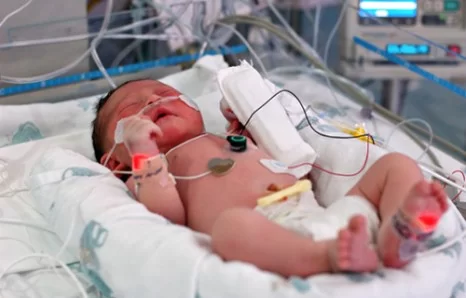
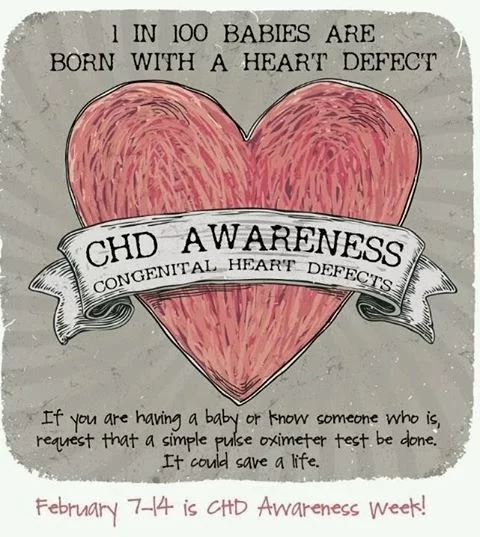
ACYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
Acyanotic heart defects are congenital cardiac malformations that affect the atrial or ventricular walls, heart valves, or large blood vessels. Common causes include genetic defects (e.g., trisomies), maternal infections (e.g., rubella), or maternal consumption of drugs or alcohol during pregnancy. Acyanotic heart defects are characterized pathophysiologically by a left-to-right shunt, which causes pulmonary hypertension and…