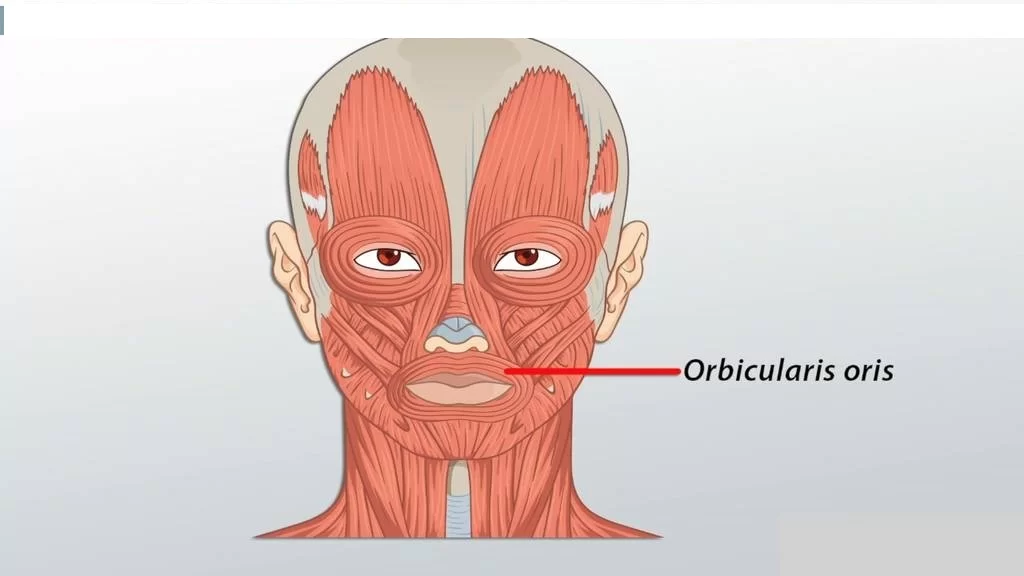
Orbicularis Oris Muscle
Introduction:
The orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth in Human anatomy.
It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.
It is also one of the muscles used in the playing of all brass instruments and some woodwind instruments. This muscle closes the mouth and puckers the lips when it contracts.
Anatomy of Orbicularis Oris:
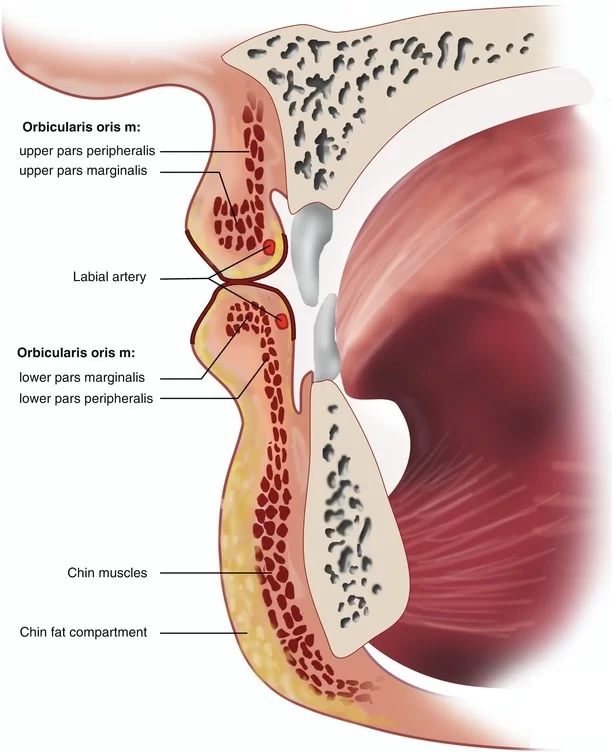
The orbicularis oris is not a simple sphincter muscle like the orbicularis oculi, it consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth, but having different directions.
It consists partly of fibers derived from the other facial muscles which are inserted into the lips, and partly of fibers proper to the lips.
Of the former, a considerable number are derived from the buccinator and form the deeper stratum of the orbicularis.
Some of the buccinator fibers, those near the middle of the muscle decussate at the angle of the mouth, those arising from the maxilla passing to the lower lip, and those from the mandible to the upper lip.
The uppermost and lowermost fibers of the buccinator pass across the lips from side to side without decussation.
Superficial to this stratum is a second, formed on either side by the caninus and triangularis, which cross each other at the angle of the mouth.
