What is the Cardiovascular Endurance?
Introduction
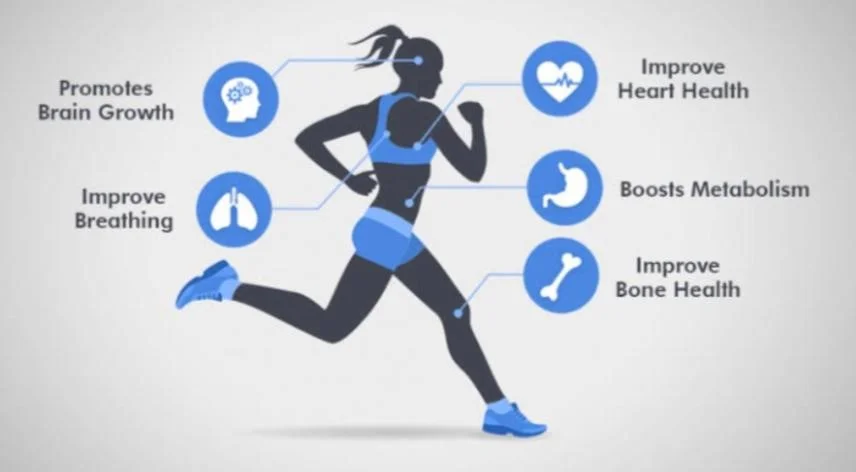
The ability to perform activities using the entire body for a lengthy period at a moderate to high level is known as cardiovascular endurance. the ability to complete daily chores more easily can increase your cardiovascular endurance. Additionally, it can lower the chance of developing conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
What is the Cardiovascular system?
Cardiovascular is a physiological term it refers to the heart and the blood vessels. A word system refers to how the two work together and use oxygen as energy. But in the world of fitness, mentions of the cardiovascular system generally refer to the aerobic energy system. The aerobic energy system is how the heart, the blood vessels, and the muscles use oxygen to perform the task.
What is Cardiovascular endurance?
Cardiovascular endurance: The heart lungs and blood vessels can supply oxygen to the muscles and the body tissues. and the ability of the muscles to utilize oxygen to allow sustained activity. The more efficiently the body delivers oxygen to its tissues, the lower the breathing rate is. While this might assist you to get a little more bottom time from each tank of air, the real benefits are being more relaxed during every dive, experiencing less fatigue, and being better able to respond to challenging currents, long swims, and any emergencies that may arise. Essentially, a stronger, more efficient oxygen delivery system permits you to dive with greater ease in any situation. It means a fit heart that can carry on the activity for a longer time i.e. working under conditions of fatigue e.g. cycling jogging swimming etc.
Cardiovascular means relating to the heart and the blood vessels. Cardiovascular endurance is a measure of how well you can do exercises that involve the whole body at moderate to high intensity for an extended time. Improving cardiovascular endurance can make it easier for you to carry out your daily tasks. It can also lessen the risk of diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. The term “cardiovascular endurance” gets thrown surround a lot in athletic circles. The advantages of cardiovascular fitness are quite expansive. Cardiovascular endurance promotes overall strength gains and health improvement or progress, and it is considered to be a crucial element of a good training regimen. Cardiovascular endurance is the ability to exercise without becoming overly tired because the heart, the lungs, and the blood vessels are healthy. Exercise eg, includes walking, jogging, cycling, dancing, running, and bike riding. Distance swimming is also a better cardiovascular endurance exercise.
The good news is that you can improve cardiovascular endurance through a sensible program of regular aerobic exercise performed within a target range of 60 to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate (MHR). Most individuals see significant improvement in about three months as the heart muscle grows stronger and pumps more blood with each beat. Blood vessels become more elastic, decreasing blood pressure, and capillaries — the tiny vessels that deliver oxygen to the tissues — create more branches. Oxygen is taken up by a tissue more effectively as the density of oxygen receptors (called mitochondria) increases. The net result is a positive effect on general health and wellness.
The definition of cardiovascular endurance simply put is the body’s ability to continue exertion while getting energy from the aerobic system used to supply body energy. This is the system that kicks in third after the phosphagen and the glycogen lactic acid system, and so the one that supplies energy to the human circulatory system and a muscle over extended periods. Endurance activity maintains the heart, lungs, and circulatory system healthy and improves overall fitness. As a result, individuals who get the recommended regular physical activity can decrease the risk of many diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Cardiovascular endurance is most useful for long-distance sports; marathon training, long-distance running, jogging, and swimming, although, it will also be useful for everyone else and a lack of it would lead to people becoming quickly tired and out of breath. In a marathon, the person who comes first (while allowing for injury or commonly poor technique) will commonly be the person with the best cardiovascular fitness. To fully understand the definition of cardiovascular endurance, it is important to understand how a body utilizes energy to power its muscles.
Essentially, all energy in the body of every living organism comes from a substance called ‘ATP’, the ‘energy currency’ of life on Earth. ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate a name that describes the chemical composition of a substance. ATP you see is an adenine nucleotide made up of 3 phosphates attached by powerful high-energy bonds. When these bonds are broken they release energy, which a body then utilizes to power the muscles etc, and which forms the basis of the phosphagen system, powering a body for 3 seconds using the ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) stored in the muscles.
