Microwave Diathermy
Introduction of the Microwave diathermy
- Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation lying between short wave and infrared waves in the electromagnetic spectrum, the microwaves are otherwise termed decimeter waves
- the wavelength of the microwave diathermy stays between 1 t0 100 cm
- microwave diathermy is the irradiation of tissues with radiation in the shorter wireless part of the electromagnetic spectrum
- the microwave occupies the part of the electromagnetic spectrum extending from wavelength 1 m to 1 mm frequency 300 Mhz to 300 Ghz
- for medical use, the frequencies are as follows
- frequency of 2450 MHZ at a wavelength of 12.2 cm
- frequency of 915 MHz at a wavelength of 32.8 cm
- frequency of 434 MHz at a wavelength of 69.1 cm
- though the frequency of the therapeutic microwave diathermy varies in different countries
- the heating effect of microwaves is known to all in microwave ovens used for cooking. when appropriately used microwaves produce therapeutic tissue heating to treat a group of musculoskeletal disorders, as for all electromagnetic radiation microwaves travel at the speed of the light
- the laws of reflection, refraction, absorption and inverse square law also conduct the electromagnetic radiation
laws of reflection
- The law of reflection defines that upon reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the tip of the incident ray, with respect to the normal to surface line that is perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact.
- The reflected ray is always in the plane defined by the incident ray and the normal to the surface at the point of contact of the incident ray.
laws of refraction
- refraction occurs when electromagnetic rays are transmitted from one medium to another medium with an angle of incidence greater than zero
laws of absorption
- when electromagnetic rays strike a new medium the waves may be absorbed and produce an effect
- the proportion of the rays absorbed on the surface depends upon the wavelength of the rays the nature of the medium and the angel of the incidence
- absorption is a medium that absorbs some electromagnetic waves and allows other waves to pass, window glass allows visible light and infrared rays to pass while absorbing ultraviolet rays, and cellphone absorbs short ultraviolet rays and allows the long waves to pass
inverse square law
- The inverse square law explains the strength of light with regard to the distance of the source.
- The intensity of the light a viewer from a source is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the viewer to the source”.
- microwaves accept the laws of radiation as the director is placed at a short fixed distance of 2 to 6 cm from the body
- the effect of reflection, penetration, and absorption is relatively small
- the microwaves accept the law of the inverse square to a greater extent which states that the intensity of radiation falling on the surface area of the body
- while applying microwaves to the patient care should be taken for fixing the skin director’s distance
Production of the Microwave Diathermy
- the extremely high frequency of the microwave diathermy is not obtained from the transformers, oscillators, and similar electronic components that are relatable but rather from the use of the unique device termed a magnetron
- the magnetron produces an oscillating current directly from high-velocity electron movement, in the magnetron the electrons flow through the donut-like construction with the tiny holes, in a manner similar to air being blown across the top of an empty bottle, creating a frequency response that alters depending upon the velocity and driving force of electron flow
- the current is generated from high-velocity electron movement achieved and attached along with a coaxial cable to the antenna or emitter which radiates microwaves
- the dimension of the coaxial cable is arranged to provide a suitable capacitance so that the microwaves of the given frequency are transferred to the emitter with maximum efficiency. the antenna is simply a suitable sized and shaped with a piece of wire which is set in front of the metal reflector so that a beam of the microwaves is directed in one direction
- the output of the microwave energy can be controlled by altering the power supplied to the magnetron, thus the machine has an intensity control and the output is indicated on the meter, the meter doesn’t tell about the accuracy of the amount of the heating produced in the tissue to be accepted as a measure of the dosage
- the frequency of the microwaves produced depends upon the structure of the magnetron and afterward, it is fixed for the machine, an on and off switch is used to start and stop the microwave diathermy and a stand-by switch is used to cut off the output of the unit without stopping the machine
- when successive treatment should start for another patient as the magnetron needs some time for warm up to give the output
- the cutoff switch avoids unnecessary delay for warm the machine
- the emitter also called director or applicator two types of emitters circular and rectangular, with a circular emitter the beam is circular in cross-section and is heavier at the periphery rather than at the center whereas a rectangular emitter provides a beam that is egg shape in the cross-section and most significant frequency in centrally
Parameters of the Microwave Diathermy
- Power supply: 230 Vca, 50-60 Hz
- Maximum main power absorption: 650 VA
- Double delayed-type mains fuse protection: 6.3
- Backlit LCD display to view and check the operating parameters: Graphic 240×128 Pixel
- Adjustable treatment time: 1-30 minutes
- Pulsed peak power on 50 Ohm load: 1600 Watt
