SI JOINT (Sacroiliac Joint) : Anatomy, Movement, Dysfunction, Exercise
Introduction :
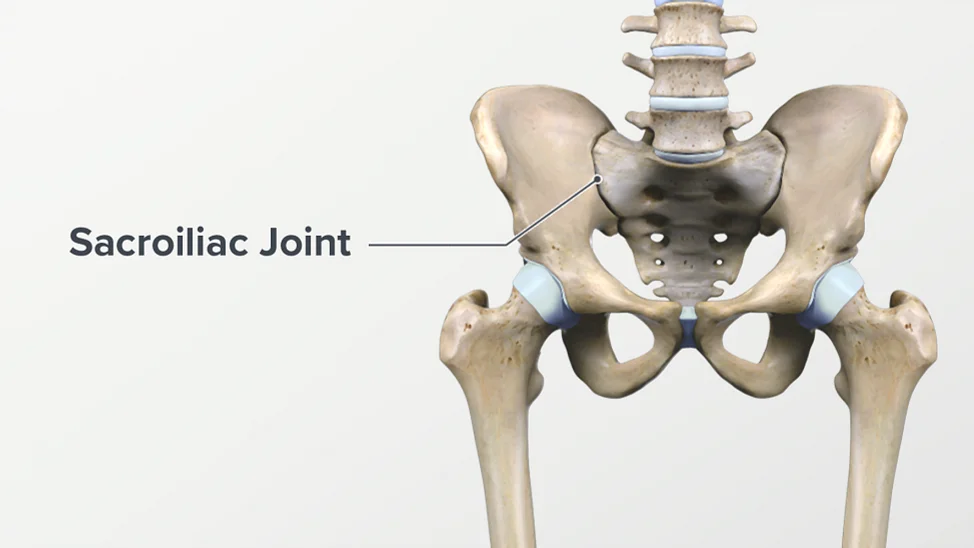
- SI joint is connected between the spine & the pelvis. Into the SI joint. there are two of them in the lower back & it is sit on each side of the spine
- The main job is to carry the weight of the upper body when to the stand or walk, and shift that load to the legs.
- Too little movement which as to the hypomobility or fixation to this joint, because of this movement patient feels the muscle tension/ pain & inhibits mobility.
- Pain is typically felt on the one side of the low back/ buttocks & also radiates down to the back of the leg.
- Inflammation of this joint produces pelvic pain & stiffness.
- This joint dysfunction is more common in young & middle-aged women.
- Women who the pregnant or have recently given birth are more susceptible to this joint pain.
Anatomy of the Sacroiliac Joint :
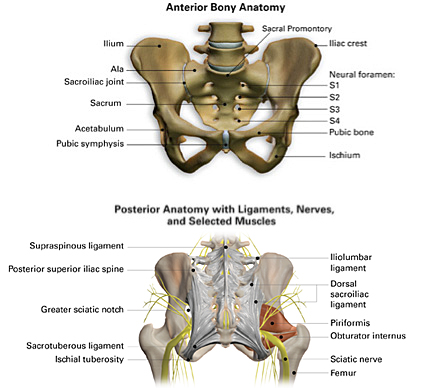
- This joint is a to the diarthrodial synovial joint.
- This joint is connected to the iliac crests of the hip bones to the sacrum.
- which is the triangular bone between the lumbar spine & the tailbone which is known as the coccyx. the primary function of these joints is to absorb the shock between the upper body & the pelvis/legs.
Joint Capsule :
- Surrounded by the fibrous capsule is contained in the joint space filled with the synovial fluid between the articular surfaces.
- This Articular surface is made up of two / strong or C-shaped layers.
- The sacral capsular surface is composed of hyaline cartilage ;
- It is made up of type II collagen & is the weakest type of cartilage.
- The Iliac capsular surface is composed of fibrocartilage ;
- It is made from type I collagen & is the strongest type of cartilage.
Ligaments :
- Strong ligamentous architecture stabilizes this joint.
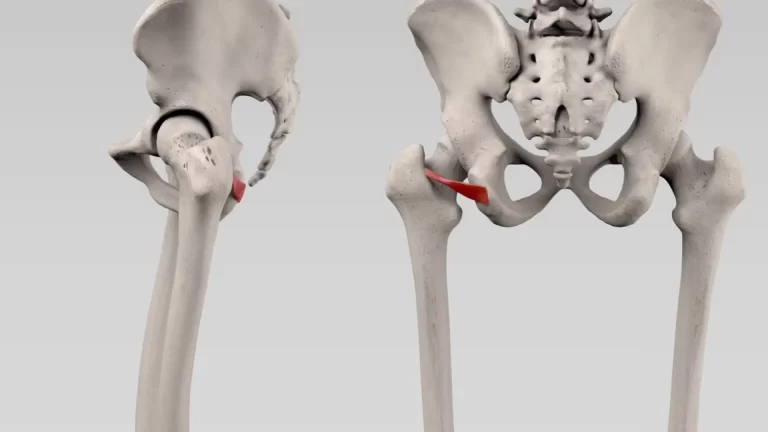
- Interosseous sacroiliac ligament :
- which forms the major connection between the sacrum & the ilium.
- It is the strongest ligament in the body that prevents anterior and inferior movement of the sacrum.
- Anterior Sacroiliac ligament :
- it is anteroinferior thickening of to the fibrous capsule which is weak & thin .
- It is connects to the third sacral ligament of the lateral side of to the preauricular sulcus.
- it is better to the develop closer the arcuate line & the PSIS.
- This ligament is to the injured most often .
- it is a common source of to the pain because of that it is thinness.
- Interosseus Sacroiliac ligament :
- It is forms to the major connect between to the sacrum & the innominate.
- It is a strong / short ligament which is deep in to the posterior sacroiliac ligament.
- It is resists to the anterior & inferior movement of to the sacrum.
- Posterior – Dorsal Sacroiliac ligament :
- It is connect to the PSIS with to the lateral crest of to the third & fourth segments of to the sacrum.
- It is very strong & tough.
- Nutation = which is to the anterior motion of to the sacrum / slackens to the ligament.
- Counternutation = which is to the posterior motion is make to the ligament taut.
- It is palpated to the directly below to the PSIS & it is often be to the source of pain.
- Sacrotuberous ligament :
- It is consists of to the three large fibrous bands .
- It is blend with to the posterior sacroiliac ligament.
- It is stabilizes to the against nutation of to the sacrum & counteracts against to the posterior & superior migration of to the sacrum during to the weight bearing.
- Sacrospinous ligaments
- It is a triangular shaped & thinner than to the sacrotuberous ligament which is from to the ischial spine on to the lateral parts of to the sacrum & coccyx .
- Then it is to the ischial spine laterally.
- Along with to the sacrotuberous ligament, it is opposes to the forward tilting of to the sacrum on to the innominates during to the weight bearing.
Nerves :
- This joint is well to the innervated but to the pattern of to the innervation varies is among to the individuals.
- This joint is receives to the its innervation from to the ventral rami of of to the L4 & L5 , superior gluteal nerve & dorsal rami of to the L5-S2.
Muscles :
- These are 35 muscles which is attached to the sacrum.
- It is innominate to mainly provide the stability of the joint rather than of the producing movements.
Movement of the SI joint :
Nutation & Counternutation :
- It is movements that which is happening into the frontal plane at the sacroiliac joint.
- Torsion is the movement that occurs at this joint into the transverse plane around the oblique axis of the rotation.
- Nutation is the motion that occurs when the force means the weight is absorbed in this joint.
- it occurs in the direction of the gravitational forces means toward the ground.
- Counternutation is the body’s response which is lifting the joint up against gravity.
- This motion is limited to 2 to 4 mm of movement due to the bony architecture & ligament structures of the joint.