As well as giving off energy, although, the phosphagen system also has two other by-products, ADP and AMP, which stand for Adenosine Diphosphate and Adenosine Monophosphate respectively. These are the same as ATP, except that they describe adenine nucleotides with just two or one phosphates respectively. In another word, they are the 2 parts of the Adenosine triphosphate once the bonds are broken. Fortunately though the body also stores and produces another substance called Creatine in the Kidneys.
Creatine is meanwhile used by the body to recombine ADP and AMP to make new ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) that can be once again used by the body. This then supplies an additional 8 to 10 seconds of energy on top of the initial 3 seconds and could be used by the body for extended explosive exercise. Using these methods combined then the body can utilize the phosphagen system for energy for a full 13.5 seconds, making it the best type of energy for explosive movements, such as weight lifting, 100-meter sprinting, or jumping. A few athletes take a creatine supplement with the belief that it will raise that by 8-10 seconds. The definition of cardiovascular endurance does not encompass this system of energy release, as the ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) and creatine are readily accessible by the body, thus cardiovascular endurance is not necessary for sprinting.
Once the body has used up its supply of ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) and creatine, it will move on to a secondary method for energy – the glycogen lactic acid system. Here a body falls back on another substance found in a muscle, namely glycogen. As a form of carbohydrate this too can be broken down into ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) and so used for energy supplying an additional 1.5 minutes, though this system is slower than the phosphagen system and also results in another by-product named ‘lactic acid’ which can lead to the muscles to feel stiff and uncomfortable. It’s the lactic acid that creates the feeling of the ‘burn’ sought after by bodybuilders and runners while training, but it can also make it difficult to continue performing when it builds up. This is why a glycogen lactic acid system is the secondary system used.
It is only after these two systems although that the aerobic system kicks in. A definition of cardiovascular endurance then is an ability to continue exertion following the initial. At this point, a muscle must find its energy from other areas surrounding a body and then transport it to the areas it is required and this is done via the bloodstream. Here the body uses oxygen to break down energy stored in the mitochondria surrounding a body in the form of foods – either fat or protein. In this way, the body begins to ‘burn’ its fuel supplies, stored as fat and muscle, to find the energy to continue exertion.
This energy, in the form of ATP(Adenosine triphosphate) of course, is transported through the blood to the muscles resulting in the feeling of being ‘pumped’. This system could supply a body with up to two hours of additional performance, though precisely how long will depend on the fitness of the individual (that being the definition of cardiovascular endurance). While this system is fairly slow, and can eventually start to damage muscle tissue, at the same time it produces no by-products other than harmless carbon dioxide and water. It is the aerobic system that the body relies on for long-distance running such as that required for a marathon.
The aerobic system relies on many other organs and systems being in place then, and another definition of cardiovascular fitness could be to have a strong heart, high VO2 max, lung capacity, breathing control, and a healthy circulatory system. It is through these bodily systems that we can extract oxygen from the air and transport it through the blood to the relevant areas. The term VO2 max refers most particularly to the body’s maximum rate at which it can draw oxygen from the air, and can be trained via cardiovascular exercise and more specifically by training where the air is thinner – in a cold or/and at high altitudes.
A strong heart is crucial for cardiovascular fitness as it is what will pump the blood surrounding the muscles to the mitochondria and the muscles. This would be transported through the veins and the arteries that make up the ‘human circulatory system’. A healthy circulatory system can be maintained through the consumption of fiber, which travels through the veins and arteries to unclog arterial plaque, and by eating a diet low in carbohydrates and saturated fats. in between this element then is found an in-depth definition of cardiovascular endurance. By understanding the exact process that goes into cardiovascular fitness you could train every aspect separately to enhance every aspect of the performance.
How Much Cardiovascular Exercise is Good?
The American Heart Association has developed guidelines for helping or assisting adults and kids to be the healthiest versions of themselves.
It is recommended those adults (people ages eighteen and older) engage in:
- 150 hours of moderate exercise each week
- 75 minutes of vigorous exercise that exerts maximum effort each or every week
Kids, ages six and older, should aim for:
- 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity each or every week
- It is important to note, exercising more than one hour per day doesn’t seem to raise the odds of being healthier and having better cardio fitness levels.
What Are the Causes of Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
Low cardiovascular endurance can occur due to several reasons. It can happen as a complication of atherosclerosis. On another hand, it can also happen due to health conditions such as diabetes, structural problems present from birth, or an inflammatory process such as myocarditis. It could also result from high blood pressure, and usually, it shows no symptoms. Thus, people need to undergo regular screening and check-ups if they have high blood pressure.
The other leads to low cardiovascular endurance could be physical inactivity, an unhealthy diet, and excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco. In addition to that, it could also be caused by stress, poverty, and hereditary factors.
What Are the Symptoms of Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
One can understand if the person has low cardiovascular endurance if people experience the following symptoms-
- Shortness of breath
- Light-headedness and dizziness
- Nausea and fatigue
- Pain or/and pressure in the chest indicating angina
- Cold sweats
- Pain or discomfort in the left shoulder, elbows, arms, back, or the jaw
Effects of Aerobic Exercise
You can raise the level of cardiovascular endurance by doing exercises that increase the heart and breathing rates, or aerobic exercises. According to more experts, aerobic exercises are the most important part of physical fitness. To achieve cardiovascular endurance, you should exercise aerobically for 30 minutes each day, 3 to 7 days per week.