- Continuous peak power on 50 Ohm load: 250 Watt
- Isolation class: I BF Type
- Risk class: type IIB
- Degree of protection from liquids
- Stored protocols: 50
- Storable programs on the internal memory: 50 programme
- Alarm in case of overheating: yes
- Weight: 40 Kg
- Size of the machine : 39 x 89 x 30 cm
Principle of application of microwave diathermy
preparation of the machine
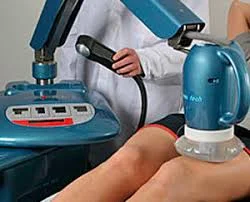
- select the particular emitter as required, depending on the size and the nature of the tissue to be heated, as the machine requires warming up before application to the patient, the power should be switched on for allowing to warm up after the machine can be left on a stand by switch
- the machine should be tested by the therapist by placing the dorsum of the hand in front of the emitter except that no tuning is done in the process
preparation of the patient
- the nature of the treatment should be explained to the patient and any instructions and warming are given
- the patient should be positioned comfortably with the part to be treated undressed
- the patient should lie on the treatment table and pair of protective wire mesh goggles is given to the patient to prevent the microwaves from reaching into the eyes
- thermal sensitivity of the skin should be tested for proper warming of the treatment area
- the patient should be instructed to call for help if the heating is excessive
setting up the position of the machine
- the emitter should be positioned so that the radiations strike the surface at the right angles
- fixate in mind that distance in the emitter diverges the beams only the essential radiations will be strictly at the right angle, while the superficial radiation will strike at small incident angles
- the emitter should be positioned at a distance of 2 to 6 cm from the part for the treatment of a small area and at a distance of 10 to 15 cm if the area to be treated is large
Application of the microwave diathermy
- the microwave output should be switched on from the standby mode and the treatment should be given for a fixed length of time
termination of the treatment
- after switching off and removing the machine, the treated area is examined and the skin surface temperature and the presence of any erythema are noted
Dosage of the Microwave Diathermy
- the most important indicator of dosage is the patient’s feedback on the perception of warmth .though the dose can be calculated from the power output of the machine which may be up to 200 watts
- to produce any detectable heating it requires absorbing a dose of 200 mW/cm the chosen dosage, which should be based on the severity, type, and progress of the disorder determined in the same way
- the treatment time of the microwave diathermy is a minimum of 20 minutes for vascular adjustments, deeper tissue takes a longer time to reach maximum temperature, and where significant muscle heating is required
- maximum treatment time 30 minutes
Physiological effects of Microwave Diathermy
- microwaves radiation is absorbed in the tissue for producing ionic movements, rotation of the dipoles, and distortion of the molecules of the insulator thereby producing heat
- the amount of heat is proportional to the amount of absorbed radiation and the water content of the tissue
- it is found that microwaves produce more heating in the muscle tissue, tissue with more water and ions contents significantly less heat in fat and bone, and more heat produced in the superficial tissue
- the heat production decrease as the depth increase, due to the fact that the microwaves reflected at various interface such as skin-air,skin-fat,fat-muscle,muscle-bone intersurface
- the microwave goes more deeply rather than infrared rays but doesn’t pass right through the tissue in any appreciable frequency
- the effective depth of penetration of microwave appears to be 4.3 cm, with the half-value depth being 3 cm, as the microwaves are more absorbed by the water the tissue that has good blood supply like the muscle half-value depth of 0.7 cm at a frequency of the 2450 Mhz are heated most while there is less heat production in tissue in the tissue that has low fluid content like fat, bone half value depth 3.5 cm at frequency 2450 MHz
- thus heating the subcutaneous fat which is a disadvantage of the microwave
- the depth of the penetration of the microwaves is also frequency dependent .higher depth lower frequency vice versa therefore it is considered that a frequency of 915 MHz is more suitable for therapeutic healing
- as far as if the wavelength is considered as an increase in the waves, the penetration increases, and absorption occurs more in deeper tissue
- the wavelength of 12.2 cm produces more superficial heating than a wavelength of 32.8 cm due to a lesser degree of penetration
- the ultimate effect of the absorption of the microwaves in the tissues to produce heat, the pattern of heating of the tissue is also dependent on the shape of the emitter
- circular emitter produces a ring-like pattern of heating
- microwaves applied to the forearm at a frequency of 2450 MHz for 15 minutes increase the local skin temperature by 10 degrees C and blood flow by 25 percent,
- generally with the application of the MWd heating occurs within the first few CM of the tissue transferred especially in the muscle, frequency increases the flow of the blood much more effectively than local muscle activity or hot packs
Therapeutic use of the Microwave Diathermy
Inflammatory conditions
- it can be used in the treatment of traumatic and inflammatory conditions which increase blood supply and relief pain and muscle spasms