Those from the caninus passing to the lower lip, and those from the triangularis to the upper lip, along which they run, to be inserted into the skin near the median line.
In addition to these, fibers from the quadratus labii superioris, the zygomaticus, and the
quadratus labii inferioris intermingle with the transverse fibers, and have principally an oblique direction.
The proper fibers of the lips are oblique, and pass from the undersurface of the skin to the mucous membrane, through the thickness of the lip.
Fibers occur by which the muscle is connected with the maxilla and the septum of the nose above and with the mandible below.
The interval between the two medial bands corresponds with the depression, called the philtrum, seen on the lip beneath the septum of the nose.
The additional fibers for the lower lip constitute a slip m. incisivus labii inferioris on either side of the middle line, this arises from the mandible, lateral to the Mentalis, and intermingles with the other muscles at the angle of the mouth.
STRUCTURE OF ORBICULARIS ORIS
- Orbicularis oris is a composite muscle that consists of two parts; a larger peripheral part, and a smaller marginal part.
- The border between these two portions corresponds to the margins of the lips that separate them from the surrounding skin.
- Both parts span between the left and right modiolus, which is a dense fibromuscular nodule at the angle of the mouth onto which most of the buccolabial muscles attach.
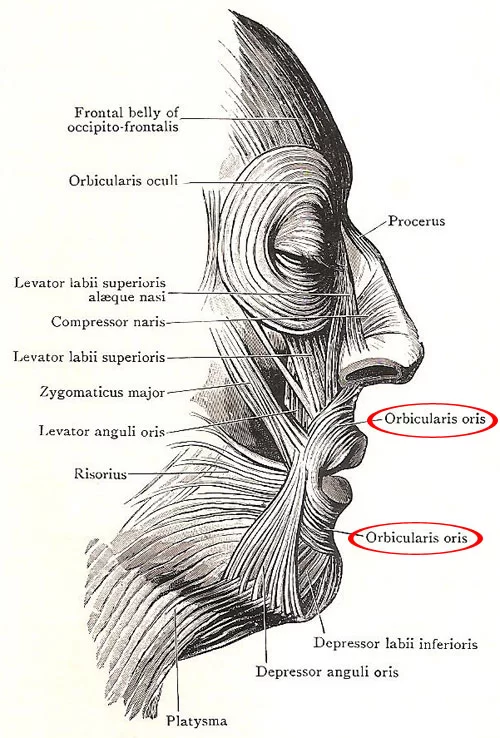
The orbicularis oris has two main parts :
- The marginal part consists of longitudinal fibers and the labial part of the orbicularis oris composed of circular fibers.
Marginal part of orbicularis oris :
- The longitudinal fibers of the marginal part of the orbicularis oris run below the skin around the mouth opening, originating and inserting within the tissue of the lips.
- The marginal part of the orbicularis oris closes the oral opening.
Labial part of orbicularis oris :
- The circular fibers composing the labial part of the orbicularis oris run between the angles of the mouth, having the origin and insertion site within the skin of the corners of the mouth.
- The labial part of the orbicularis oris pushes the lips forward.
Innervation :
- Both parts of the orbicularis oris are innervated by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply :
- The orbicularis oris is supplied with arterial blood mainly by the superior and inferior labial branches of the facial artery.
- The mental and infraorbital branches of the maxillary artery and the transverse facial branch of the superficial temporal artery.
