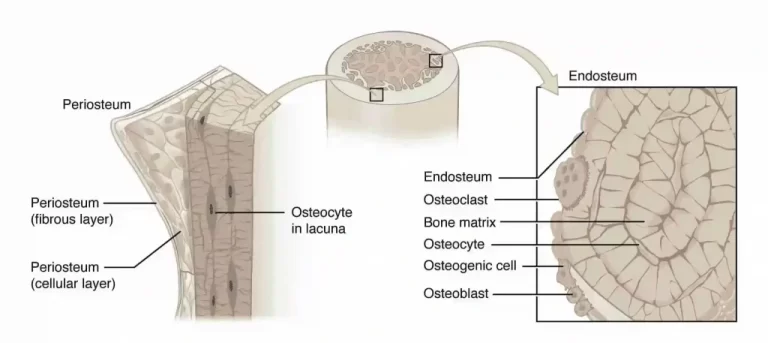
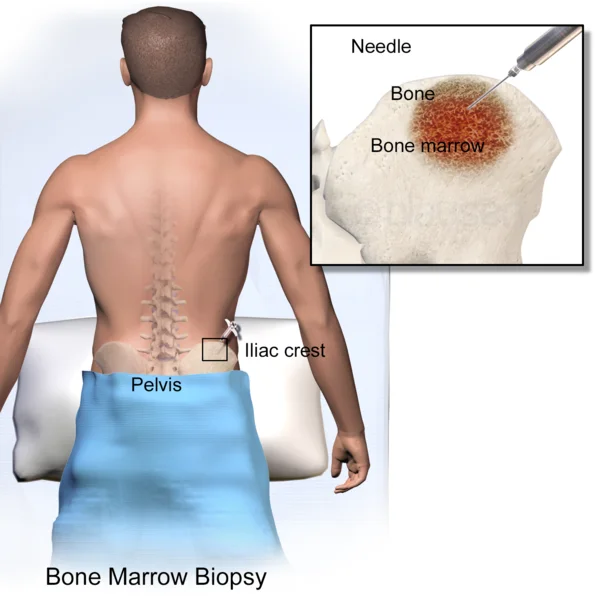
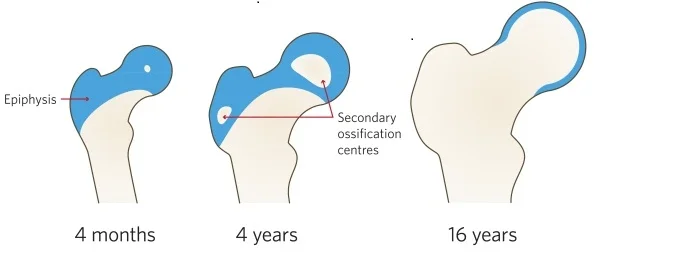
Potassium
What is Potassium? Potassium is an element in chemistry with the atomic number 19 and the symbol K (from Neo-Latin kalium). The metal has a silvery white color and is sufficiently soft to cut with a knife with ease. In a few seconds, potassium metal and air oxygen combine to generate flaky, white potassium peroxide….