Test for the capsule & joint instability in the wrist joint
- These tests are applied to the clinic to check the capsule & joint instability in the wrist joint.
- These tests are applied by the physiotherapist [ examiner ] when the patient complains about wrist joint pain.
Name of the Test for the capsule & joint instability in the wrist joint
- Axial load test
- Catch-up clunk test
- Dorsal capitate displacement apprehension test
- Finger extension
- Litchment test
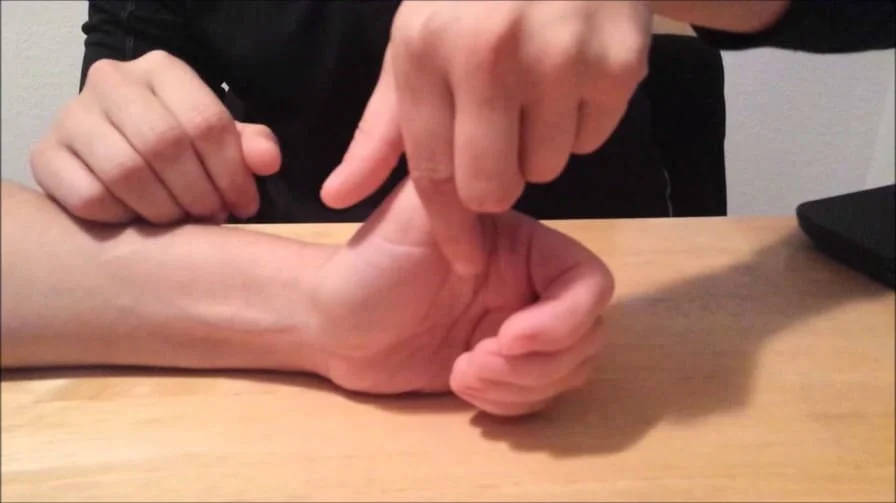
Axial load test
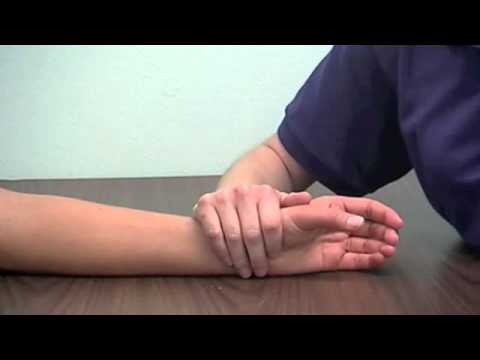
- Purpose = These axial load test is used to check the fracture of the metacarpal or adjacent carpal bones or joint arthrosis.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the test is sitting position.
- The patient sits while the examiner [ therapist ] stabilizes the patient’s wrist with the help of one hand.
- With the help of the other hand, the examiner [ therapist ] carefully grasps the patient’s thumb & applies the axial compression.
- Result = Pain & crepitation indicate a positive test for a fracture of the metacarpal or adjacent carpal bones/joint arthrosis.
- A similar test may be performed for the fingers.
Catch-up clunk test
- Purpose = These catch-up clunk test is used to check the instability in the mid carpal or radiocarpal joint.
- Technique = the patient in sitting position for the test
- The patient has the forearm in pronation while radially & ulnarly deviation the wrist.
- Normally, during this movement, the proximal row of carpals rotates from flexion to extension while the distal row translates from anterior [ palmar] to posterior when going from radial deviation to ulnar deviation.
- Result = if there is mid carpal or radio carpal instability during the movement from radial deviation to ulnar deviation the
- proximal row remains flexed & the distal row remains anteriorly & takes longer to translate.
- As the soft tissue restraints become tighter, there is a sudden catch-up of the proximal row into extension & the distal row posteriorly often accompanied by a clunk indicating a positive test.
Dorsal capitate displacement apprehension test:

- Purpose = These dorsal capitate displacement apprehension test is used to check the stability of the capitate bone.
- Technique = Starting position for the patient of the test is sitting position.
- This patient sits facing the examiner.
- The examiner holds the forearm with the help of one hand.
- The thumb of the examiner’s other hand is placed over the palmar aspect of the capitate while the fingers of that hand the patient’s hand in neutral [ no flexion /extension, no radial or ulnar deviation] & apply a counter-pressure when the examiner [therapist ] pushes the capitate posteriorly with the thumb.
- Result = reproduction of the patient’s symptoms, apprehension, or pain indicates a positive test.
- A click or snap may also be heard when the pressure is applied.
Finger extension test

- This test is also known as the shuck test.
- Purpose = this finger extension test is used to check the inflammation, scaphoid instability, radio carpal or mid carpal instability & Kienbock disease.
- Technique = the patient is placed in a sitting position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] holds the patient wrist in flexion position & the examiner instruct the patient for doing to actively extend the fingers against resistance – loading the radio carpal joints.
- Result = pain would indicate a positive test for radiocarpal or midcarpal instability, scaphoid instability, inflammation &Kienbock disease.
Lichtman test

- This Lichtman test is also known as the mid carpal shift.
- Purpose = This Litchment test is also used to check the instability of the mid-carpal.
- Technique = the patient’s forearm is pronated with the help of a handheld in support by the examiner [ therapist].
- The examiner moves the patient’s hand from radial to ulnar deviation while axially compressing the carpus into the radius while applying an anteriorly directed force to the capitate.
- Result = If the distal carpal row jumps or snaps dorsally means from its subluxed position primarily & reproduces the patient’s symptoms, the test is considered positive.