When you do aerobic exercise, the body responds in the following ways:
- The heart pumps more efficiently.
- The lungs work better.
- The blood volume and delivery system are improved.
- The resting heart rate is lowered.
- The heart pumps out more blood.
- The muscles get stronger.
- The ligaments, tendons, and bones get stronger.
- The body is additionally or more able to use fat as an energy source.
Lowered risk of disease. Aerobic exercise reduces the risk of developing many diseases, including:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Some types of cancer
- Stroke
Benefits of the Cardiovascular Endurance
As you increase your cardiovascular endurance through aerobic exercise, you will get stronger and fitter. You would also reap the following benefits:
- Better strength and stamina. The heart and lungs would get stronger as you exercise. people would also gain bone and muscle fitness. You may feel tired when you first begin exercising, but you will develop stamina over time.
- A more active immune system. You are less likely to catch viral illnesses such as colds and flu if you are a regular exerciser. The immune system is activated by aerobic exercise.
- Managed weight. Aerobic exercise, together with a healthy diet, can assist you to lose weight and keep it off.
- Stronger bones. Weight-bearing aerobic exercise, such as walking, can help decrease the risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Better mood. Aerobic exercise may assist you to relieve tension and anxiety. It may also assist you to relax and sleep better. For a few individuals, exercise is as effective as antidepressants at lessening depression.
- Staying independent longer. Exercising makes you stronger and can assist you to stay mobile longer. It could also lower the risk of falls and injuries. Fitness will improve your quality of life as you age.
- Fewer unhealthy behaviors. Time spent exercising is better than that spent smoking, drinking alcohol, or/and gambling. Exercise may also assist regulate overeating.
Examples of aerobic exercises to improve or enhance cardiovascular endurance. While there are plenty of aerobic exercises to perform to build cardiovascular endurance, the ones listed below are the most popular:
- Walking
- Jogging
- Running
- Hiking
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Stair Climbing
- Boxing
- Rowing
In addition to making you feel great on neighborhood runs or bike rides with pals, improving your cardiovascular endurance provides more health. benefits.According to experts, these benefits might include:
- Improve cardiovascular health
- Lessen the risk of 2 types of diabetes and the heart attack
- You can get a healthy sleep quality to make the day more productive
- Stress reduction
- Weight reduction (or decrease) is more straightforward (when combined with a healthy diet, of course)
- Make the bones stronger and enhance the immune system
- Performance during cardiovascular exercise is improved
- Lower blood pressure and control cholesterol levels
- Regulate blood sugar
- Aid in weight loss – when combined with the healthy diet
- Strengthen ligaments, tendons, and bones
- Improve sleep
- Strengthen the immune system
- Lower resting heart rate
- Improve mood
Almost everyone can benefit from exercise. When initiating an exercise schedule, it is best to begin simply and with something you enjoy. Whether that be walking around your neighborhood or going for a bike ride, starting with something you enjoy will assist with continuing the routine. Another benefit of cardiovascular exercise is that you don’t require a gym membership or workout equipment at the home. There are a lot of little or “no space” exercises that you can perform in the living room.
How to Increase Your Cardiovascular Endurance?
Almost everyone can benefit from physical exercise. Although, not each exercise is right for everyone. Talk to the doctor about the best type of exercise for you.
Start simple. If you are new to exercise, you might benefit from as little as 15 minutes of exercise. Work the way up to 30 minutes every day at least 3 days every week. Doing these should result in a measurable improvement in your cardiovascular endurance in eight to twelve weeks.
Pick something you enjoy. Aerobic exercise is any nonstop activity that uses large muscles and makes the heart and the lungs work harder. You can pick the one you enjoy or rotate through many various ones. A Few examples include:
- Walking
- Running
- Jogging
- Hiking
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Cross country skiing
- Aerobics
- Stair climbing
- Rowing
Physical activity is beneficial to almost everyone. Although, only some actions are appropriate for some people. Before beginning cardio, you must concern with the doctor: in the meantime, we will suggest to you how to improve your cardiovascular exercise:
- Don’t overdo it. Doing the same type of exercise more than 5 days every week puts you at a higher risk for injuries. If you want to work out more than 5 days every week, change it up with exercises that use different muscle groups. Do some low- and then some high-impact activities to avoid too much stress on the joints and the muscles, and alternate between low- and high-impact exercises.
- Start with baby steps: If you are new to exercising, you might benefit from as little as 15 minutes. Increase your time to 30 minutes daily at least three times every week. You should see a noticeable improvement in your cardiovascular endurance in eight to twelve weeks.
- Gradually work up. You should aim to push yourself slightly more than the normal movement level. Bump up the speed or distance no more than 10% to 20% every week. You shall feel challenged, but not completely exhausted. For every 10 minutes you exercise, add 1 or 2 minutes weekly for every ten minutes you work out.
- Warm up, cool down, and stretch. Start by working at a low level for five to ten minutes to warm up. Then gradually build up how hard you work until you reach the limit.
