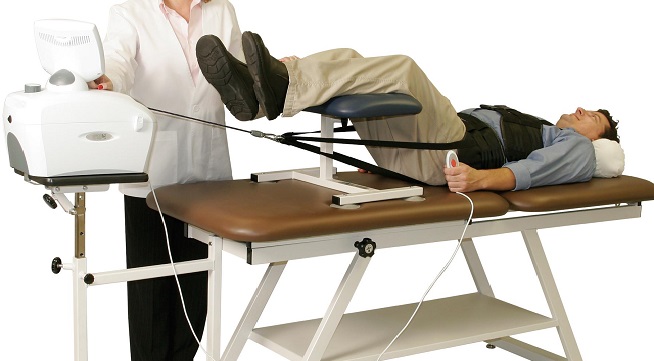
Lumbar Traction for Low Back Pain: Benefits, Indication and Contraindication
What is Lumbar Traction?
Lumbar traction helps to improve the reduce spaces between your two vertebrae, the bones that make up your spine. Reduce space between two vertebral bones can help relieve the pressure on compressed nerves (eg. sciatic nerve) to relieve your pain and improve your mobility of spine.
Definition
Lumbar traction is a process of applying traction force to the lumbar vertebra through body weight/ weights /and or pullies to distract individual joints of the lumbar spine.
The traction word is a taken from Latin word “tractico”, which means “a drawing or pulling, and different types of spinal traction have been used, since the time of Hippocrates(circa 460-377 BC), for the relief of Back pain.
James Cyriax make a famous of lumbar traction during the 1950s and 1960s in the treatment for disc prolapse(PIVD), However even today, it is still used a common modality for the treatment in Low back pain and sciatica pain.
However The effectiveness of Lumbar Traction has been questioned by a few Medical trials and recent guidelines published by NICE in the UK, KCE in Belgium, the Danish Health Authority and the American College of Physician’s no longer recommended traction as a modality in the treatment of low back pain.
James Cyriax explain three benefits of lumbar traction:
- distraction to improve the intervertebral space,
- Lengthen of the posterior longitudinal vertebral ligament to apply centripetal force at the back of the joint
- suction to draw the prolapse disc towards the center of the joint.
Other lumbar traction benefits are widening of the intervertebral foramen and distraction of the apophyseal joints and also helps to improve body’s ability to heal by itself.
Related Anatomy of Lumbar Spine:
The lumbar spine is made up of a five individual vertebra which are numbered L1 to L5 and together they creat the concave lumbar curvature in the lower back.
The lumbar vertebra starts just below the thoracic vertebrae in the thorax region and after lumbar vertebrae sacrum and coccyx vertebrae starts located in the pelvis region.
this vertebra carries all the upper body weight while providing flexibility and movement to the trunk region.they also protects the spinal c
cord and spinal nerves.
Each of the vertebra is connected via intervertebral disc which is made up of a fibrocartilage with a jelly like center.the outer layer of a disc the annulus fibrosis, holds the vertebrae together and provides strength and flexibility in the lumbar region.
The lumbar vertebral body makes up the majority of the vertebral mass and takes most of the body’s weight during back movement. Posteriorly the body is connected to the small thin ring of bone called as the Arch of the body .
The arch covers the hollow or empty vertebral foramen and connects the body to the bony processes on the posterior side of the vertebra.
The vertebral foramen is a large. the center of the foramen provides space for the spinal cord, cauda equina, and meninges .
Extending from the vertebral arch the bony processes are involved in muscle attachment and movement of the spine.
The spinous process extends from the posterior end of the arch as a thin rectangle of the bone.
It obeys as a connection point for the muscles of the back region and pelvis region, such as the psoasmajor and interspinales muscles.
On the left and right lateral sides of each vertebra are short, triangular in shape and has transverse processes. The transverse processes form important connection points for many muscles, like the lumbar rotatores and multifidus. this muscles extend and rotate the trunk.
Types of Lumbar Traction:
There are mainly 7 types of Lumbar Traction as per below:
(1) Continuous Traction:
used for temporaraly immobilization of a symptomatic spinal area.
a low force(4.5 to 9 kg) is applied for long periods(hours to days).
but this method of appling traction is rarly used because patients with spinal pain do not benefit from prolonged bed rest and inactivity.
(2) Sustained Traction:
greater force is used as compared with countinuous traction.
the pull is maintened for 20 to 60 minutes.
it is very effective when applied on a split traction table.
(3) Intermittent Traction:
it allows the application of a greater forces for a short period of time.
the force is gradually increased and decreased during each cycle.
ex-7 to 10 sec tractional force with 5 secs rest up to 30 to 60 secs tractional force followed by 10 to 15 secs rest.
total duration of on and off cycle is 15 to 25 mints.
(4) Manual Traction:
Manual traction is applied directly by the therapist and/or a belt are used to pull on the patient’s legs.
It is generally applied for a few seconds or can be applied as a sudden, quick thrust.
(5) Auto Traction:
it utilizes a specially designed table. it consist two sections that can be individually tilted and rotated.
the traction force is provided to the patient by pulling the arms or by pushing the feet.
(6) Positional Traction:
as the name suggest by applying various positions the tractional force is applied.
the traction force is given by placing the patient in various positions by using pillows , blocks or weight coughs to effect a pull on a spinal structures.
(7) Gravity Assisted Lumbar Traction:
in this it involves using a chest harness to secure the patient on the treatment table is tilted to a vertical position , there by using the weight of the lower half of the body to provide a traction force to the body.
Mechanism Of Action Of Traction:
it is based on the mechanical and reflex mechanism.
spinal elongation through an increase of the intervertebral joint space and also relaxation of the spinal muscles . by which the traction could be effective
Indications:
Following are the list of conditions where Lumbar traction are used for the treatment purposes.
