Triceps Muscle Tightness: Cause, Symptoms, Stretching Exercise
What is Triceps muscle tightness?
In the triceps muscles tightness, you may feel heaviness or stiffness at the backside of your arm during elbow movement. triceps muscle tightness refers to a tight decent feeling in the back of your arm muscles and also you feel discomfort while bending or extending elbow joints.
In the present climate, stiffness is time-varying and thus has dynamic attributes. Classically, triceps muscle tightness refers only to the flexibility of the muscle, and thus static, element of impedance. Still, muscular properties are nonlinear, and thus muscular impedance can not fluently be partitioned into factors corresponding to the derivations of position.
The most common reasons for tightness are dehydration, poor sleeping positions, muscle weakness, muscle inhibitions, and overusing of the muscle without changing the position of the arm which lead to muscle stiffness or tightness which is most common nowadays Researchers have chosen to retain the term “ stiffness” to describe the resistance of muscle to length change.
The Soft tissue changes, similar to muscles shortening after overuse injury. which are also common problems we treat in the clinic. All soft tissues are susceptible to shortening adaptions. Primary causes are the geriatric process, complaint, limited physical exertion over a sustained period of time, or poor posture. training or lately starting a new modified exercise or over athletics can also be an illustration of soft tissue changes seen in the body and become more prone to developing triceps tightness.
when soreness, pain, or cramping makes your muscles feel tight. The symptoms make it hard to make any type of movements that are generally enough simple, similar to stretching out your arms, gentle stretching of the tight triceps muscle, and holding it for a few seconds without change in length of the muscle. in a healthy person, the stiffness will generally go down on its own; especially if it was caused by exercise or sleeping in an awkward position, or overusing of the particular muscle.
Still, if the person has a beginning condition the stiffness can become chronic. it may develops over period of time. basically, The triceps brachii is a large, thick muscle on the forward part of the upper back of your arm. It frequently appears in the shape of a horseshoe on the posterior aspect of the arm. The main function of the triceps is the extension of the elbow joint. so mainly triceps tightness is an unknown cause and it can occur in people with overusing of the primary muscle.
Anatomy of the triceps muscle :
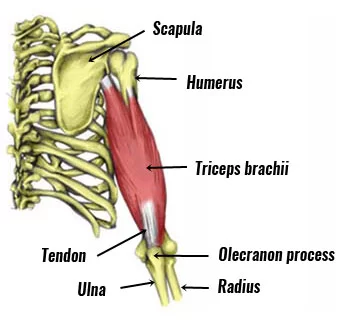
The triceps brachii is a large, thick muscle on the dorsal part of the upper arm. It frequently appears as the shape of a horseshoe on the posterior aspect of the arm. The main function of the triceps is the extension of the elbow joint.
The Triceps brachii gets its name with tri pertaining to”three” muscle heads or points of origin (with Brachii pertaining to the arm). These include the Medium head; Shorthead; Long head
Origin :
- infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
insertion :
- Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint and antebrachial fascia.
Arterial Supply:
- Branches of deep brachial artery
Action :
- Chief extensor of forearm; long head steadies head of abducted humerus
- Because it attaches to the scapula, the long head not only extends the elbow but will also have a small action on the glenohumeral joint. With the arm adducted, the triceps muscle acts to hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity. This action helps prevent any displacement of the humerus.
- The long head also assists with the extension and adduction of the arm at the shoulder joint. The lateral head is also active during extension of the forearm at the elbow joint when the forearm is supinated or pronated.
- Innervation radial nerve Long and Side head triceps
Lateral head :
- Origin posterior aspect of the humerus, superior to the radial groove
- .Insertion Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint, and antebrachial fascia.
- Action Strongest head of the three. It’s active during the extension of the forearm at the elbow joint when the forearm is supinated or pronated.
- Innervation radial nerve
Medial head :
- Origin posterior aspect of the humerus, inferior to the radial groove
- Insertion Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint, and antebrachial fascia.
Symptoms of triceps muscle tightness :
- You may feel the muscle tight around the back of your arm while moving or while performing any moving arm.
- Pain in the tendon caused by movement.
- may be seen Swelling in the tendon that is sometimes accompanied by heat
- A grating feeling when moving the tendon of the biceps
- Redness in the tendon can get darker over time.
- chiness in the area of your triceps, shoulder, or elbow
- pain that occurs when you use your triceps muscles
- a limited range of motion in your arm
- a bulge or area of swelling on the back of your upper arm, near your elbow
- weakness in or around your triceps, elbow, or shoulder
- a popping noise or feeling of a tight arm while moving after overuse of the triceps muscle
Causes of the triceps muscle tightness :
Triceps muscle tightness can develop slowly over time after overusing the muscle.