After you finish or complete working at full intensity, slow down for 5 to 10 minutes before you stop. Stretch at this point, since the muscles will be warmed up.
Tips to Improve Cardiovascular Endurance
What are the strategies for increasing endurance? According to experts, you should raise the volume (the total number of minutes of exercise you track) and intensity by doing the following:
- Increase the difficulty slowly: It is vital to gradually increase the difficulty of your exercises since your cardiovascular system adjusts to more challenging workouts more quickly than the bones, muscles, and connective tissues (think tendons and ligaments). Otherwise, you risk being hurt.
- Improve the time of the training: Just 10% you should spend more time exercising every week. If you run for 80 minutes overall this week and aim to run for 88 minutes total the following week.
- Observe the progress: You may measure the development by seeing how long you can exercise at a specific intensity. For eg, Let’s say you were able to jog on the treadmill for 20 minutes at a comfortable five mph a few weeks ago. That indicates that the endurance is improving.
Exercises to Improve Cardiovascular Endurance
- Cardiovascular endurance is required for any workout that elevates the heart rate. many sports are renowned for their emphasis on endurance. Basketball or tennis also meets the bill. According to experts, beginning small is reasonable, if not preferable, if newcomers are eager to raise their stamina and cardiovascular endurance quickly. Injuries might happen if something is overdone or done too quickly.For the first week, experts advise starting with 10-15 minutes of work. Then, progressively build up by adding 10% to 20% more distance, time, or inclination per week. Alternatively, gradually but steadily increase a length of an exercise over time. Pay attention to the body as you go, and take it easy when you require additional time to recuperate.
How is cardiovascular endurance measured?
Cardiovascular endurance is measured by how well the body can utilize a certain amount of oxygen — that is, how much oxygen you can take in during high-intensity aerobic activity, such as sprinting or swimming. There are a few various ways to measure cardiovascular endurance and aerobic fitness — a few you can do at home, and others that are more sophisticated.
To measure cardiovascular endurance, it’s important to understand the different types of heart rates and what they indicate. The resting heart rate is the heart rate when you are at rest — ideally taken right after you wake up in the morning, but at least more than two hours after exercising or any stressful event. The normal resting heart rate for an adult is 60 to 100 beats each minute. The target heart rate is the heart rate you require to achieve to give your lungs and heart a solid workout, and this varies by age. For adults approximately 55 years old, for example, the target heart rate is between 83 and 140 beats per minute. To measure the heart rate, find the pulse, either on the wrist just below the thumb, or on your neck. Press two fingers on the pulse, and count the number of beats for 15 seconds. Multiply that number by four — that is the heart rate.
How’d you do? Is the resting heart rate closer to 60 beats per minute or closer to 100? This can give you an indication of how high the cardiovascular endurance is — or, how much room you have for improvement. More sophisticated tests to measure cardiovascular endurance include or contain metabolic equivalents or METs, and maximum oxygen uptake, or VO2 max. These tests would likely be done by a sports physician or professional athlete hoping to enhance their performance.
Cardio Endurance Tests
Luckily, being breathless while running alongside a friend is not the only way to determine cardiovascular fitness levels. In this section, two specific methods that measure cardiovascular endurance would be discussed. VO2 max and METs(metabolic equivalents of task) are two types of tests that can give an accurate cardiovascular endurance level reading. Let’s see how they work.
VO2 Max Test
The VO2 max test is a machine that measures the maximum amount of oxygen being used by the body during cardiovascular exercise. This method examines how many milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight is being used by a person for every minute of exercise. In another word, how much blood is the heart pumping to a muscle and how effectively are the muscles using the oxygen they receive from the blood?
To get a VO2 max test, a few pieces of equipment are required: a mask, including a:
- Mask
- Heart rate monitor
- Stationary bike or treadmill
The machine is connected to a mask that is worn to examine the volume of oxygen inhaled and exhaled by the person exercising. The intensity of exercise is slowly raised to the point that the machine measures a steady oxygen exchange; regardless of the boost in resistance or speed of the bike or treadmill. A person’s VO2 results can vary based on age, fitness level, altitude, and gender; just such as heart rates vary from person to person.
METs Test
The METs (metabolic equivalents of task)test is another type of fitness test used to assess cardiovascular endurance. This test is a bit more straightforward than the VO2 max because less equipment is needed. Similar to the VO2 max, this test needs the use of a treadmill to measure the ratio of energy used per unit of time. In simpler terms, it records the intensity of activity over some time by measuring the amount of oxygen consumed per body weight per minute. For eg, a person who is sitting behind a computer to read this lesson is using one MET. That is four times the energy it took to sit still behind a computer. Everyone’s MET is a bit varied because age, body weight, and physical fitness are all factors that come into play.
Cardiovascular Endurance Examples
Cardiovascular endurance is the ability to exercise without becoming overly (or extremely) tired. and cardiovascular endurance examples include high-impact activities, low-impact activities, and no-impact activities. Vigorous activities, such as running, are often high-impact. While more moderate activities are generally low and have no impact.
What are some cardiovascular endurance activities?
While there are hundreds of examples of these types of activities in cardiovascular endurance, here are a few.