Nutation occurs:
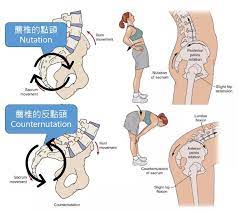
- When to the sacrum ia absorbs the shock ;
- So that it move to the down, forward & rotates of to the opposite side.
- The sacrum is moves to the anteriorly & inferiorly;
- Then coccyx is moves the posteriorly relative of to the ilium.
- The motion is opposed by the wedge shape of the sacrum, the ridges & depression of the articular surface. the friction is coefficient of the joint surface & the integrity of the posterior, interosseous & sacrotuberous ligaments which is supported by the muscles and then insert into ligaments.
Counternutation occurs :
- The sacrum is moves up, backward & rotates to same side which is absorbs the force.
- The motion is opposed by the posterior sacroiliac ligament which is supported by to the multifidus.
Torsion:
- To the right or left base of the sacrum is moves to the anterior / posterior.
- Torsion is typically classified to the right onto right sacral base which is moving to the anterior around to the right axis of the rotation ;
- Then left onto the left which is to the right sacral base move to the anterior around to the left axis of the rotation
- After that right onto the left means right sacral base is move to the posterior around to the left axis of the rotation.
- Then left on to the right means the left sacral base is to the move posterior around to the right axis of the rotation .
- This joint is produce to the typically for the little motion.
- Small movements of this joint is help with to the shock absorption & forward/backward to the bending.
- Joint is reinforced by the strong ligaments which is surrounding the joint so that some of the joints is which is extend across the joint in to the back of to the pelvis.
- Soft tissues are provides to the support / limits to the movement at to the joint & assists with to the absorbing pressure.
- Other muscles which is support to this joint function which is include to the gluteus maximus & the piriformis muscle.
Primary mechanisms of to this joint dysfunction include to the :
- More much movement which is known as to the hyper mobility or instability of to this joint , because of this movement patient feel to the pelvis unstable & lead to the pain.
- Patient feel the pain during to the too much motion & typically felt in to the lower back / hip & also radiate into the groin area.
Causes & Risk Factors of this Joint Dysfunction :
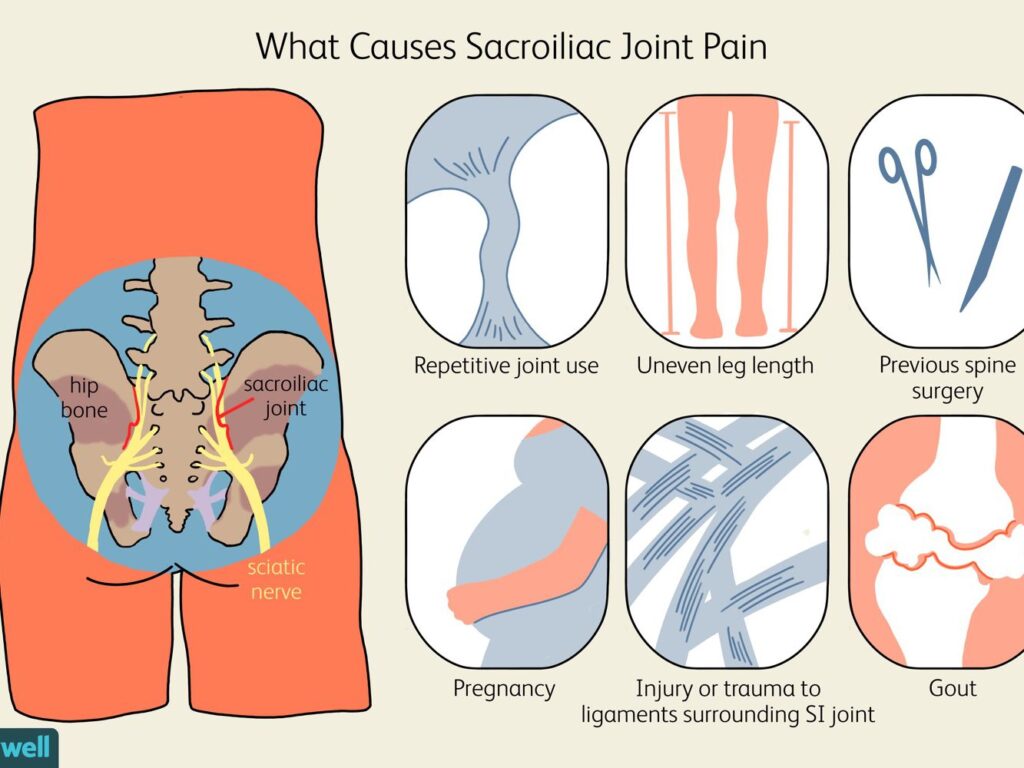
- Gait issues = leg length discrepancy / scoliosis, which is place onto the uneven pressure on to the one side of to the pelvis which is produce to the causing wear & tear on to this joint & an increase onto the risk of to the pain.
- Pregnancy / recent childbirth = which is commonly cause of this joint pain into the women due to the weight gain & hormonal changes which is do to the joint to the relax means hyper mobility & pelvic changes associated with to the childbirth.
- During to the some women & ligaments are remain loose after to the childbirth & produce to this joint pain & instability to the continue.
- Traumatic injury. = into the sudden impact, such as to the motor vehicle accident or to the a fall which is damage to this joints.
- Arthritis. Wear & tear arthritis means osteoarthritis which is occur into this joints & also ankylosing spondylitis which is type of to the inflammatory arthritis so that they affects to the spine.
Symptoms of to the joint dysfunction commonly include:
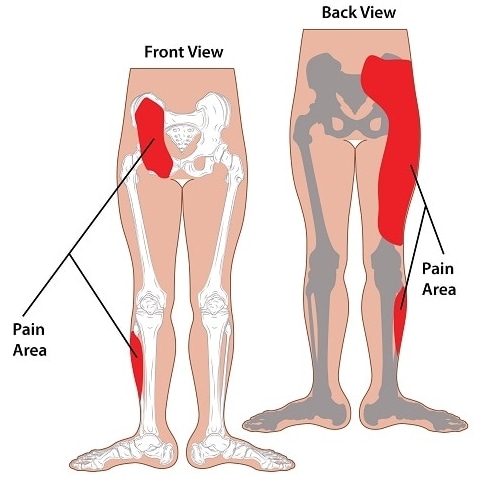
- Patient feel to the Lower back pain which is dull, aching & range from to the mild to the severe.
- Patient feel to the dull or sharp pain.
- This pain is typically feel only on the one side but into the some cases are feel on to the both sides.
- This Pain is spreads to the hips, buttocks & groin.
- Into the most common areas which is feel to this joint pain in to the buttocks / upper back & side of to the thigh.
- This pain is like as to the Sciatic pain in to the buttocks / backs of the thighs .
- Which is feels like to the hot, sharp & stabbing like as to the numbness & tingling.
- Stiffness & reduced to the ROM in to the lower back, hips, pelvic & groin & also patient feel to the which may cause difficulty with the movements like as to the walking up stairs/ bending at to the waist.
- This pain is become to the Worsen when to the put to added pressure on this joint. like as to the climbing stairs / running or jogging & lying or put to the weight onto the one side.
- Aggravation of this joint is commonly result into the inflammation,which is known as the sacroiliitis.
- It’s more common than you might think.
- About 15%-30% of people who hurt like this have a problem with the SI joint.
- Aggravation point of this joint :
- Stair climbing
- Prolonged standing
- Taking large strides
- Bearing more weight on one leg than the other
- Running
Medical History & Physical Examination of the SI Joint:

