OCULOPHARENGEAL MUSCULAR DYSTROPY (OPMD)
Introduction:
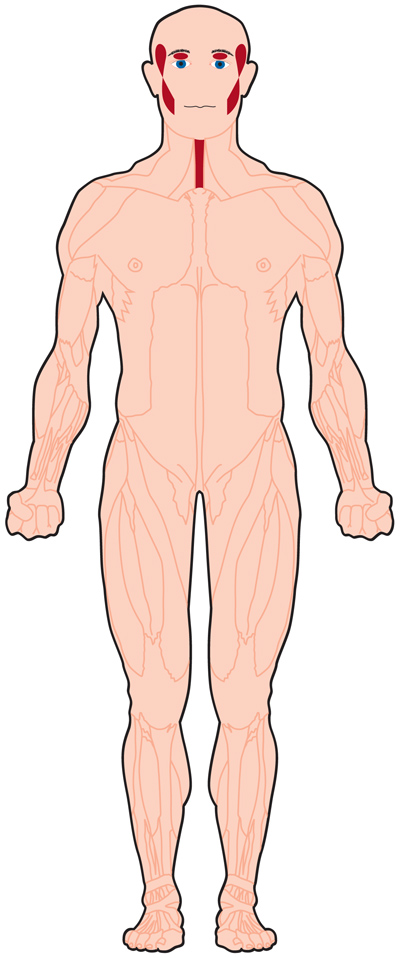
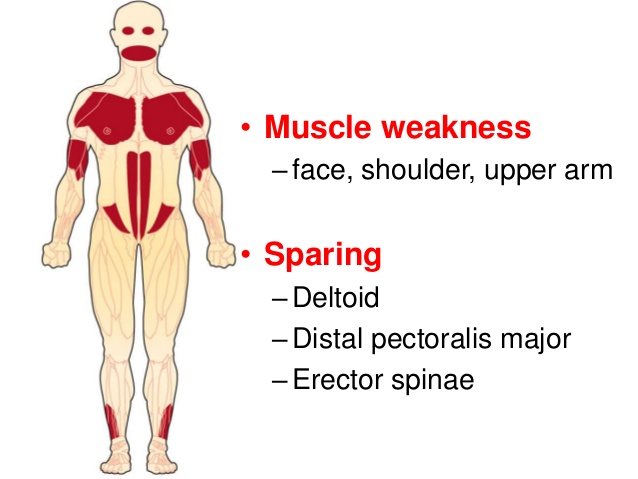
→ Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) is a rare form of muscular dystrophy with symptoms generally starting when an individual is 40 to 50 years old. It can be autosomal dominant neuromuscular disease or autosomal recessive.OPMD is a group of genetic, degenerative diseases primarily affecting voluntary muscles.It affects first — the eyelids (oculo) and throat (pharyngeal) — OPMD also can affect facial and limb muscles.
Causes of Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD):
→ OPMD is caused by a genetic defect leading to production of extra chemical material that forms clumps in the muscle cells. It can be inherited from either one or both parents, and affects men and women equally.
Symptoms:
→ Difficulty swallowing and keeping the eyes open are common. Later on, some people with OPMD may have mobility problems.
→ Ptosis
→ Weakness of the extraocular muscles
→ Dysphagia
→ Aspiration pneumonia (complication)
→ Proximal limb weakness
Diagnosis:
→ The diagnosis of oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy can be done via two methods, a muscle biopsy or a blood draw with genetic testing.The genetic blood testing is more common.
Treatment of Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD):
→ Currently no cure or specific treatment exists to eliminate the symptoms or stop the disease progression
A consistent diet planned with the help of a dietitian along with exercises taught by a speech therapist can assist with mild symptoms of dysphagia.
→ Surgical intervention can also help temporarily manage symptoms related to the ptosis and dysphagia. Cutting one of the throat muscles internally, an operation called cricopharyngeal myotomy, can be one way to ease symptoms in more severe cases.
→ Many of those affected with the proximal limb weakness will eventually require assistive devices such as a wheelchair.

→ As with all surgical procedures, they come with many risk factors. As the dysphagia becomes more severe, patients become malnourished, lose significant weight, become dehydrated and suffer from repeated incidents of aspiration pneumonia. These last two are often the cause of death.