1. Overuse or overexertion :
- Symptoms be like this
- Dull painful pain over the entire triceps muscle
- Both contracting the muscle ( straightening the arm) and relaxing the muscle ( bending the arm) may worsen the feeling of soreness OR stiffness Soreness may take 1 to 2 days to set in after you overexerted it and generally lasts just many days.
- Triceps soreness is caused by micro-tears in the muscle filaments. It can be after working out or an exertion like digging or a night of axe-throwing. This is a normal part of the recovery process after a muscle is worked hard.
- You generally do not feel sore or tight until the coming day or two.
- Because the soreness generally goes down on its own, you just need to rest, do light stretching, and light massage.
2. Triceps strain :
- Symptoms when u have injury around your triceps muscle
- unexpected pain during emphatic or forceful exertion.
- Pain may be accompanied by a “ tearing or ripping” sensation in the muscle
- Pain worsens when extending the arm, particularly against resistance after the immobilization phase.
- A triceps strain is when the muscle gashes, causing unforeseen and sharp pain. How painful it is depends on how multiple muscle filaments are torn.
- Treatment should include rest originally along with icing. When the pain is tolerable, light movement and stretching will help avoids stiffness.
3. Tendonitis and tendinopathy :
- Symptoms if you have triceps muscle tendonitis :
- Pain and tenderness at the reverse of the elbow may come and go and is generally worse with exertion that involves uncurling the arm.
- Weakness when uncurling the arm
- Tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendon, the cord that connects the triceps to the bone at the elbow. It occurs after repetitious movement at the elbow that causes micro-tears in the tendon. Still, because the tendon doesn’t have the capability to heal itself well, over time tendonitis may develop into tendinopathy, which is a habitual degeneration of the tendon.
- For both tendonitis and tendinopathy, pain will get worse with movements that bear you to unbend your arm, particularly against resistance, similar as doing drive-ups. Triceps tendonitis can be treated by rest, ice, contraction, and light stretching. Anti-inflammatory specifics, like ibuprofen or naproxen, may also help with the pain.
- Because tendinopathy is a degenerative condition rather than seditious, these specifics may not be effective, and warming the area with heat- packs is more likely to help than icing
4. Tendon rupture :
- These kinds of symptoms may you saw if you had an open injury around the triceps and muscle got ruptured :
- Unforeseen pain at the reverse of the elbow, frequently with a “ popping” sound or sensation
- You may feel a “ gap” if you press just above the reverse of the elbow where the tendon should meet the bone.
- Weakness or incapability to unbend the arm
- Bruising near the reverse of the elbow
- A tendon rupture is a large gash of the tendon that you can see with the naked eye. The rupture can be partial, meaning that some of the tendon is still attaching the triceps muscle to the bone. A full rupture is a complete gash where the triceps muscle is fully detached from the bone at the elbow.
- Triceps tendon ruptures frequently do when the tendon has formerly been weakened and tight. This may be because of habitual tendinopathy. In addition, underpinning medical conditions may weaken the tendon leading to rupture, including habitual steroid use, endocrine diseases, original steroid injections, or previous elbow surgery.
- Treatment for full ruptures generally involves surgery to repair the tendon, while partial ruptures may or may not bear surgery depending on pain and function.However, see a croaker within a many days, If you believe you have either a partial or full triceps tendon rupture.
5. Radial nerve injury :
- Cervical spine or brachial plexus injury
- Cellulitis ( original skin and soft towel infection)
- Compartment pattern of the upper arm ( COMPARTMENT SYNDROME )
- The radial nerve is also in close contiguity to this region, and divides into the superficial radial nerve and the posterior interosseous nerve
- The area of minimal tenderheartedness is generally an area just distal to the origin of the extensor muscles of the forearm at the side epicondyle. Utmost generally, the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) is involved, but others may include the extensor digitorum, extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL), and extensor carpi ulnaris.
- Some symptoms that indicate that you may have triceps muscle involvement after radial nerve palsy that affect your muscle around back of your arm and become tight after immobilization phase this includes symptoms like:
- achiness in the area of your triceps, shoulder, or elbow
- pain that occurs when you over use your triceps muscles
- a limited range of movement in your arm
- a bulge or area of swelling on the reverse of your upper arm, near to your elbow
- weakness in or around your triceps, elbow, or shoulder a popping noise or feeling at the time of injury
6. Bruising :
- Visible bruise on the back of the upper arm
- Pain or tenderheartedness at bruise point
- Bruising of the triceps muscle generally occurs from direct impact, similar as being punched in the reverse of the arm or hitting into a door.