- microwave diathermy used a frequency of 434 Mhz superior to 1 Mhz ultrasound for resolving pain and inflamation after the muscle injury, however, the pulsed more for microwave diathermy should be used immediately after trauma and conventional microwave diathermy should be used in low doses of 72 hours following trauma
Traumatic condition
- microwave diathermy can be applied for remediation of the early trauma where the aim is to resolve inflamation and pain
- in chronic trauma where there is soft tissue tightness, joint stiffness joint deformity
- microwave diathermy is applied to improve the extensibility of the collagen fibers so that the mobilization and stretching following microwave diathermy application are promoted to create an improved range of motion
- microwave diathermy at a frequency of 915 MHZ applied with direct contact method achieved lengthening of the quadriceps muscle when combined with stretching
arthritic condition
- microwave diathermy is found to be effective to reduce pain, and swelling, and improving function in patients with different types of arthritis, including small superficial joints
- care should be taken so that the inflamation is not occur
- the use of the microwave diathermy in the patient with rheumatoid arthritis has conducted to decrease pain and increased the walking time
- microwave diathermy is also used in other arthritic conditions like poly/oligo arthritis
- the effect gained in arthritic condition with the application of microwave diathermy is the reduction of inflammation, increase in the extensibility of collagen tissue afterward reduce joint stiffness
pain relief
- the mechanism of the microwave diathermy for relieving pain include the removal of harmful chemical by increasing blood flow, pain modulation at the pain gate, and a placebo effect as it is generally possible to irradiate only one aspect of the body at a time
- microwave diathermy is generally used in the treatment of localized lesions rather than widespread lesions
Conditions required for the microwave diathermy
- jumper knee
- tennis elbow
- muscle sprain
- muscle strain
- sports injuries
- surgical lengthening of the tight muscle
- rheumatoid arthritis
- low back pain
- dysmenorrhea
Risk factor of the Microwave Diathermy
- the microwave machine should be tested regularly for output and safety
- the possible risk factor of microwave diathermy in the physiotherapy
burns
- microwave diathermy produces heat burns which could be due to
- poor techniques
- the inability of the tissue to consume heat
- the inability of the patient to detect heat-poor thermal sensation
- treatment over areas with surface or metal implanted
- treatment of moist open wounds or even wet dressing water concentrates microwaves
- treatment near the eye involving sinuses, and temporomandibular joint which is due to high fluid volume having higher dielectric continuous wave resulting in an increase in the local temperature of symptoms
increasing the symptoms
- inflammatory condition
- infective disorder
- areas of increased fluid tension like bursitis, edema, synovial effusion
- hemorrhagic condition
- menstruation is unlikely to be affected by microwaves due to their limited depth of penetration
- severe cardiac diseases
- cardiac failure due to electric shock, interference with the cardiac pacemaker
- spread of existing pathologies include tumors, active tuberculosis, acute infection
- early pregnancy where heat may be toxic
- damage to the eyes in animal opacities of the lens has been found on exposure to MWD therefore microwave diathermy should not be irritated the eye or near to eye the therapist and the patient both should use protective wire mesh goggles to prevent irradiation
- precipitation of the gangrene if the ischemic area is irradiated with microwaves there is a chance of the gangrene being precipitated for the reasons like burger’s disease the metabolic demands produced by the heat can not be met by the ischaemic tissue
- damage to the equipment damage to the magnetron can occur from keeping the machine on with the emitter facing metal that reflects the microwaves
Avoid the use of the application of the Microwave Diathermy
- diminished thermal sensation
- defective arterial circulation
- recent hemorrhage
- metal in the area under the treatment
- malignancy
- implanted cardiac pacemakers
- eyes and testes, due to poor heat recreation and opacity of the lens of the eyes
- pregnant uterus
Treatment of the microwave diathermy with chronic low back pain
- The incidence of chronic low back pain is increasing day by day which leads to long-term disability. Low back pain is a symptom complex, if it persists for at least 3 months it is known as chronic low back pain. Almost 80% of all people experience back pain to some extent during their lifetime; a price paid for upright posture. Low back pain affects the area between the lower rib cage and gluteal folds and often radiates to the thigh. Back pain is one of the most prevalent medical diseases in industrialized countries and a common disability in patients under the age of 40 years. Common abnormalities in the lumbar spine are degenerative changes found in all older people. Back pain in most cases is self-limiting with recovery in 70% within 1 month and 90% within 2 to 3 months while in about 4%, duration exceeds 6 months. Men and women are in general equally affected most commonly between the age of 30 and 55 years. The herniated disk is found in 5% of all cases of chronic low back pain
- The other causes of low back pain include infections, tumors, fractures osteoporosis, ankylosing spondylitis of the spine, and rheumatoid arthritis. The other associated risk factors include involvement in an occupation requiring forward bending, lifting heavy weight, and exposure to vibration caused by vehicles, or industrial machinery.