FUNCTIONS:
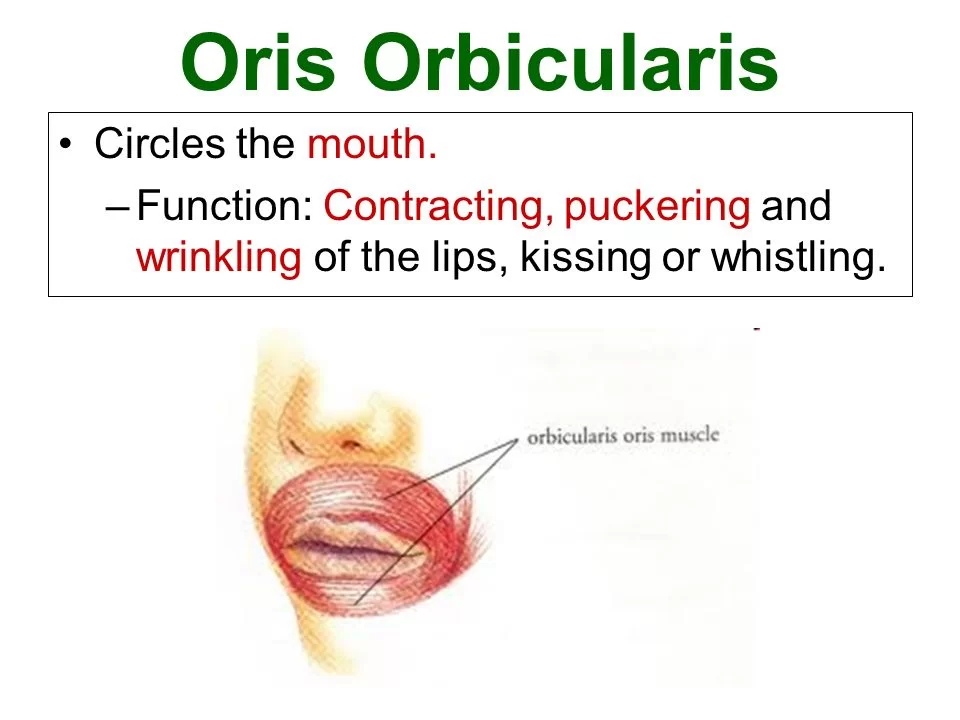
- Bilateral uniform contraction of the muscle will bring the lips together and close the mouth.
- This action is important for mastication, as it works in cooperation with the buccinator muscle and the tongue to prevent the food from escaping the teeth and accumulating in the oral vestibule during eating.
- Isolated contraction of respective parts of the muscle causes the movements such as lip pouting, twisting, pursing, and others.
- These movements greatly contribute to facial expressions and speech.
- Marginal portions of muscle are also referred to as the labial cords, as by changing their length and tension similar to the vocal cords, they produce some consonantal (labial) sounds.
- These consonants include /p/ of peas, the /b/ of a basket which are produced by bringing the lips together /f/ of feet, or /v/ of valley are produced by pressing the lower lip against the upper teeth, and others.
- In addition, the labial cords can act as vibrating strings and enable whistling or playing a wind instrument.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF ORBICULARIS ORIS
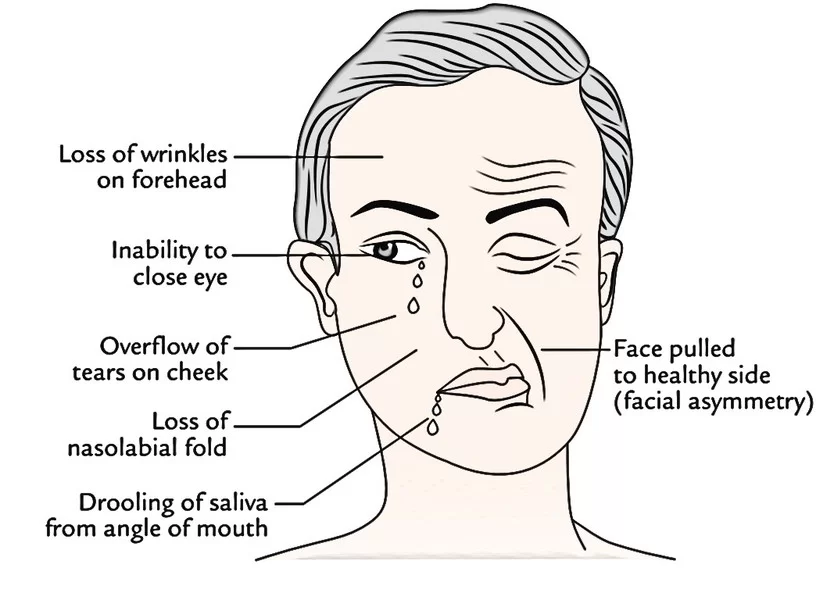
Babies are occasionally born without one or both sides of this particular muscle, resulting in a slight droop to the affected side of the face.
In facial palsy :
As the muscle receives nerve supply from the seventh cranial nerve, thus, injury to this nerve can result in paralysis of the muscle. In Bell palsy, sagging of the muscle results in drooling.
Loss of tone :
Loss of tone of this muscle to these muscles leads to drooping of the commissure as it controls the oral sphincter, which can cause drooling and difficulty in eating.



4 Comments