- Diagnostic process is usually start with the collected into the medical history, including the information onto current pain & symptoms.
- In to the a medical history patient is asked to the questions includes to the questions of to the information on diet, sleep & exercise, activity habits,
- Physiotherapist is check the gait & leg-length inequality .
- Also examination of the lower lumbar region.
Diagnosis of to the SI joint :
X-ray / CT or MRI scans :
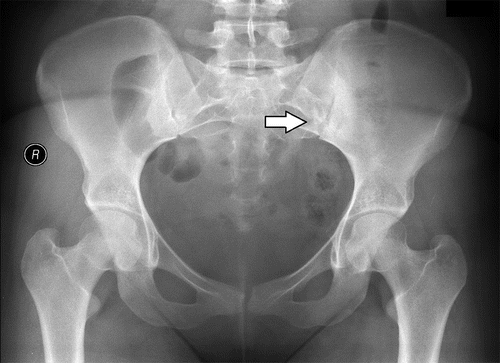
- It is used to the rule out the other possible causes of lower back or pelvic pain like as to the a herniated disc / facet joint arthritis.
- Mostly used for this method for diagnosis is to this joint is as the pain source is the injection test .
- Imaging tests
- X-ray = pelvis is to the reveal signs of to the damage this joint.
- If to the ankylosing spondylitis is to the suspected, doctor is recommend to the MRI .
- In to the MRI = it is used to the radio waves & a strong magnetic field to the produce a very detailed to the cross-sectional images of to the both bone & soft tissues.
Special test for the SI joint :
Sacral thrust test :
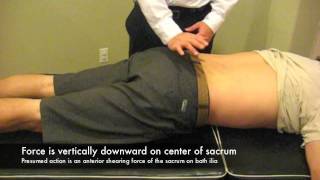
- Test position is supine .
- In the test pressure is to the applied on to the back of to the hips while lying on to the face down prone on to the an the examination table.
- This test is considered to the positive when to the pressure apply onto the reproduces of to the pain.
Distraction test :
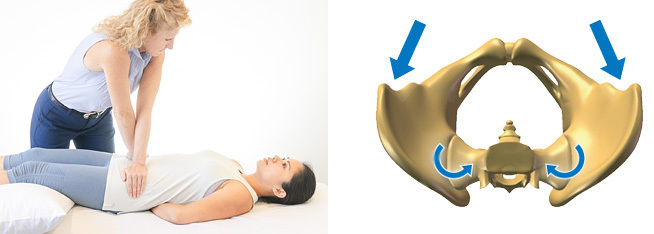
- Test position is supine .
- In this test pressure is applied onto the front of to the hips.
- This test is positive to the occurs when to the pressure applied to the hips reproduces to the pain.
FABER test :
- Test position is supine .
- Lying on to the back
- One leg is kept into the other foot touch into the inside of to the straight knee.
- Pressure is applied on to this joint by on the gently push to the bent knee down & out.
- Into the Modifications of to this test include to the pulling to the bent knee then straight up toward to the chest & moving it from to the side-to-side.
- Downward pressure is also applied on to the opposite hip.
- This test is considered to the positive if to the movements are reproduce to the pain .
- It is cannot to the completed due on to the limited of to the rom .