High-impact activities are those that are weight-bearing and put more force on the bones and the joints. These activities generally involve both feet lifting off the ground at the same time.
- Running
- Jumping rope
- Basketball
Low-impact activities put less force and jolt on the joints and the bones.
- Walking
- Yoga
- Cycling
- Activities in the water; such as water aerobics and swimming, have no force on the joints.
No impact cardio activity
- No-impact activities are activities where the feet never leave the ground; resulting in no extra weight or force being exerted on a body.
Importance of Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance is the sign of a healthy heart that is capable of pumping blood efficiently. Over time, this is important because that means less wear and tear on this important organ. Since the body’s systems work as a team, the heart requires to function well because it protects the rest of the body’s vital organs.
- Swimming
- Elliptical machine
- Water aerobics
Many types of activities can be modified to be a higher impact or lower impact. Dancing and HIIT (high-intensity interval training), for eg, can be done with more or less impact depending on whether the workout includes jumping or the feet leaving the ground.
So how can you improve cardiovascular endurance? The answer is simple: incorporate better cardio into your daily physical activity. But before you groan and stop reading, hear me out — it does not have to be all running or all joyless. I have gathered my four favorite ways to enhance cardiovascular endurance below.
Dancing
- Dancing is a great way to do a little cardio, get some sweat off, and at the same time have immense fun. Dancing is not only restricted to Zumba or/and professional dance classes; one can simply dance around in one’s room. So, instead of waiting more, one can tune in to their favorite dance playlist and dance to their heart’s content without being judged.
- One of my favorite ways to enhance cardiovascular endurance is dancing and there is no better way to get a workout in and relieve stress than busting a move. To get begun with dancing, check out the local YMCA or gym — they likely offer many different types of dance classes, from Zumba to ballroom dance to aqua dance.
- It could be difficult to push yourself enough to reach the target heart rate on your own, but a fitness instructor will make sure that you’re working muscles and getting in that perfect zone. Plus, you can attend with any person or friend, or group— a workout and social hour. Yes, please! If you do not have a gym membership or/and feel shy about dancing in front of a group, you have another resource at your fingertips — there are hundreds and hundreds of exercise or workout programs on Youtube, including dance lessons. Whatever the skill level or time commitment, there is a YouTube workout available. You can get those dance moves in and increase your cardiovascular endurance without ever leaving the comfort of your home.
Swimming
- Swimming is low-impact cardio that is efficient in improving cardiovascular endurance while also being joint-friendly. Though, if one is not completely confident in his or her swimming skills, one can grab a kickboard and try doing a few laps. This will assist him/her exercise both (or bilateral) his or her legs and abs.
- Another one of people’s favorite cardio workouts is swimming. such as dance, you can likely find tons of swim workout classes at your local gym or YMCA — or check out when lap swimming is open and do your own thing. While swimming might be less accessible than other types of cardio — it is not like you can do a YouTube swim workout in the basement — I put it at the number two spot on my list because of how fantastic it is for the heart and the lungs. The double whammy of using an entire body while also periodically holding the breath means that a good swim will push the fitness level and overall health to a max. A few studies indicate that swimming may be the best thing you can do to lower blood pressure and cholesterol and increase your cardiovascular endurance. Talk about a good workout!
- But the real reason why swimming so much is the lack of impact. Water cushions and supports the joint, making it possible to do high-intensity aerobic activity or workout or exercise without the impact of running, dancing, or any other type of cardio. For those of us aging out of our marathon days, cardio does not get much better than swimming.
High-intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
- There is no resource more (or additional) valuable than time, which probably explains the explosive popularity of high-intensity interval training or HIIT. High-intensity Interval Training or HIIT packs the best workout in the least amount of time by alternating between high-intensity cardio and low-intensity cardio (hence, “interval training”).
- For example, you might run three miles, with a one-minute sprint for each half mile. Or you might do a thirty-minute dance workout, with one minute of burpees every six minutes. A combination of endurance and bursts of high-intensity exercises pushes the heart and the lungs to the max and it is scientifically proven to enhance your aerobic capacity, burn fat, and improve your overall fitness level.
Resting the Heart Rate: An Indicator of Cardiovascular Endurance
- The resting heart rate (RHR) is both a reliable indicator of cardiovascular endurance and the baseline measure for monitoring your aerobic workouts. An untrained person has a resting heart rate or RHR of approximately 70 beats per minute (bpm). A healthy goal is around 65 bpm. Try measuring the resting heart rate on three separate occasions; multiple attempts minimize any impact of nervousness or technique. If you discover a resting heart rate above 80 bpm, see a physician before beginning a cardiovascular training program.
- Your resting heart rate can be determined by taking the pulse (radial or carotid) first thing in the morning before you get out of bed, generally after a good night’s sleep. Count beats for thirty seconds and multiply by two to determine beats every minute. Repeat the process over many days, and take the average as your true resting heart rate. Check for accuracy by comparing the count to a heart rate monitor or by having a partner count, too; have him or her count the radial while you count a carotid pulse, and see if you get an equal result.
The FITT Principles
Once you know your RHR(resting heart rate), it’s time to build an aerobic exercise regimen. An effective workout is a balance between the FITT(frequency, intensity, type, and time). FITT principles will help you manage the fitness plan but always listen to the body to achieve an appropriate balance. An aerobic training program is supposed to reduce stress levels, not increase them.
