Breathing Exercises for The Lungs
Introduction
Lung capacity indicates how much air your lungs can keep. Functioning breathing exercises can enhance your lung ability over the period. lung capacity is the whole quantity of air that your lungs can keep.
Breathing is an essential of life that usually happens without much thinking. When you respire in, blood cells acquire oxygen and discharge carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that’s held back through your body and exhaled.
Breathing incorrectly can disrupt the interaction of oxygen and carbon dioxide, which can lead to exhaustion, anxiety, panic attacks, and other mental and physical health problems. Over the period, our lung capability and lung function naturally decline slowly.
Some disorders such as asthma can enormously speed up the low lung capacity and decrease normal functioning. This shows difficulty in breathing and shortness of breath.
Some exercises can support maintaining lung capability, making it more effortless to keep your lungs fit and convey your body the oxygen it requires. If you’re feeling nervous, there are several different breathing techniques you might try. Discover how to utilize breathing exercises to assist in reducing tension and anxiety.
What are the Breathing Exercises?
Exercises designed to improve certain aspects of respiratory control are called breathing exercises. They are frequently used to enhance relaxation, reduce tension, and enhance lung function.
Breathing exercises are purposeful, regulated changes in breathing patterns that provide targeted health advantages. They involve using diverse breathing patterns and strategies to affect your body and mind in numerous ways, not merely prolonging your breaths.
A breathing exercise is a simple yet powerful technique that involves consciously controlling your breath to improve your physical and mental well-being. It’s like a mini-workout for your lungs and nervous system.
What is Normal Lung Capacity?
- Lung capacity is a measurement of how much air your lungs can maintain. It is an important element in how sufficiently you can breathe. Lung capacity and function can differ widely from person to person and even alter during our lifetimes.
- The normal lung capacity for an adult is about 6 liters. This can vary depending on age, gender, height, and weight. For example, men generally have a larger lung capacity than women and taller someones normally have a larger lung capacity than shorter someones.
- If you have a low lung capacity, you may sense shortness of breath or have problems exercising.
How to measure Lung capacity?
Generally spirometry test is used to measure normal lung capacity.
Spirometry Test for Lung Capacity
A spirometry test is a common pulmonary function test that estimates how much air you can breathe in and out, as well as how fast you can exhale. It is used to analyze and monitor lung disorders like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis.
During a spirometry test, you will be asked to blow into a mouthpiece that is connected to a machine called a spirometer. The spirometer will record how much air you exhale as well as how frequently. The results of the test will be compared to normal values for your age, gender, height, and weight.
Three main measurements are taken during a spirometry test:
- Forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1): The amount of air you can exhale in a single second is known as your forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1).
- Forced vital capacity (FVC): This is the total amount of air you can exhale after taking the deepest breath you can.
- FEV1/FVC ratio: This is a measure of how quickly you can exhale. A lower FEV1/FVC ratio is a sign of airway obstruction.
A spirometry test is an easy and non-invasive test that can be performed by physicians in a clinic. The test usually takes about 15 minutes to finish.
Here are some things to keep in mind before and during a spirometry test:
- Don’t smoke for at least 8 hours before the examination.
- Sport loose-fitting garments that will permit you to carry deep breaths.
- Avoid consuming a big meal previous to the test.
- Tell your physician about any medicines you are taking, as some medicines can affect the results of the test.
During the test, you will be asked to take several deep breaths and then exhale as forcefully as you can into the mouthpiece of the spirometer. You may be asked to repeat the test several times to get the most accurate results.
The results of your spirometry test will be explained to you by your doctor. They will discuss the results with you and recommend any further testing or treatment that may be needed.
Here are some of the benefits of spirometry testing:
- It is a non-invasive and painless test.
- It is a quick and easy way to measure lung function.
- It can help to diagnose lung diseases early on.
- It can help to monitor the progression of lung diseases.
- It can help to guide treatment decisions.
If you are concerned about your lung health, talk to your doctor about whether a spirometry test is right for you.
Causes of Low Lung Capacity
There are several causes of low lung capacity, ranging from lifestyle factors to chronic diseases.
- Smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of preventable lung disease, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema. Smoking injures the lungs and airways, making it difficult to breathe.
- Air pollution: Exposure to air pollution, both indoor and outdoor, can damage the lungs and reduce lung capacity. Air pollution can come from a variety of sources, including cars, factories, and power plants.
- Respiratory infections: Some respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, can damage the lungs and reduce lung capacity.
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder that induces inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This can make it difficult to breathe and reduce lung capacity.
- COPD: COPD is a chronic respiratory condition that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Emphysema damages the air sacs in the lungs, while chronic bronchitis causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Both conditions can reduce lung capacity.