- The test is reproduce to the pain into the hip, lower lumbar region or to the SI joint , this pain is like as to the pin-pointing of to the pain location .it is important before to the concluding this test as a positive for to the SI joint pain.
Palpation tests :
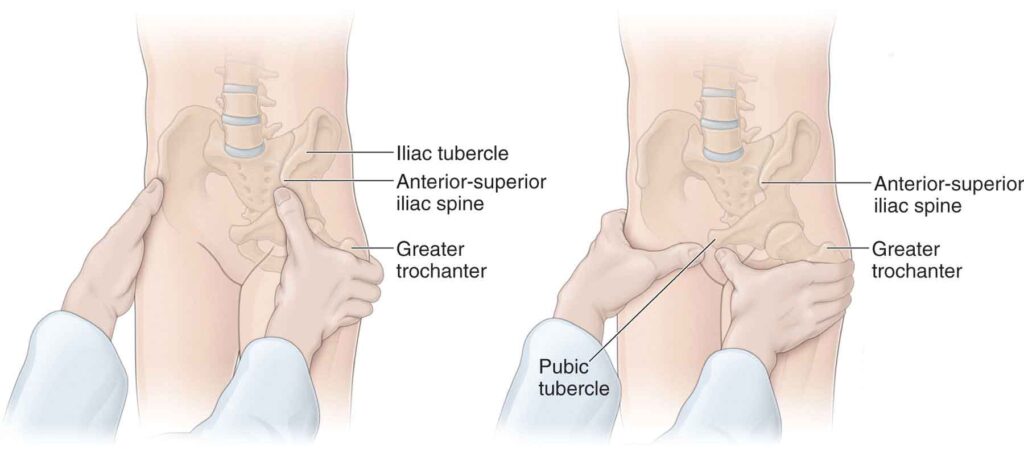
- Test position is supine .
- In which to the use of to the deep thumb is applied pressure directly over to the entire this joint onto the each side.
- This test is positive
- The patient feel to the tenderness over to the affected joint after that it is correlated with to the other provocative tests. When to the several types of to the motion are palpation tests are included with to the clusters of provocative tests , which is to the highest level of to the accuracy found into the 1,2 .
- This joint is to the confirmed as to the pain source if ato the patient is combination of to the movement test which is reproduces to the similar pain response over to the involved to the SI joint .
Fortin finger test :
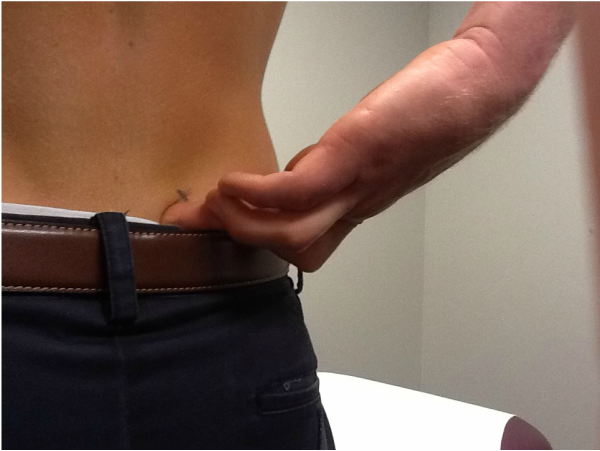
- Test is to the considered positive when to the point of to the tenderness is within 2 cm .
- It is around to inferomedial of to the posterior superior iliac spine.
Gillette test :
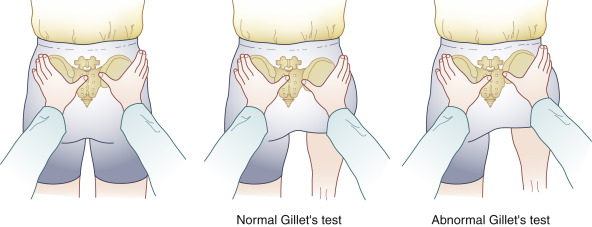
- Patient position is to the standing position.
- In the patient standing onto the one leg while flexion to the opposite hip& knee into the chest.
- Motion of to this joint is assessed by to the placing one thumb under to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) on to the side of to the hip flexion
- The other thumb is put into the mid line at to the S2 level.
- Normally, the thumb is under to the PSIS drops to the inferiorly & laterally with to hip flexion.
- Restriction is to the indicated by to the decreased to the motion compared of to the normal side.
Sacroiliac joint injection :
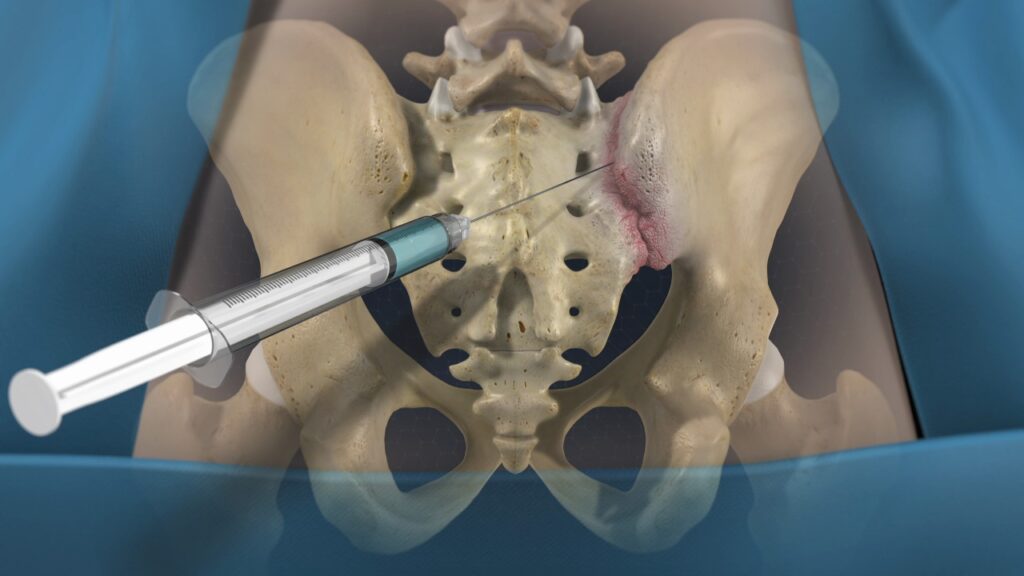
- It is known as to the a sacroiliac joint block which is consists of to the injecting a numbing solution lidocaine or bupivacaine into this joint .
- If to the injection are relieves to the pain which is to this joint is confirmed as to the pain source.
Fluoroscopic guidance :
- It is typically used to the guide of to the needle of to the joint .
- The use of to the ultrasound guidance it is reported to be the equally accurate,
- It is eliminating to the ionizing radiation patient , which is exposure to the associated with to the fluoroscopic guidance techniques.
Initial treatments for SI joint Dysfunction:

- Advice to the patient for to the RICE principle . (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Do to the rest for to the of 1 to 2 days .
- But do not Rest after 2 days because it is lead to the worsen stiffness / it is also increased to the pain & generalized de conditioning.
- Apply to the ice / heat.
- Ice is reduce to the inflammation of to the low back & pelvis & it is also reduce to the alleviate pain / discomfort.
- Heat is relieve to the pain by reducing to the muscle tension / spasms.
Medical treatment for to SI joint Dysfunction :
- Give to the patient Analgesics- pain relievers drug = acetaminophen .
- Also give to the patient anti-inflammatory medications = NSAIDs [ ibuprofen / naproxen] .
- This drug is recommended for to the mild to moderate pain relief.
- Give to the patient Muscle relaxants like as cyclobenzaprine.
- TNF inhibitors means Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors like as to the etanercept [ Enbrel ] , adalimumab [Humira] & infliximab [Remicade]
- It is help to the relieve sacroiliitis which is associated with to the ankylosing spondylitis.
- Give to the Corticosteroids injected into the joint for to the reduce inflammation & pain.
- Muscle relaxants & narcotic painkillers it is used to the during episodes of to the severe / acute pain.
- But this drug is take to after doctor perception because it is highly addictive & severe side effects.
Surgical treatment of this joint :
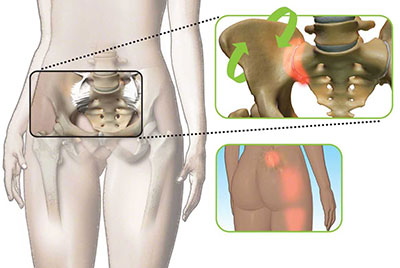
- It is used to the address to the joint pain is do to this joint fusion.
- Goal of the procedure is to the completely eliminate to movement at the joint by to the grafting together into the ilium & sacrum.
- Into the fusion involves to the use of to the implant of to the screws or rods as well as to the possible the bone graft across to the joint.
- Apply to the Minimally-invasive procedures for to the developed into the recent years for to the improve outcomes into the pain disability .
- Under to the general anesthesia do to the small incision onto made over the lower back and muscles are gently moved to the side.
- Used to the device for to the drill a small hole through to the ilium & access to the joint.
- This joint is cleared of to the ligaments & muscles / bone graft & surgical implants are put into the place across to the joint for to the encourage the bone growth.
- Muscles are put back into the place for to the surgical site is closed using standard sutures.
- Hospital stay of 1 to 2 nights are needed after that the surgery.
Treatment for the SI joint :
Manual manipulation :
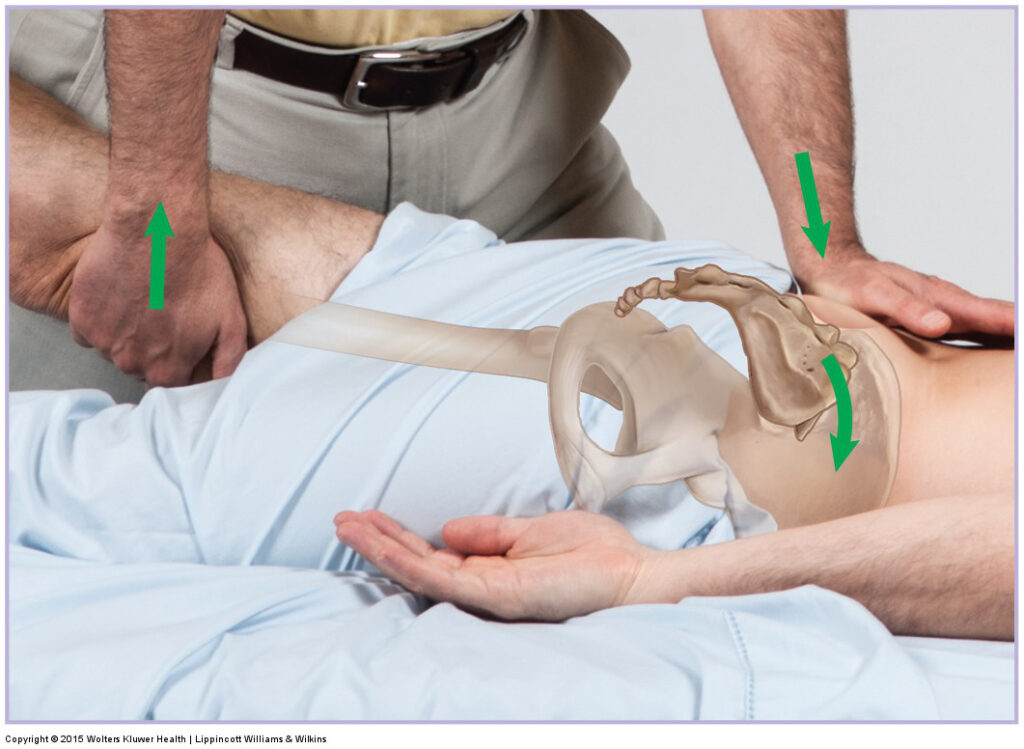
- It is applied by to the by to the chiropractor / osteopathic doctor & other qualified health professional .
- It is highly effective if the joint pain is caused is too little motion means immobility.
- In the therapy is to the consists of the manual procedures which is applied on to this joint & lower back region with to the goal of to the reducing joint fixation / muscle tension & restoring normal range of motion.
Supports or braces :
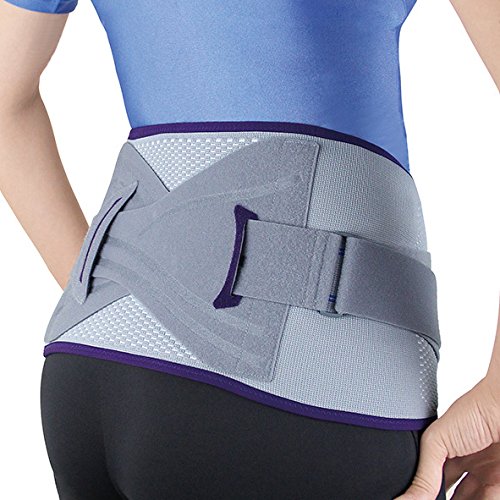