Frequency
- The American College of Sports Medicine currently recommends that healthy adults participate in moderate aerobic exercise 30 minutes per day, five days per week, or vigorous cardio exercise 20 minutes per day, three days every week. Follow these guidelines, and you should begin feeling the results within the first few days. Unfortunately, detraining also happens fast, so it is important to make sure there are no more than two days of rest between cardio workouts. However these guidelines are ideal, remember that any exercise is good than no exercise or no workouts. If you can squeeze in even 5-10 minutes, it will assist to maintain your current fitness level.
Intensity
- Cardiovascular endurance enhances when you exercise in an aerobic training zone that raises your heart rate to somewhere between 60 and 80 percent of your maximum heart rate. To find your MHR(maximum heart rate). Your true maximum heart rate should fall within 12 beats above or below this number.
- Then use these formulas to find the upper limit of the range and lower limit of the range:
- Aerobic Training Zone
((MHR(Maximum Heart Rate) – RHR(Resting Heart Rate)) × .60) + RHR(Resting Heart Rate) = Lower Limit of Range
((MHR(Maximum Heart Rate) – RHR(Resting Heart Rate)) × .85)+ RHR(Resting Heart Rate) = Upper Limit of Range
- A table of the RPE Scale
Shorter workouts will be closer to the upper limit of the range, while longer workouts will be closer to the lower limit of the range.
Interval training, which alternates bursts of vigorous (or strong)and moderate intensity, has a greater impact in a shorter time. Use the low-intensity range for a warm-up, then begin with the 1:1 work/rest ratio. For eg: Follow thirty seconds of the activity with 30 seconds of recovery. There are countless variations of intensity levels depending on the duration of the workout, work/rest ratios, and where you want to be within the lower limits or upper limits of every training zone.
The Borg Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) is one way to measure the intensity. It is a 15-point scale based on heart rate; add a 0 to the right of the rating to find the heart rate. A rating of six should correspond to 60 bpm, while a rating of 20 should correspond to 200 bpm. You can also monitor the heart rate during exercise by using a basic heart rate monitor or by taking the pulse for 15 seconds and multiplying it by four to get beats per minute.
Type
- Common aerobic activities include walking, swimming, jogging, cycling, and stair climbing, but it doesn’t matter what type of exercise you choose as long as you stay in the training zone. Choose aerobic activities that you enjoy and can realistically fit into your everyday routine. Consider combining activities to alleviate boredom, work for various muscle groups and avoid overuse injuries. Strength training can also meet cardiovascular requirements if you minimize or eliminate the waiting time between exercises and keep the heart rate elevated. The push-pull structure of the strength training workouts in the last 3 “Dive Fitness” columns allows you to improve cardiovascular endurance while improving muscle strength.
Time
- Time is the duration of a given workout. Your goal should be a minimum of thirty minutes in your target range (20 minutes for interval training) for each workout. If you are maintaining trouble reaching that at first, take baby steps. Start with accumulating 30 minutes in the target range over each day; try 10 minutes before breakfast, 10 minutes before lunch, and 10 minutes before dinner. Keep the heart rate up for a little while today and a little longer tomorrow or the next day.
- Once you have established or specified an aerobic workout routine, stick with it. If time is tight, shorten the workout but improve the intensity. If you are tired before you begin, plan for a less intense workout, but extend the time.
- Above all, be realistic with the goals, and remember this is a program for life.
Why does Cardiovascular Endurance matter?
Having high cardiovascular endurance means you can perform strenuous activities or workouts for longer periods. This is important not just in the gym, but for performing everyday tasks in everyday life. Improving cardiovascular endurance has a positive impact on overall health and fitness. Focusing on enhancing cardiovascular endurance can also help maintain healthy body composition, due to performing higher levels of aerobic activity. Additionally, you may experience improved sleep, reduced stress, and an improved immune system.
The good news is that cardiovascular endurance can be increased with small changes to everyday movement and exercise.
Why is cardiovascular fitness important?
Cardiovascular fitness benefits us in a variety of various ways; two of the biggest of which are health and sports performance.
Health
Higher levels of cardiovascular fitness are associated with improved health across a wide range (or broad range) of markers. A 2009 meta-analysis (Kodama et al.) reviewed results from 33 studies and a total of over 100’000 individuals to find that better levels of cardiovascular fitness are strongly associated with lower all- leads to mortality. In other words, being fitter makes you less likely to die of essentially each natural cause or reason! That includes…
- Peripheral artery disease
- Blood clots
- Congestive heart failure
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Arterial blockage
- Ischemia
- Coronary artery disease
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Insulin resistance syndrome
- Angina
- Cardiac Arrhythmia
- Sport & Performance
Another major benefit of cardiovascular fitness is its impact on sports performance.
Many sports need a significant base of cardiovascular fitness to perform at a good or even half-decent level. Then we have to consider that there are sports like running, swimming, and cycling in which cardiovascular fitness is more or less a main determining factor for success.
What is the best exercise for cardiovascular fitness?