- Cystic fibrosis: Cystic fibrosis is a congenital condition that induces thick mucus to be produced in the lungs and different organs. This mucus can block the airways and reduce lung capacity.
- Lung cancer: Lung cancer can damage the lungs and reduce lung capacity. Treatment for lung cancer, such as surgery or radiation therapy, can also damage the lungs and reduce lung capacity.
- Obesity: Obesity can put pressure on the lungs and make it difficult to breathe. This can reduce lung capacity.
Here are some additional things that can contribute to low lung capacity:
- Age: As we age, our lungs become less elastic and have a reduced capacity to breathe.
- Gender: Typically, men can breathe deeper than women.
- Height: People with bigger lung capacities tend to be taller than those with smaller ones.
- Weight: Due to the additional weight on their chest and diaphragm, those who are obese or overweight may have a reduced capability for lung function.
- Environmental factors: The lungs and airways can be harmed by exposure to air pollution, dust, and other irritants, which can lead to decreased lung capacity.
Signs of Low Lung Capacity
Some of the signs and symptoms of low lung capacity include:
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea: Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is the most typical sign of reduced lung capacity. It can happen when at rest or even during effort. Visiting a doctor if you have shortness of breath is critical as it may indicate a dangerous medical issue.
- Wheezing: You might produce a high-pitched whistling sound when you breathe. It may be brought on by a constriction of the lungs’ airways. A wheezing fit may indicate COPD, asthma, or other respiratory disorders.
- Tightness in the chest: Tightness is a sensation of pressure or pain. It may be brought on by lung inflammation or by a constriction of the airways. Tightness in the chest may indicate COPD, asthma, or other respiratory issues.
- Cough: A cough is a quick lung exhalation of air. Numerous factors, including infections, allergies, and irritants, might contribute to it. If a cough persists for several weeks, it may indicate a significant medical issue.
- Mucus production: One of the most typical signs of respiratory infections is mucus production. On the other hand, it could potentially indicate a more serious illness like pneumonia or COPD.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is the state of being weak or exhausted. Low lung capacity is one of the many possible causes. Daily tasks may be challenging to do while fatigued.
- Loss of weight: Loss of weight can indicate several conditions, including a weakened lung. Individuals who have reduced lung capacity may lose weight as a result of eating too little or finding it difficult to exercise.
- If you are experiencing any of these signs, it is necessary to see a physician. They can analyze the cause of your symptoms and recommend treatment.
Breathing Exercises to Improve Lung Capacity
Diaphragmatic Breathing
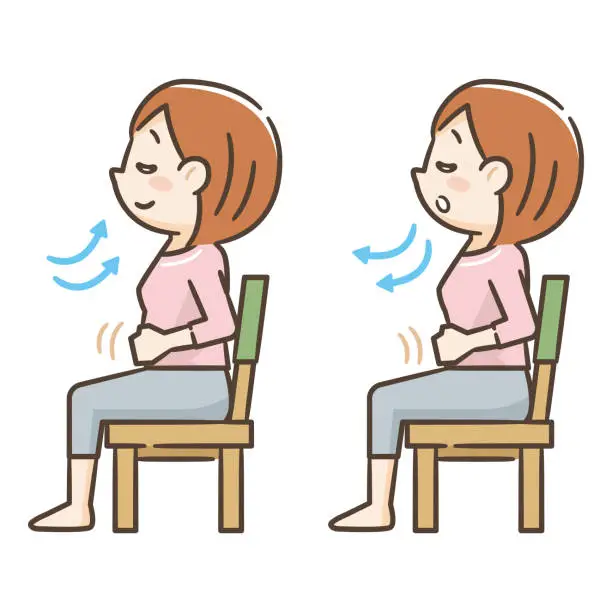
The primary respiratory muscle, the diaphragm, is engaged during diaphragmatic breathing, sometimes referred to as belly breathing or deep breathing. This activity can assist to enhance lung function, lessen anxiety and tension, and enhance the quality of sleep.
To perform diaphragmatic breathing, do the following:
- With your feet flat on the ground and your knees bent, lie down on your back.
- Maintain your abdomen with one hand and your chest with the other.
- Breathe gently through your nose, letting your stomach expand.
- Breathe out gently through your lips, letting your stomach tighten.
- Continue for ten to fifteen minutes.
Pursed-Lip Breathing
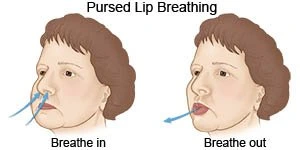
Breathing carefully and gradually with your lips pursed might assist in relaxing the airways and lowering the pace of breathing. Those who suffer from asthma, COPD, or other respiratory disorders may find this activity beneficial.
