The Prone Anterior Drawer Test :
- This Prone Anterior Drawer test of ankle is used in the clinic to check the ligament instability in the ankle.
- This test is an orthopedic test that is used to assess the integrity of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle such as calcaneofibular ligaments/anterior talofibular & posterior talofibular.
- This Prone Anterior Drawer test of ankle is applied by to doctor or therapist.
- This test is an alternative test of the conventional ways for the performing of the anterior drawer test of the ankle.
What is the purpose of the Prone Anterior Drawer of the Ankle?
- This Prone Anterior Drawer test of the Ankle is designed the primarily of the injuries of the ligament of anterior talofibular in the ankle joint.
- This test is also used to check the ligamentous instability.
How do you perform of the Prone Anterior Drawer of the Ankle?
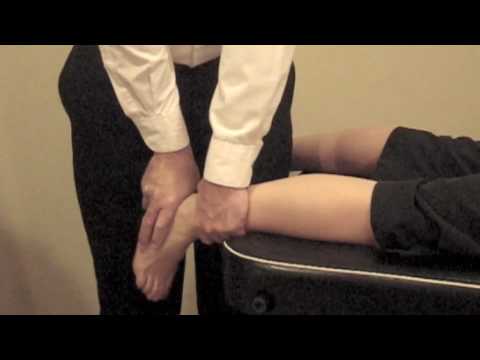
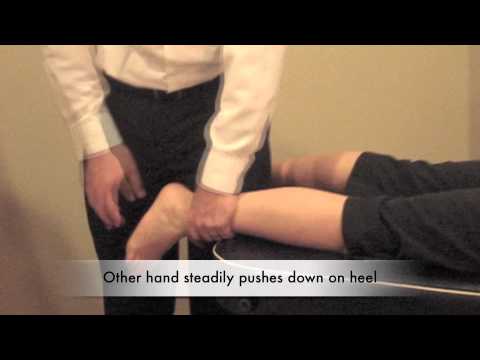
- Starting position of the patient for the test is the prone position.
- In the prone position with the feet extending over the end of the examining table.
- With the help of one hand, the examiner pushes the heel steadily forward.
What is the result of the Prone Anterior Drawer of the Ankle?
- Excessive anterior movement & a sucking in of the skin on both sides of the Achilles tendon indicates a positive sign.
- This test, like the previous one, indicates ligamentous instability, primarily the anterior talofibular ligament.
What is evidence of the Prone Anterior Drawer test of ankle?
- No psychometric properties is reported for this Prone Anterior Drawer Test.
Duchenne test :-
- The patient lies supine with the leg straight.
- The examiner pushes up on the head of the first metatarsal through the sole, pushing the foot into dorsiflexion.
- The test is positive for a lesion of the superficial peroneal nerve or a lesion of L4, L5, S1 nerve root if, when the patient is asked to plantarflex the foot, the medial border dorsiflexes & offers no resistance while the lateral border plantar flexes.