There is no single ‘best’ exercise or workout for cardiovascular fitness. Cardiovascular exercise is simply any vigorous activity that raises heart rate and respiration and raises oxygen and improves blood flow throughout the body.
For most individuals, the ‘best’ exercise is simply the exercise that they enjoy doing regularly and can see themselves consistently doing for many months or years. It is also totally fine to mix and match cardio exercises based on your changing interests.
Examples of cardiovascular fitness
Right at the top of our list, we have the most generally thought of cardio exercise examples…
- Running
- Swimming
- Cycling
All of which are fantastic options.
Although, there are loads of other great cardio options for us to explore.
- Rowing
- Skiing or ski-erg machine
- Cross-trainer machine
- Power walking
Plus what about exercise classes
- Zumba
- Boxing
HIIT and circuits
Or, if none of those seem such a thing, you might also be interested to know that resistance training of high enough intensity has also been shown to enhance cardiovascular fitness. So you can include…
- Bodybuilding
- Strength training
- Crossfit
You are not going to magically be able to run a marathon or/and complete an iron-man triathlon with these resistance training approaches, but they would improve cardiovascular fitness far beyond that of sedentary people.
How to test cardiovascular fitness?
There are hundreds of various ways to test cardiovascular fitness.
Most typically, maximum oxygen uptake (VO2 max) is tested, as it forms a major component of cardiovascular fitness. For best results, this type of test is conducted in a sports science lab setting. Although, for most fit and healthy individuals we can use gym and field-based submaximal tests to estimate VO2 max with a good degree of accuracy. Common tests include…
- The Astrand treadmill test
- The 2.4 km run test
- The Yo-yo intermittent recovery test
For the sedentary person who cannot manage these tests, we might use something like the Cooper 1.5-mile walk-run test. It is not quite as good of an estimator as the above tests, but it’s still accurate enough to be a useful test.
Alternatively, a more practical measure of cardiovascular fitness would simply be to track the performance in exercises and types of sessions that are relevant to the goals and interests. A simple example might be…
If you are a runner, how fast can you run 5k? If you run it in 30 minutes today and then run it in 25 minutes in a few months, you can be pretty sure that your cardiovascular fitness has improved.
What Are the Best Exercises to Recover from Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
Here are the best exercises for cardiovascular endurance which can assist one to increase his or her heart health.
Power Walk
- Power walking refers to walking briskly and it is a popular form of exercise to help recover from low cardiovascular endurance. One could start by simply stepping outside of one’s house and picking up the pace while walking. One could opt for a treadmill if the weather is bad or/and one does not have a suitable place to power walk.
Regular Walk
- If anyone is wondering whether he or she can begin with this simple exercise, the answer is, of course! that is a great option for beginners who are just beginning their fitness routines. A ten-minute walk too can contribute to enhanced heart health.
Jump Rope
- Jump rope is another easy cardio exercise that one can do just anywhere. People can jump to the beats of their favorite songs by turning up a playlist while doing this form of cardio. One can just toss his or her jump rope in a purse, backpack, or suitcase and be able to perform his or her 150 minutes of exercise every week anywhere, whenever he or she gets a little spare time.
Running
- Running is one of the best or more useful exercises for cardiovascular endurance. and Running is equipment-free cardio which is great for burning a lot of sweat and also building endurance. Moreover, as compared to walking, running could burn more calories. Though, running is additionally strenuous and has a high impact. Therefore, it has a high chance of causing injury to the legs. So, one should be alert while running and only carry out these exercises as long as one’s body permits.
HIIT or Bootcamp
- For someone with a shorter time but in good shape, this cardio exercise might interest you. Although, this is a vigorous exercise that involves boot camp-style workouts and High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). These exercises include full-body workouts such as jumping rope and push-ups, which are great for boosting one’s heart rate.
Organized Sports
- One requirement is not to be a sports person or/and even think of oneself as one. There are plenty of adult sports leagues that are filled with individuals who just want to have fun and be healthy. One could sign up for basketball, football, soccer, or something that interests him/her. Running around a court or field is sure to make one’s heartbeat raise, thereby assisting in overcoming low cardiovascular endurance.
Dance
dance also exercise
- Dancing is a great way to do a little cardio, get some sweat off, and at the same time have immense fun. Dancing is not only restricted to Zumba or/and professional dance classes; one can simply dance around in one’s room. So, instead of waiting more, one can tune in to their favorite dance playlist and dance to their heart’s content without being judged.
- One of my favorite ways to enhance cardiovascular endurance is dancing and there is no better way to get a workout in and relieve stress than busting a move. To get begun with dancing, check out the local YMCA or gym — they likely offer many different types of dance classes, from Zumba to ballroom dance to aqua dance.
- It could be difficult to push yourself enough to reach the target heart rate on your own, but a fitness instructor will make sure that you’re working muscles and getting in that perfect zone. Plus, you can attend with any person or friend, or group— a workout and social hour. Yes, please! If you do not have a gym membership or/and feel shy about dancing in front of a group, you have another resource at your fingertips — there are hundreds and hundreds of exercise or workout programs on Youtube, including dance lessons. Whatever the skill level or time commitment, there is a YouTube workout available. You can get those dance moves in and increase your cardiovascular endurance without ever leaving the comfort of your home.