- The steps to pursed-lip breathing are as follows:
- With your shoulders relaxed, sit up straight.
- Take a calm, deep breath through your nose.
- As though you are going to blow out a candle, purse your lips.
- Breathe out slowly through pressed lips.
- Continue for ten to fifteen minutes.
Alternate Nostril Breathing

Breathing through your alternate nostrils might assist in calming the nervous system and encourage relaxation. Those who suffer from headaches, congestion, or allergies may find this exercise beneficial.
The steps to perform alternating nostril breathing are as follows:
- Maintain your back straight and sit up straightforwardly.
- Put your left ring finger over your left nose and your right thumb over your right nostril.
- Breathe in using your left nostril.
- Using your ring finger to close your left nose, release the air via your right nostril.
- Breathe in using your right nostril.
- Using your thumb to seal your right nose, release the air via your left nostril.
- Continue for ten to fifteen minutes.
4-7-8 Breathing

Stress, anxiety, and sleeplessness can all be lessened with the use of 4-7-8 breathing techniques. Those who have high blood pressure may also benefit from this type of exercise.
The steps to perform 4-7-8 breathing are as follows:
- Give out a full whooshing sound by closing your mouth.
- Shut your lips and take a quiet four-count breath via your nose.
- Breathe in and out for seven seconds.
- Make a whooshing sound as you fully release the breath from your mouth while counting to eight.
- Continue with four to seven rounds.
Benefits of Breathing exercise in lung capacity
Regular breathing exercises can offer a range of benefits for lung capacity and overall respiratory health.
Here are a few of the main advantages:
- Improved Lung Function: Breathing exercises are a good way to strengthen the diaphragm, intercostals, and accessory muscles, which are part of the respiratory system. By making these muscles stronger, the lungs can expand to their maximum potential and these muscles can function more effectively.
- Increased Oxygen Intake: Breathing exercises encourage deeper, longer breaths by boosting the respiratory muscles. This results in increased oxygen intake, which is necessary to provide the body with the oxygen it requires to operate as planned.
- Improved Lung Elasticity: Consistent breathing exercises support the preservation of the lungs’ elasticity, which enables the airways to expand and constrict appropriately during inhalation and to stretch and expand during expiration. Efficient gas exchange and proper lung function are dependent on this flexibility.
- Decreased Respiratory exhaustion: People with respiratory disorders such as COPD and asthma frequently experience respiratory exhaustion, which can be minimized with the aid of breathing exercises. Breathing exercises facilitate breathing and lessen the effort needed for regular breathing by strengthening the respiratory muscles.
- Increased Respiratory System Effectiveness: Breathing exercises help the respiratory system function more effectively overall. They improve the lungs’ capacity to absorb oxygen, expel carbon dioxide, and supply oxygen-rich blood to every body part.
Apart from these advantages, breathing exercises can provide several other beneficial results, such as:
- decreased stress and anxiety
- enhanced quality of sleep
- Improved physical capabilities
- enhanced vitality
- Enhanced attention and concentration
Summary
Age, obesity, certain medical conditions, and a sedentary lifestyle can all reduce lung capacity. There are, however, several things you can do to keep your lungs healthy. Regular exercise, a good diet, and avoiding tobacco smoking can all help your lungs operate well.
Breathing exercises are an effective way to improve lung capacity and general respiratory health. They are easy, safe, and suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels. Regular breathing exercises can significantly enhance lung function, respiratory efficiency, and general well-being.
If you have symptoms of reduced lung capacity, such as shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor to determine if an underlying illness is the cause.
FAQs
Do Breathing exercises strengthen the lungs?
Yes, breathing exercises can strengthen your lungs in several ways including;
What are the symptoms of weak lungs?
Breathlessness, Weight loss, Fatigue, Wheezing, Chest infection, mucus production, coughing up blood, etc..
Which exercise is good for the lungs?
Deep breathing exercises are good for the lungs. The primary breathing muscle, the diaphragm, is strengthened by this exercise. It facilitates deeper, more effective breathing, which can increase lung capacity and endurance.
What are the benefits of breathing exercises in improving lung capacity?
Breathing exercise benefits include Improved Lung Function, Increased Oxygen Intake, Improved Lung Elasticity, Decreased Respiratory exhaustion, Increased Respiratory System Effectiveness, etc.
References
- Gotter, A. (2022, September 29). Breathing exercises to increase lung capacity. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-increase-lung-capacity
- American Lung Association. (n.d.). Breathing exercises. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/wellness/breathing-exercises
- Crna, R. N. M. (2023, May 16). What exercises can help increase lung capacity? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323787
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Diaphragmatic breathing. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9445-diaphragmatic-breathing





One Comment