- spinal nerve root impingement
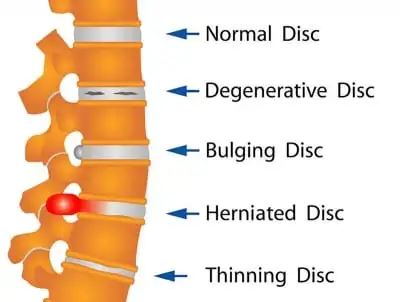
- herniation of the lumbar disc
- ligament encroachment
- narrowing of intervertebral foramen
- encrochment of the osteophytes
- lumbar spinal nerve root swelling
- joint hypomobility
- spondylolisthesis of lumbar vertebra
- degenerative joint diseases
- extrinsisc muscle spasm and muscle gaurding
- discogenic pain
- Lumbar joint pain
- compression fracture
- lumbar disc disorders of primary origin
- lumbar disc disorders of secondary origin
- sciatica pain
Contraindications:
Following are the list of conditions where Lumbar traction are not used (Not Recommended)
- osteomyelitis or discitis
- bone/spinal cord tumor
- unstable fracture
- severe osteoporosis
- hypertension
- cardiovascular disease
- inadequate expertise
- pregnancy
- cauda equina compression
- cord sign
- acute strains /sprains
- claustrophobia
- rheumatoid arthritis
- hernia
- post-operative patients within 3 months of back surgery
- vertebral fracture within 6 months of initial injury
- fusion with internal fixation
Uses Of Lumbar Traction:
- to reduce muscle spasm
- to stretch the spinal muscles
- to rupture previous adhesions
- to stretch the facet capsule
- to achieve intervertebral joint distraction
- to reduce herniated discs
- to decrease the pain
- to mobilize hypomobile joints
How to Prepare for Lumbar Traction?
the traction is applied by using motorised device that utilize pelvic and thoracic belt.
this belts are applied directly in contact with the patients skin and not over the clothing.
both belts should be tight enough to prevent slipping.
Placement Of Thoracic Belt:
lower edge aligns with the upper limit at which the traction force is required.
upper edge aligned approximately with the xiphoid immediately below the greatest diameter of thorax.
Placement Of Pelvic Belt:
its superior edge aligns with the inferior limit at which traction force is desired.
supine position -just superior to the iliac crest.
prone position-superior to the superior edge of sacrum.
machine has got the a fixed and mobile part and a lower body that rests on the mobile unit get separated from the fixed unit as the tactile force is applied.
colachis and strohm found that with the hips flexed 70 and angle of pull of 18 is created which provides the greatest vertebral separation.
Positioning:
generally, a supine position is selected because=there will be separation of posterior elements and also to localize traction force to upper lumbar and thoracic segments.
How to Calculate Weight in Lumbar Traction Machine?
The following Parameters are used to calculate weight in the Lumbar Traction Machine.
Parameters Of Traction:
(1)Acute Phase:
- force=13 to 20 kg
- hold/relax= static
- duration 5 to 10 minutes
(2)Joint Distractions:
- force=50% of body weight
- hold/relax=15sec/15sec
- duration =20 to 30 minutes
(3) Decrease Spasm:
- force=25% of body weight
- hold/relax=5sec/5sec
- duration=20 to 30 mints
(4) Disc Problems (Stretching Of Soft Tissue)
- force=25% of body weight
- hold/relax=60secs/20secs
- duration=20 to 30 mints
What are the side effects of lumbar traction?
Lumbar traction may sometimes hurt more than the original condition.
patients who are suffering from osteoporosis or some type of cancer should not take lumbar traction.
some patients may also suffer from spinal muscle spasms after taking therapy.
What are the risk factors for the lumbar spine?
lumbar traction is not for everyone. so it is determined by the physical therapist if the risk are worst based on the medical history of the patient.
there are no long term risk of lumbar traction.
some side effects may occur during or after the treatment session.
some patients may feel pain in the treated area.
What is the outlook after spinal traction?
With the help of physical therapy many people get success and achieve their goals. treatment reduces pain and make their body heal by itself.
some patients only need traction therapy for short period of time but some patients might require it throughout their lives.
How to take self-lumbar traction?
the purpose of the traction is to reduce or nullify your pain. here are some methods of self-lumbar traction.
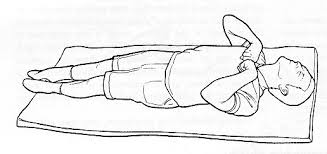
(1) Back lying matters pull:
lie on the back with both knees bent. grab the edges of the mattress, gently pull to provide traction.
(2)Stand between two chairs:
stand between two chairs and place your hands on the back of the chair. keep your arms straight as you bend your knees to unload your back.
Lumbar Traction Home Kit
Equipment of Lumbar traction kit
(1)Traction pulley bracket
(2)Traction cord
(3)Spreader bar with hooks
(4)Water weight bag
(5)Lumbar belt
Procedure:
How to apply Lumbar traction kit?
Use your Traction pulley bracket is swing on the leg side of the bed.
Then take measure circumference of waist and select size according to the table as shown in video.
place the lumbar belt below the waist and wrap it around the waist.
both the belts of the pelvic belt are attached to the spreader bar with the hook.
tie the traction cord to the hook of spreader bar and pass the other end of traction cord through the pully.
tie the traction cord to the water weight bag.
the weights are carefully calculated by therapist as considering the age, weight and ailment of the patient. which is usually 1/8th of the body weight.
How to remove the traction kit?
Remove the weight bag.
untie the traction cord from the spreader hook.
release the belts.



12 Comments