Scapular stabilization exercises: Health Benefits, Variations, How to do?
What is Scapular stabilization exercise?
scapular stabilization exercises is the exercise that helps to strengthen the muscles that helps to stabilize the scapula.
- Your shoulder blades are attached to your rib cage by certain muscles. These muscles work in a different direction to help keep the scapula stable while your arms move and take the weight. These muscles are known as scapular stabilizers. this exercise strengthens muscles that support the spine and prevent upper back pain. Also helps the patient to maintain a neutral spine position.
- Scapulohumeral rhythm is synergistic movement between the scapula and shoulder joint. This synergistic pattern is important for the normal function of the shoulder joint. Poor interaction causes poor positioning of the shoulder blade and altered scapulohumeral rhythm.
Benefits of doing Scapular stabilization exercises :
Following are the few benefits of the exercise, these are:
- Provides a full range of motion like overhead activities
- Beneficial for upper back hypertrophy
- Improves muscle-building potential
- Gives training to scapular stabilizer muscles
- Increase muscle-building stimulus to the triceps and pecs
- Prone push-ups include abdominal muscles to improve core
- The best way to increase the intensity of push up without increasing the weight
- Provide strength, and joint stability and prevent impingement of shoulder joint complex
- Decrease pain in shoulder and neck
- Improve and maintain good posture
Which muscles are involved in scapular stabilization?
The following listed muscles are strengthened during the scapular stabilization exercise:
- serratus anterior
- trapezius muscle
- levator scapula
- rhomboids
There are so many exercises involved in scapular stabilization exercises, some of which are:
- Reverse band flye
- Reach and row
- Push – up to plus
- Stability ball push-up
- Retraction
- Corner press out
- Protraction
- Depression
- Upright press
- Superman position
1) Reverse band flye :
This exercise mainly focuses on scapular retraction. This also provides a full range of motion. Because of this extended range of motion your shoulder joint muscles work more freely rather than limited ROM ( range of motion ).
How to perform – Use a resistance band. Loop the band around the handles and go back until the elbows become straight. Then slowly stretch the band outside while the hands pull apart . Make T – shape by hand .and slowly return to the first position. Then repeat this. (2 repetitions 15-second hold)
2) Reach and Row :
This exercise is performed by using a band or cable and involves one arm at a time.in this movement, the scapula goes outside and feels strech in upper body muscles.
How to do – Grab a resisting band or cable with one hand and the other end is a loop around the static object. Then go backward while stretching the band until the band is taut. Lean forward by the torso, and stretch the band towards the hip by using one hand. Now keep your shoulder down and stand straight. (2 repetitions 15-second hold ).
3) Push-up to plus :
Most people do push up by locking their elbows but in this works beyond locking, like body shapes turn to a round position. This protects scapular muscles and targets scapular movements. Gives training to the serratus anterior muscles.
How to do – Set body in a push-up plank position, shoulder straight at right angle then elbow is straight, palm touches to the ground, heel in position. Start to push up by slowly taking the body downward and the hand pushes towards to ground. then make round back as a cat do. Strengthen back out return to the first position and repeat. (2 repetitions 15-second hold )
4) Stability ball push up :
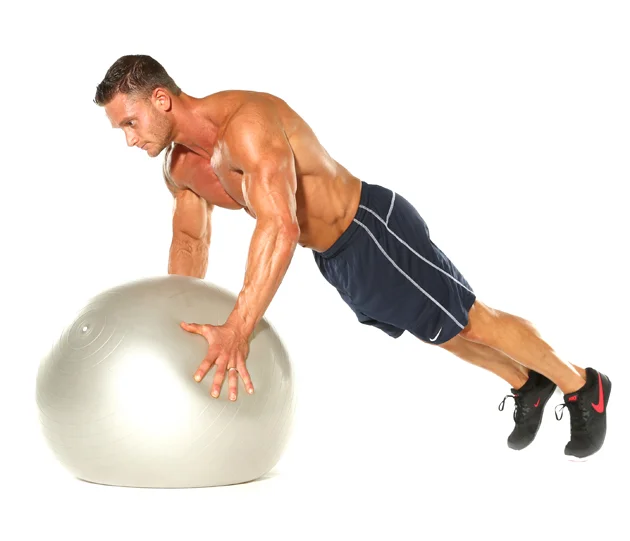

It is performed on a stability ball though it’s harder. But it challenges scapular stability by doing on an unstable surface.
