Injury of Radial Nerve: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise
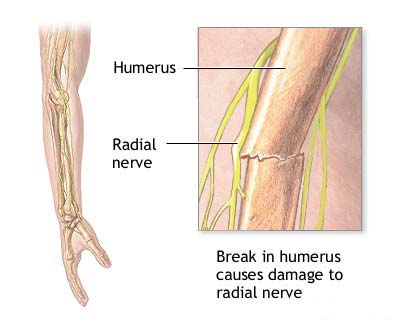
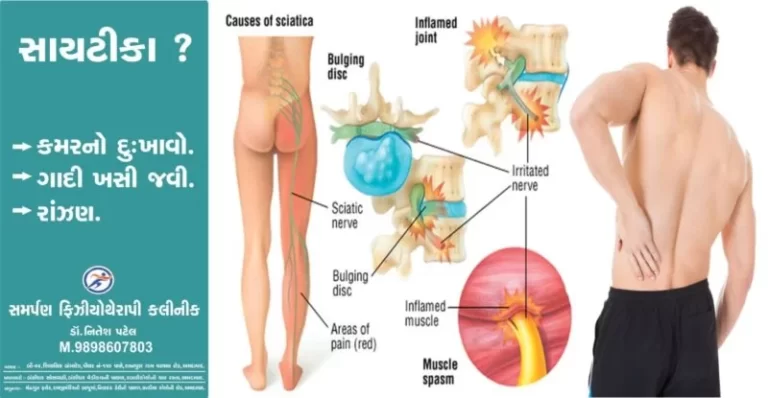
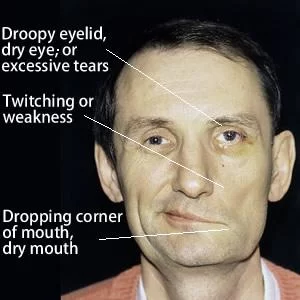
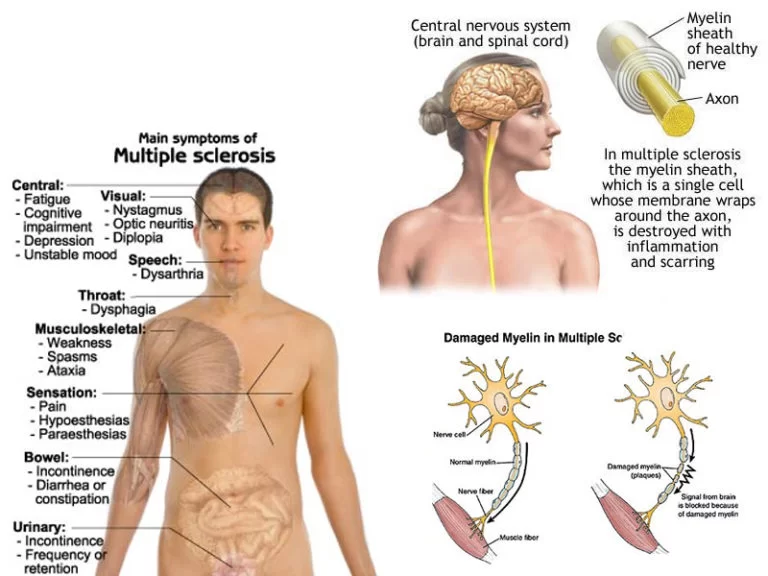
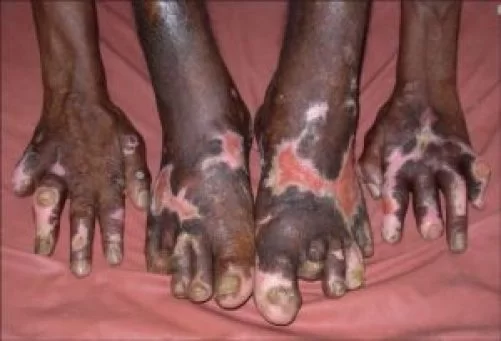
Description: Injury to the radial nerve may result in radial neuropathy, also called radial nerve palsy. Radial nerve injury may be due to physical trauma, infection, or even exposure to toxins. It often causes numbness and tingling or burning pain. It can also be painless. The condition may cause weakness or difficulty moving your wrist,…