- In high impact trauma, similar as auto accidents or being hit with a baseball club, bruising may be a sign of a fracture of the humerus (the upper arm bone). The pain will be severe, and any attempts to move your arm will be indeed more painful. There may also be a visible deformity.However, you should go to the ER incontinently, If you suspect that your arm is broken.
- In this condition of humerus bone or elbow joint fracture post immobilization tightness of triceps is the most commonly seen now days.
- A number of conditions may also cause triceps tightness, but they may be uncommon or triceps pain may not be a hallmark symptom
Benefits of Triceps Stretching :
- Stretching can diminish muscle soreness.
- Still, stretching can help relieve some of this discomfort, If you have soreness in a muscle or muscle group from a recent drill or from a muscle strain. Numerous times, when we’re injured, the muscles around the injury point strain up as a defensive response. By stretching these tight muscles out, pain and soreness can be soothed.
- Stretching can ameliorate range of shifting and prevents loss of range of stir.
- As we progress, our joints lose range of movement. We can offset this by stretching regularly. Indeed if range of stir in some joints is limited, stretching can help to ameliorate this.
- Stretching can help to prevent injury.
- Still, it’ll come simulated or torn, If you stretch a muscle too far.However, the liability of injuring it decreases, If your stretch and increase the range in which a muscle can move.
- Stretching before physical exertion specifically helps help injury by bringing blood inflow to the muscles, warming them up, and dwindling any miserliness they might have to help a strain or a tear.
Technique for stretching :
1. Static Stretching :
- Static stretching (SS) is a type of stretching exercises in which extension of muscle with operation of low force and long duration ( generally 30 sec).
- Static stretching has a relaxation, extension effect on muscle, perfecting range of stir (ROM), diminishing musculotendinous stiffness and also reduces the threat of acute muscle strain injuries.
- It’s a slow controlled movement with emphasis on postural mindfulness and body alignment.It’s comfortable for all patient types.
2. Dynamic Stretching :
- Dynamic Stretching (DS) involves the performance of a controlled movement through the available ROM.
- Involves precipitously adding the ROM through consecutive movements till the end of the range is reached in a repetitious and progressive manner.
- Dynamic Stretching Can be functional and mimic the movement of the exertion or sport to be performed performed.
- eg ; a swoon may circle their arms before getting into the water. Helps to restore dynamic functions and neuromuscular control through repeating and rehearsing movement therefore enhancing motor control.
- Occasionally considered preferable to SS in the dosage for physical conditioning.
- Though kindly parallel, dynamic stretching is distant from Ballistic stretching.
- Dynamic stretching involves moving region of your body and gradationally adding the range of stir and or speed of movement.
- In comparison, ballistic stretches involve trying to force a part of the body beyond its range of stir. In dynamic stretches, there are no bounces jerky’ movements. Because of increased threat for injury, ballistic stretching is no longer recommended.
The Stretch Reflex :
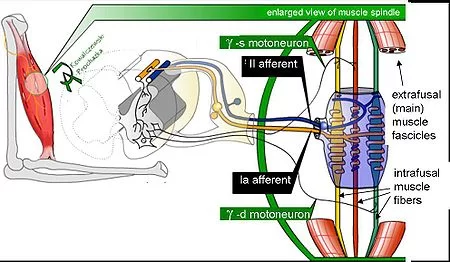
- When the muscle is stretched, so is the muscle spindle. The muscle spindle records the change in length (and how fast) and sends signals to the vertebral column which convey this information.
- This triggers the stretch reflex which attempts to resist the modification in muscle length by causing the stretched muscle to contract. The further unexpected the change in muscle length, the stronger the muscle compression will be (plyometric training is grounded on this fact). This elemental function of the muscle spindle helps to maintain muscle tone and to cover the body from injury.
- One of the reasons for holding a stretch for a prolonged period of time is that as you hold the muscle in a stretched position, the muscle spindle habituates and reduces its signalling.
- Gradationally, you can train your stretch receptors to allow higher stretching of the muscle
Indications of Triceps stretching :
- stretching exercise can help to improve mobility and flexibility of the joint
- to gain better joint ROM
- Increase extensibility of muscle tendon unit and periarticular connective tissue
- Return normal neuromuscular balance between muscle groups
- Reduce compression on joint exteriors
- prevent injuries around muscles.
- May be used previous to and after vigorous exercise to potentially reduce post-exercise muscle soreness
Contraindications :
- Joint movement limited by bony blocks
- After fracture and before bone healing is complete
- Acute inflammatory or contagious process
- When dislocation of soft tissue recovery is likely
- Sharp, acute pain with joint movement or muscle stretching
- Hematoma or other soft tissue trauma
- Hypermobility exists.