- When to this joint is too loose means hyper mobile apply to the a pelvic brace .
- It is also wrap around to the waist & pulled to the snugly for to the stabilize to the area.
- This brace is about to the size of to the wide belt & it is helpful for to the joint is inflamed & painful.
Sacroiliac joint injections :
- local anesthetic like as to the lidocaine / bupivacaine which is injected with to the anti-inflammatory medication like as to the corticosteroid for to the reduce inflammation & help for to the alleviate the pain.
- This pain relief injection is help to the minimize pain .
- There is no single approach to managing SI joint pain that will work for everyone.
Radio frequency denervation :
- Apply to this Radio frequency on to the this joint .
- This energy is to the damage / destroy to the nerve tissue cause to the pain.
Electrical stimulation :
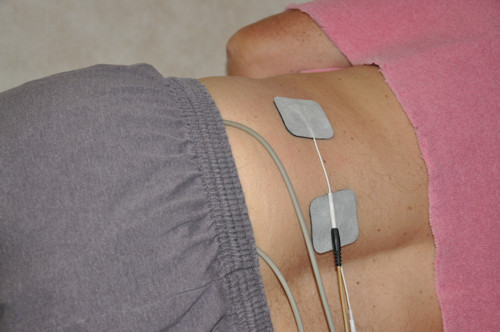
- Apply to the electrical simulator means electrical pad into the sacrum for to help the reduce pain into the sacroiliitis.
Chiropractic treatment :
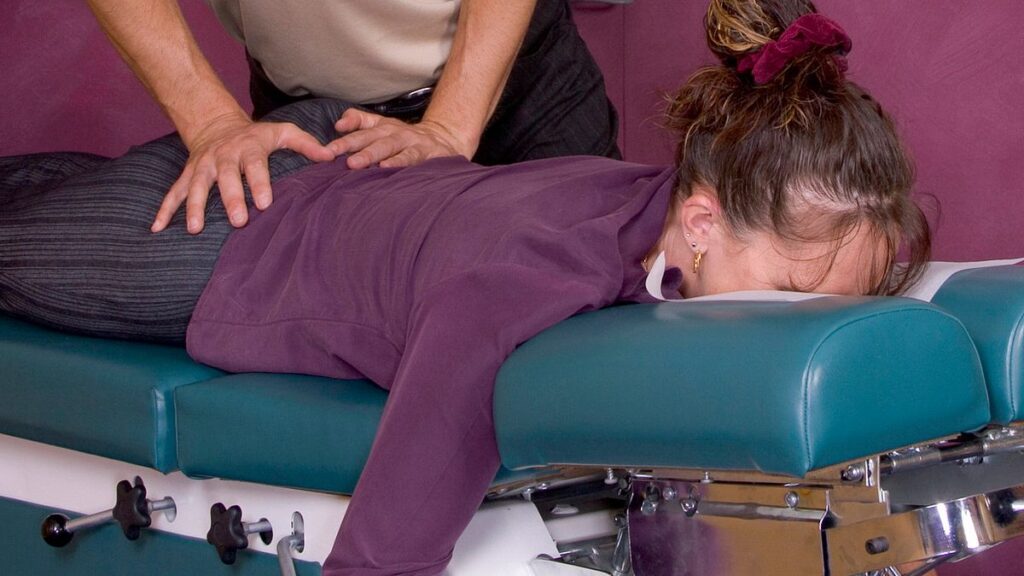
- It is chiropractor help to the relieve pain.
- It is techniques that move to the muscles & joints.
Nerve treatment :
- Use to the needle for to the permanently damage of the nerve which is sends to the pain signals from to this joint to brain.
- They may also freeze it with an injection, though that technique isn’t used much.
Physiotherapy Treatment for to SI Joint Pain :
Physiotherapy treatments mainly are symptomatic pain relieving Electrotherapy Modalities such as Short Wave Diathermy (SWD), Interferential Therapy(IFT), TENS, Ultrasound Therapy. These modalities help to relieve joint pain, muscle spasms.
Exercise mainly SI Joint mobilization with stretching of tight muscles and strengthening exercise of weak muscles are Best common treatment Physiotherapists mostly are used for SI Joint pain.
- Given to the Stretching to the patient for to the reduce muscle tension & spasms in to the lower back, hips & pelvis including to the piriformis , gluteus maximus & hamstring muscles.
- Strengthening exercises :
- It is give to the better support for to this joint & pelvis/lower back.
- It is also give to the Better support for to the joint come to the strengthening to the abdominal muscles, lateral trunk muscles & low back muscles.
- Do the Aerobic exercise for to the elevate to the blood flow & bring nutrients to the oxygen to the damaged tissues, healing process.
- Low-impact aerobics exercise it is needed for this joint dysfunction to the minimize pain to the exercise include to the stationary cycling, running & elliptical / water aerobics.
- Exercises is improve to the strength & make to the more flexible.
- Exercise is learn to correct the any habits to the might to the picked up when to the trying to the avoid pain like walking with to the limp / leaning to the one side.
- Therapist is apply to the ultrasound, heat & cold treatments, massage & stretching.
- Inject to the solution of to the natural ingredients like as saline & numbing drugs into the joint.
Stretching exercise for SI Joint :
- One Knee to Chest
- Both Knees to Chest
- Outer Hip Muscles Stretching
- Twist to the Spine
- Sidelying Quadricep Stretch
- Trunk rotation stretch
- Quad stretch into the standing
One Knee to Chest :