How to perform – Starts to the plank position but hand on either side of the ball. Shoulder and elbow straight with knee and heel in position to hip-width. Starting to push lower down body and press hand against ball and chest downside toward the ball. Then back to the starting position. (2 repetitions 15-second hold)
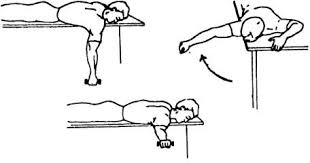
5) Retraction :
It includes rhomboids and middle trapezius muscles.
Patient position and procedure – This movement has been done by standing, sitting and prone position.
Sitting position – Instruct the patient to bend their arms together behind the lower back. This movement causes the adduction of the scapula. again instruct the patient to hold that position and watch the adducted scapulae. then tell the patient to repeat this motion without moving the arm.
Prone position – Patient is in prone lying position at the edge of the table. Arm over the edge of the table in a dependent position and held some weight in hand. Instruct the patient to adduct their scapula and lift the object upward against gravity.
Standing position – Patient is in standing position with the shoulder is 90-degree flex and elbow straight .Instuct the patient to held elastic band in both hands and pull the band towards body .so, the scapula adducts during motion.
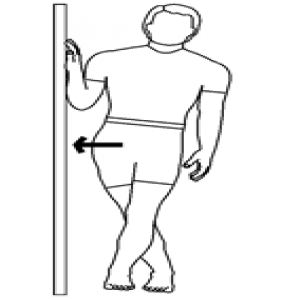
6) Corner press out :
How to do : Patient standing in a corner, facing back towards the wall. Then take a position, the shoulder is abducted 90 degrees, elbow flexed touching to a wall. Instruct to press the elbow towards the wall like a wall pushing and pushing the body away from the corner. This motion adducts the scapula and strengthens the muscles.
7) Protraction :
It includes the serratus anterior muscle.
Patient position and procedure – The patient is in a standing or sitting position. The shoulder is in 90 degrees abduction and the elbow is extended. Use an elastic band back of the body and stretch that band forward away from the body without rotating your body. Hold that position and repeat. Also, this movement is done in the supine position. Shoulder flexed 90 degrees and elbow extended and held weight in hand. Then push the weight upward.
8) Depression:
It includes the lower trapezius and lowers serratus anterior muscles.
Patient position and procedure – The patient is in a sitting position with the elbow flexed. Put your hand under the elbow to give resistance. Then give upward resistance and tell the patient to lower the shoulder to give movement against resistance.
9)Upright press :
How to do – The patient is in a standing or sitting position with hands on a block or armrest on a chair or parallel bar. Then press the block and lift your body upward. Elbow extension gives depression of the scapula.
10)Superman position :
It includes the trapezius and serratus anterior muscles and does scapular upward rotation.
Patient position and procedure – The patient is in a standing or sitting position. The shoulder should be overhead to a held resistance band and pull the band over more flexion and depression of the scapula. Scapular depression is more important to use the lower trapezius and avoid scapular elevation.
Scapular instability causes :
Nerve damage: Long thoracic nerve palsy
Inflexibility factors: Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit, any problem in a full range of motion or pectoralis minor or levator scapula muscles tightness
Muscular issues: Lower trapezius, rhomboids or serratus anterior muscle weakness, hyperactivity of upper trapezius muscle, and peri-scapular muscle detachment
Kinetic chain problems: Hip or leg and core muscles weakness
Bone factors: Increases anterior scapular tilt, kyphosis, clavicular and scapular fracture, subluxation event with glenoid bone loss
Joint factors: Acromioclavicular arthritis, GH instability, tendinitis of biceps, and labral damage