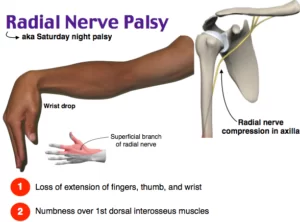
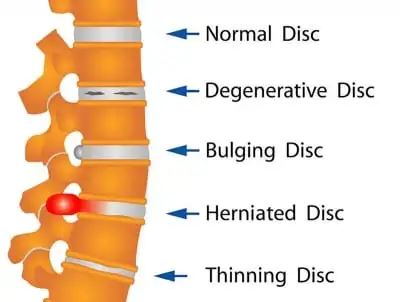
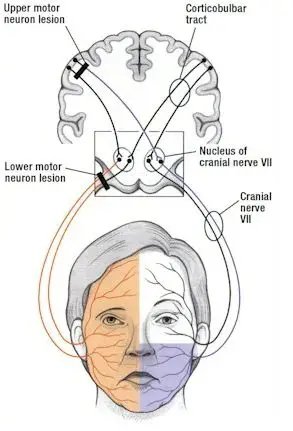
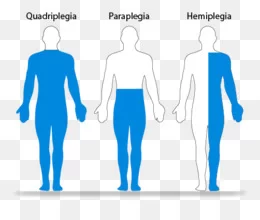
Ulnar Nerve Injury/Palsy/Compression
Introduction Anatomy Related to Ulnar Nerve Injury COURSE OF THE ULNAR NERVE GUYON’S CANAL: MECHANISMS OF Ulnar Nerve Injury: CLINICAL PRESENTATIONS in Ulnar Nerve Injury: Cubital tunnel syndrome: Guyon’s canal syndrome : SYMPTOMS OF Ulnar Nerve Injury/ PALSY/ COMPRESSION: CAUSES OF Ulnar Nerve Injury/ PALSY/COMPRESSION: Contributing factors to Ulnar Nerve Injury: DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE in Ulnar…