- Starting position is supine .
- Into the lying position bend to the knees & place to the feet flat on to the floor.
- Gently grasp to the one knee & bring it to towards to the chest.
- Go to the as soon as without pain.
- Hold to the position for to the 30 second .
- Then return to in the starting position .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Both Knees to Chest :

- Starting position is supine .
- Into the lying position with to the bent knees & feet flat on to the floor.
- Bring to the one knee is up towards to the front of to the trunk .
- Keep to the knee ,then gently perform to the same move with to the other leg.
- Then Grasp both legs just below the knees and pull them towards you.
- Hold for to the 30 second .
- After that lower onto the legs means return into the starting position .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Outer Hip Muscles Stretching :
- Starting position is supine position .
- Into lying position with to the knee is bent & feet flat on to the floor.
- Place to the ankle of the one foot onto the knee of to the other.
- Wrap to the hands under to the supporting knee.
- Use to the abs then gently lift to the supporting knee off to the floor.
- Go to only as high as without to the pain at to the this joint.
- Stay up for to the just in a short time & set to the leg down again.
- Hold for this position for to the 30 seconds .
- Then return to in the starting position .
- After that repeat into the opposite side .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Side lying Quadriceps Stretch :

- Starting position is side – lying .
- Lie onto the one side & grasp to the foot, ankle & even to the shin behind to the body .
- Pull heel through to the bottom.
- If the patient cannot reach, apply to the tying a strap or belt around to the foot .
- Then hanging to the other side for to the strap to the pull to the foot in.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Trunk rotation stretch :

- Starting position is supine.
- Lie on to the ground with to feet flat on the floor & arms are outstretched into the T-position.
- Knees are keep to the together& pointed toward to the ceiling.
- Keep to the knees are together & twist to the one side for to the comfortably .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day
Quad stretch into the standing :
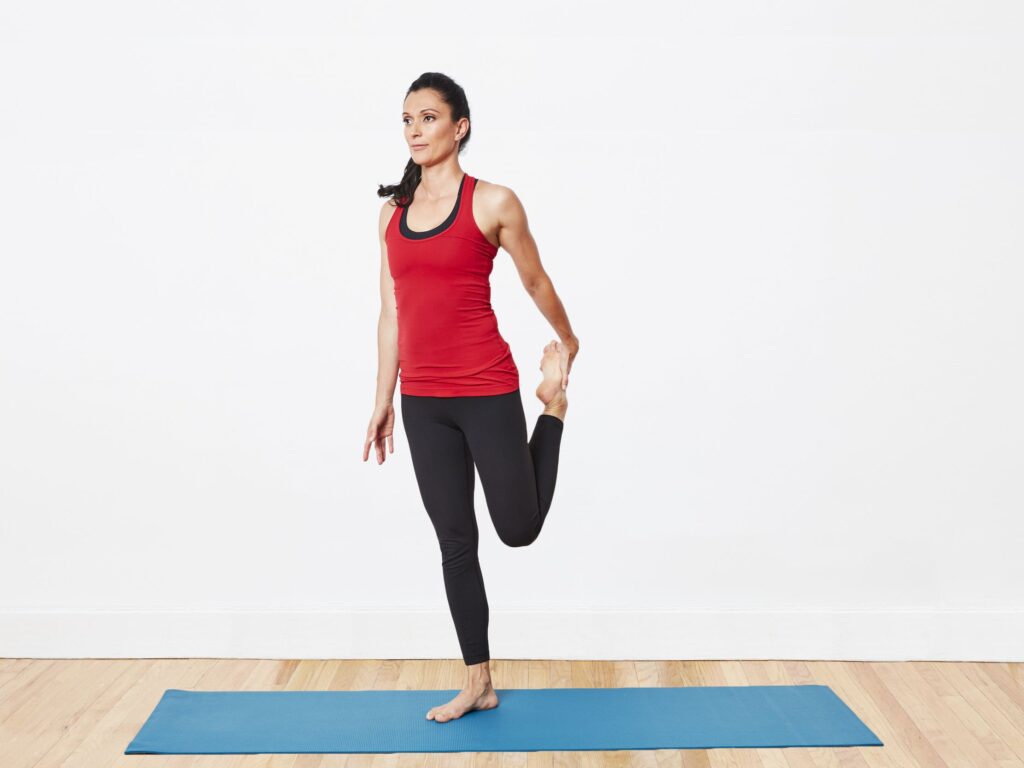

