Cervical Traction: Indications, Contraindications, When to use?
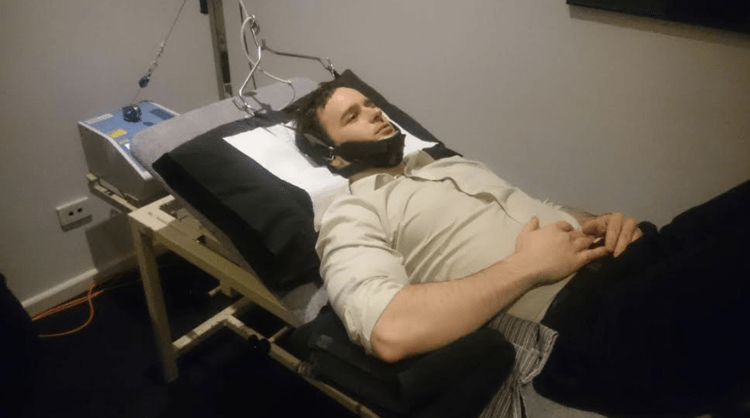
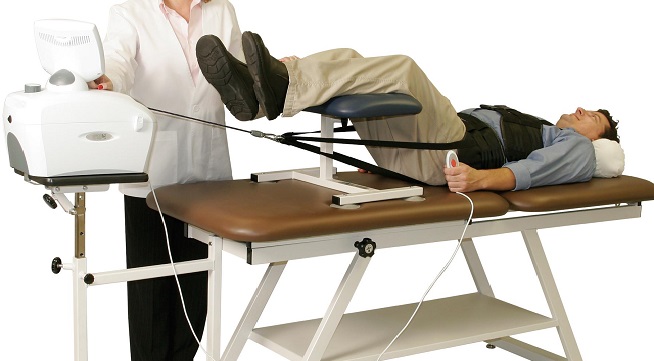
Introduction of cervical traction: Cervical traction is a well known treatment for a bulging disc in the neck or cervical region that relieves pain by opening of the cervical foramen.it will reduce pressure on compressed nerve roots exiting the spinal canal.Traction can be applied manually or by traction devices. The practice of giving traction is…