- open wound or recent surgery
Stretching exercise for triceps muscle tightness :
Triceps Stretching exercise is easy and fast and you can do it anywhere, but there are still some rules to follow. Before you try any of these moves, warm up and loosen your muscles a bit. Do many twinkles of brisk walking, a light jam in place, or many jumping jacks.
The idea is to warm up your body many degrees so stationary stretching ( stretching while standing in place) does not cause an injury.
Remember that stretching is not a competition. It’s not supposed to hurt, so if it feels like you are about to snap something off, stop! Do not push yourself so hard that you’re in further pain than before you started.
1) Overhead triceps stretch :
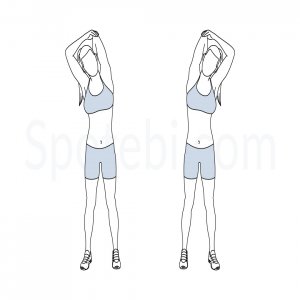
- You can do this stretch while either sitting or standing. It’s a great one to do at your office during work, too.
- Reach your right arm toward the ceiling, also bend at elbow and reach for your upper reverse. Try to place your right hand toward the middle of your reverse, middle cutlet on your chine.
- Place your left hand on top of right elbow and gently push right arm down so your hand slides down your back a bit.
- Hold for about 30 seconds, also repeat on the other side. Reprise 3 – 4 times as demanded.
2) Towel stretch :
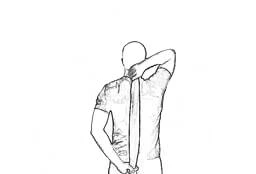
- This one requires a mount — a rolled-up kerchief or commodity analogous — and offers a deeper stretch than the outflow option.
- Holding one end of a rolled-up kerchief in your right hand, reach right arm toward the ceiling. Bend at elbow, letting kerchief hang down your reverse.
- Reach left hand behind you and snare the other end of the kerchief. Try to keep the reverse of your left hand against your reverse.
- Use left hand to pull the kerchief as far down as you can without pain.
- Hold for 20 – 30 seconds, also repeat on the other side.
3)Cross-body stretch :

- This is another easy stretch that can be done anywhere, whether you ’re sitting or standing.
- Raise your right arm to about shoulder height, also reach across to left side of your body.
- Bend left arm at elbow and use left arm to gently pull right arm toward your body, which will consolidate the stretch.
- Hold for about 30 seconds, also repeat on the other side. Repeat a many times as demanded.
4) Leaning stretch :
- Do this stretch using a president, settee, banquette, or bench — principally, commodity you can lean on that won’t slide forward.
- Kneel far enough down from a president so you can bend forward and be resemblant to the bottom without your head touching the president.
- Spare forward so you ’re parallel to the bottom. Place your elbows on the president, above your head. Bend elbows so they support you, and be sure not to strain your lower reverse.
- Look at the bottom, lining up your head with your neck and back. Make sure elbows are the only part of you touching the president.
- Bring forearms toward your neck and place hands on the reverse of your neck.
- Press torso toward the bottom while exhaling sluggishly.
- Hold for 30 seconds, also precisely bring arms down and return to a kneeling position. Reprise as demanded.
5) Wrist pull :
- While not specifically a stretch for your triceps, this bone will stretch your whole arm and is easy to do anywhere.
- Extend your right arm in front of you. Snare right fritters with left hand and gently pull right arm down a bit until you feel a stretch.
- Hold for 30 seconds, also repeat on the other side.
- Make it easier If holding your fritters is too deep of a stretch, try holding your wrist.
6) Chair Tricep Stretch :
- starting position for stretching : Begin by sitting in a sturdy chair, with both bases planted forcefully on the bottom at a shoulders- range piecemeal.
- With both hands snare the front of the president and sluggishly move your body off the president’s edge. Keep your reverse upright, and push your legs out so they’re straight out in front of you.
- What Muscles Does This Stretch Engage?
- Main Muscle is the Triceps
- Secondary Muscles Deltoid, Pectorals, Lats.
- How Long Should I Hold This Stretch? 3 Sets of 10 reps
- This triceps stretching exercise is slightly different from others to appear on our list, as it requires you to concentrate more on reps and sets, rather than the quantum of time it’s held for.
- If you are start the exercise initially you should start 2 sets of 5-10 reiterations, adding or dwindling as you suppose necessary grounded on your current position of fitness.
- Miscalculations To Avoid : Incorrect President Whilst this does sound kindly pedantic, please insure that you have a sturdy president that wold not roll or break under the pressure of your weight.



2 Comments