- Into the Hold on to the chair / wall if to the need for to the help balancing.
- Grab to the left ankle .
- Then pull to the foot to the buttocks with to the knee pointing is downward.
- Hold for to the 2 to 5 seconds.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Exercise of to the SI joint :
Strengthening exercise :
- Hip abduction
- Hip adduction
- Bridge.
- Adductor squeeze
- Band abduction
- Light Aerobic Exercises
HIP ABDUCTION :
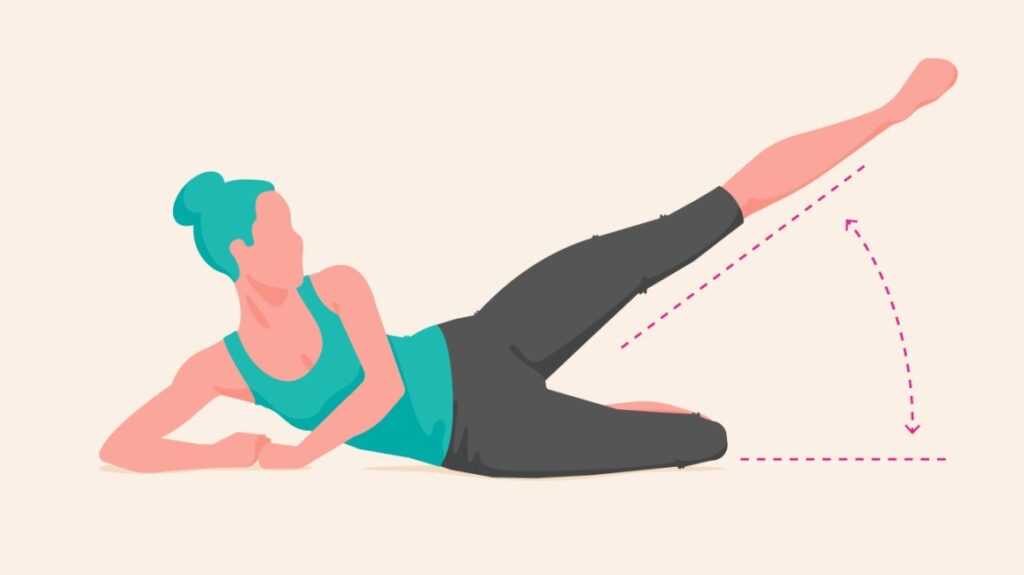
- Starting position in side lying .
- Lie on to the back with to the knees are slightly bent .
- Put to the a resistance band around to the knees.
- Keep to the back arched .
- Gently push to the knees apart to the strengthen of to the outer thigh & buttock.
- Hold for to the 5 seconds .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Hip adduction :
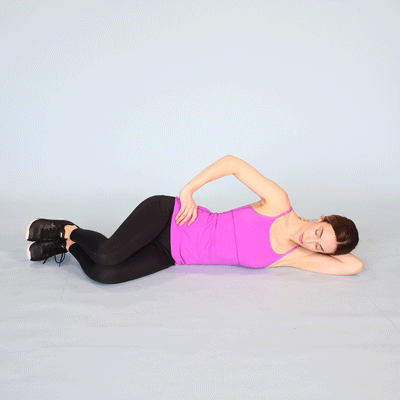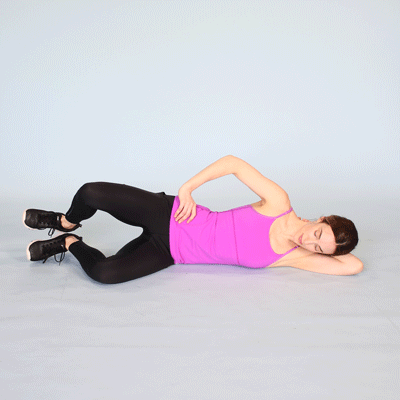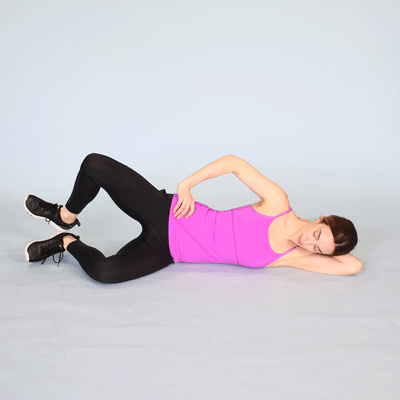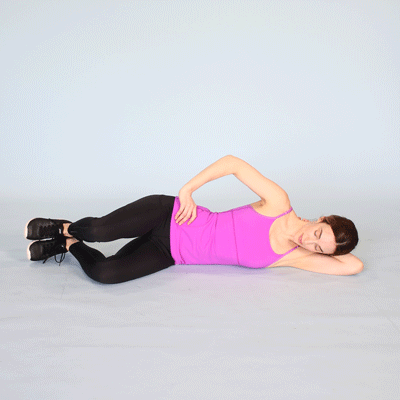
- Starting position in side lying .
- Lie down on to the back with to the both knees are bent .
- Place to the medium rubber exercise ball between to the knees.
- Keep to the back slightly to the arched .
- Squeeze to the ball with to the both knees for to the 5 seconds,.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Bridge :

- Starting position in supine .
- Lie on to the back with to the knees are bent & the palms are flat on to the floor.
- Keep to the palms on to the floor .
- Lift the hip and buttocks onto the air .
- Hold for on to the 5 second in to the strengthen muscle & lower abdomen, lower back, & hips.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Adductor squeeze :

- Starting position is supine ,
- Lean back with to the weight on to the elbows with to the knees bent to the about 90 degrees.
- Put to the soft ball / similar-sized object between to the knees.
- Squeeze to the ball comfortably & hold for to the about 3 seconds.
- After that Relax & return into the starting position .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Band abduction :

- Starting position is supine .
- Lie on to the back with to the knees bent to the about 90 degrees & feet flat on to the floor.
- Put to the band around to the knees.
- Push to the knees apart & pause for to the moment.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day.
Twist to the Spine :

- Start position is supine .
- Into the lying position but without to the bent knees.
- Keep to the shoulders flat onto the ground then lift to the knees & bend them at to the 90-degree angle.
- After that lower to the one side of to the body.
- Move to the gently & thoughtfully.
- Stay only for to the few seconds & bring to the legs back up.
- After that Return to in starting position.
- After that repeat into the opposite side .
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Light Aerobic Exercises :

- Into aerobic exercise including to the exercise
- Walking= it is the most straight forward way to the raise to the heart rate either by / with to the a friend.
- Water aerobics =Swimming is to the one of the best low-impact exercises for to the people which is suffer form to the chronic pain.
- If to the swimming is do not work for the patient then try to the walking in to the pool / wading while hold onto body .
- Stationary cycling = If to the patient have not stationary bike at home after that therapist advice to the joining a class.
- But always go to slow do not feel pressured to the keep up with to the those around to the patient .
Yoga pose for to the exercise :
- Triangle pose
- Bird dog pose.
- Cat-Cow pose for to the Hips & Back
Triangle pose :

- Starting position is standing .
- Begin with to the feet a little more than shoulder-width to the apart point to the right foot outward.
- Extend to the both arms straight in to the sides so that parallel to the floor.
- After that slowly bend to the side so that right hand is touch to the right shin or to the floor .
- The left arm is over to the head.
- Hold the stretch for to the 10 to 20 seconds.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Bird dog pose :

- It is help to the strengthen to the lower back & core muscles support to the pelvis.
- Starting on to the hands & knees .
- Keep to the shoulders are square & the face is toward to the floor.
- Lift to the one leg & the opposite arm is straight into the air .
- Hold this position for to the 5 seconds.
- Keep to the back & pelvis level is straight during to the exercise.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Cat-Cow pose for to the Hips & Back :

- Starting position is prone .
- Start on to the hands & knees with to the chin up, do the back flat & eyes for to the forward.
- Slowly do to the arch on to the back up like as to the draw to the chin towards to the chest.
- Hold this position for to the 30 seconds.
- Slowly bring to the chin away from to the chest & return to the eyes forward as to the arch of to the back down.
- Hold for to the 2 to 5 seconds.
- Do to the exercise for to the 10 times in one session & 3 session per day .
Complications :
- This is a conditions which is produce to the chronic pain.
- So that produce to the result in to the depression & insomnia.



5 Comments