- The treatment and management of Low back pain need a multidisciplinary approach. Current multidisciplinary bio-psychological rehabilitation regards disabling chronic pain as a conclusion of multiple interconnecting physical, psychological, and social or occupational factors. Microwave diathermy produces heat with deeper penetration of the tissue and after that used as a modality of treatment in patients with chronic low back pain. So the major aim is to rule out the effects of microwave diathermy in the management of patients with chronic low back pain.
Treatment Procedures
- All patients were treated in the department with microwave diathermy in the lower back part for 15 min, 6 times a week for four weeks. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and therapeutic exercises with activities of daily living procedures were prescribed to all the patients.
application of microwave diathermy with nonspecific chronic neck pain
- Although the use of deep heat therapy is widespread, there is little information available on its effectiveness in treating back or neck pain. to rule out the effectiveness of microwave diathermy in treating nonspecific chronic neck pain. patients with nonspecific chronic neck pain, pain intensity using a visual analog scale, disability Neck Disability Index, and health-related quality of lifeSF-36 scale at 3 weeks, patients’ perceived overall conclusion and achievement with the microwave diathermy treatment; at 6 months, 3-week measures, therapeutic co-interventions, and attachment to exercises. Patients were arranged at random numbers into one of three groups. The first group received continuous microwave diathermy, the second group received pulsed microwaves, and the third group received unplugged microwaves. All three groups achieved the same general treatment which includes the range of motion, the isometric exercises, and the transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. The three groups decreased pain and decreased disability and improvement examined. No differences were found in any of the parameters of the microwave diathermy measured among all three therapeutic groups.
- Microwave diathermy doesn’t give further benefit to a treatment procedure for chronic neck pain that already includes other treatment approaches.
- In the nonspecific chronic neck pain method, the tissues are heated by the absorption of microwave energy.
- Microwave diathermy treatments are highly focused electromagnetic radiation, directed from a machine shaped like a stick at the damaged area.
- This form of microwave diathermy is best used for more localized injuries or small muscles.
- Microwave diathermy treatments last about 20 to 30 minutes. It consists of a power source that sends electrical current into a magnetron, a tube-like structure with exterior magnets.
- The machine cabinet is one or/and two adjustable arms, each arm having an end applicator that has a flat surface on one side that acts as an antenna through which the microwave travel.
- Microwave diathermy is very simple, usually, two designs of applicators are common.
- Circular design: Used for small (or) large areas with different shed applications.
- Rectangular: For elongated areas.
- The frequency used is about 2450 MHz.
- Better results are collected by the microwave procedure and it is more advantageous rather than the short-wave procedure.
- There are no pad electrodes or flexible cables.
- Microwave diathermy is transmitted into the body and treated directly from the direction of the unit.
- Microwaves diathermy is generated with the help of a magnetron.
- Proper cooling arrangements are made for the goal of cooling the magnetron.
- No tuning is needed for individual treatments.
Precautions for the Microwave Diathermy
- Necessary precautions should be taken during this microwave diathermy method of application in the treatment
- Extreme dosage causes skin burns and the skin should be dry as the waves are instantly absorbed by water.
- treatment with the microwaves indicates that the safe level of radiation is not exceeded under almost any condition at more than 1 meter in front or at the side of the emitter and 25 cm behind the emitter
- reflection of the microwaves maybe by 50 to 75 percent from the patient and nearly 100 percent from the metal of the machine
Advantages of the use of microwave diathermy
- This type of therapy is used to treat rigid joints and joint pains often connected with arthritis without using electrodes and cables.
- increased the healing of an injured area.
Disadvantages of the use of microwave diathermy
- Patients with an implanted pacemaker should not undergo the microwave diathermy treatment There are possibilities of overheating
- Care should be taken while the treatment is made near the eye region
FAQs
When the microwave diathermy is used?
The common indications for microwave diathermy therapy include soft tissue lesions of traumatic origin, degenerative or chronic arthropathy, and some localized infections,
What are the benefits of microwave diathermy?
Hyperthermia produced by microwave diathermy into the tissue can stimulate repair processes, increase drug activity, give permission for more efficiency to relief from pain, help in the removal of toxic wastes, elevate tendon extensibility, and reduction of the muscle and joint stiffness
What wavelength is microwave diathermy?
Microwave Diathermy is high-frequency electromagnetic radiation that stays between infrared and shortwave. Their frequency ranges between 300 MHz to 3000 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of 1m to 10mm.
What is microwave diathermy in physiotherapy?
Microwave diathermies are electromagnetic radiation emitting systems that are generally used by physiotherapists for thermotherapy treatment
What is the purpose of microwave diathermy?
microwave Diathermy is the composed production of “deep heating” under the skin in the subcutaneous tissues, deep muscles, and joints for therapeutic purposes. There are generally two types of diathermy devices on the market today: radio or high-frequency diathermy and microwave diathermy.




2 Comments