Swimming
swimming exercise

- Swimming is low-impact cardio that is efficient in improving cardiovascular endurance while also being joint-friendly. Though, if one is not completely confident in his or her swimming skills, one can grab a kickboard and try doing a few laps. This will assist him/her exercise both (or bilateral) his or her legs and abs.
- Another one of people’s favorite cardio workouts is swimming. such as dance, you can likely find tons of swim workout classes at your local gym or YMCA — or check out when lap swimming is open and do your own thing. While swimming might be less accessible than other types of cardio — it is not like you can do a YouTube swim workout in the basement — I put it at the number two spot on my list because of how fantastic it is for the heart and the lungs. The double whammy of using an entire body while also periodically holding the breath means that a good swim will push the fitness level and overall health to a max. A few studies indicate that swimming may be the best thing you can do to lower blood pressure and cholesterol and increase your cardiovascular endurance. Talk about a good workout!
- But the real reason why swimming so much is the lack of impact. Water cushions and supports the joint, making it possible to do high-intensity aerobic activity or workout or exercise without the impact of running, dancing, or any other type of cardio. For those of us aging out of our marathon days, cardio does not get much better than swimming.
Cycling
cycling exercise

- One can fit cycling into his or her day as a form of cardio in many ways. people can choose to cycle to the grocery store instead of taking a car or motorcycle. people can also choose the stationary bike in the gym for cardio instead of walking on the treadmill. One could also learn to cycle and ride it on the house’s lawns or in a garage.
Hula-Hooping
- Someone wondering if Hula-Hooping is an inappropriate thing to do as an adult and probably did it when people were younger is wrong. It is a fun activity and also available in adult sizes which can assist one to unleash his or her inner kid. Just swinging the hips around raise the heart rate and improves core strength.
Stairs
stairs climbing
- Climbing up and down the stairs is a great way to begin sweating and raise the heart’s pumping. This is also a very convenient way to do cardio because stairs are just present everyplace or everywhere. However, one must also remember to stay safe while climbing up and climbing down the stairs as one might slip and fall and even get fractures.
Jumping Jacks
Jumping jacks are another great home exercise for cardiovascular endurance since it needs no equipment. One could do this activity anywhere, anytime, and it could get one’s heart rate up in a very short period. One could do it anytime, be it early in the morning after waking up or while waiting for lunch to get ready.
- Start by standing upright with the legs together and arms at the sides of the body.
- Jump up. While in the air, open the legs to spread the feet wide apart and extend the arms overhead.
- While landing, bring the feet and the arms back to the starting position.
Burpees
Burpees are another high-intensity full-body workouts it can get the heart pumping faster in no time. The burpee exercise focuses on building muscle strength and improving cardiovascular and lower and upper body endurance. That strengthens one’s legs, abdomen, arms, chest, hips, buttocks, and shoulders.
- Begin standing with the feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend the knees and place the hands on the floor in front to come down into the squat position.
- Jump the legs out behind to get into a push-up position, shifting the body’s weight onto the hand.
- Jump the feet back into a squatting position.
- Jump up into the air with arms extended above the head.
- Land back in the squat position.
13 Cardiovascular Endurance Exercises To Do At The Home
Is it possible to do cardiovascular endurance exercises at a home and get the same results as going to the gym? Well, it certainly is. Cardio is not about where you do an exercise; instead, it is all about how you do it.
The key to any successful workout session at the home is thinking outside the box. All you have to do is find an exercise that you like, and fun will come with it. Also, you will be improving your health while you are at it. Here are a few cardiovascular endurance exercises examples you can do at home:
High Knees
If you have been wondering what exercises gain cardiovascular endurance in beginners, this is it. See, the high knees are all about running in the place. You can therefore do it at home with much relief while reaping similar benefits to the person running outside. Here are steps you could follow for a successful high knee workout session:
- Put the arms at your sides while standing with the legs together.
- Lift a knee toward the chest, then lower the leg. Next, switch to the other knee.
- Continue alternating the knees and pump the arms up and the arms down.
Butt Kicks
Only put, the butt kicks are opposites of the high knees. In but kicks, you do not lift the knees. Although, you raise your heels toward your butt. Here are a few steps you can follow when doing butt kicks:
- Out the arms, at the sides, while standing with the legs together.
- Lift one heel toward the butt while lowering the other. Repeat this with the other heel.
- Continue this motion while alternating the meals and pumping the arms for a successful session.
Toe Taps
Being new to a workout routine could be confusing. It is okay to ask yourself questions from time to time about how to go about an exercise. In this case, you are probably wondering what exercises would improve cardiovascular endurance for beginners without taking a toll on you.
Toe taps may be just the thing that you are looking for. These exercises are easy, low-impact workouts that you could do on a curb or the lowest step of a staircase. Interesting right? Here’s how to get started:
- Stand in front of a step or curb. Rest one of the feet on top of it, with the toes facing downward.
- Switch the legs, bringing the other foot on top of the step in one quick motion. Continue changing the feet such as this throughout the movement.
- Try moving left or right during the toe taps once you begin getting used to a movement. Doing this will add an extra challenge to the workout.
Jumping Jacks
Jumping jacks are another great home exercise for cardiovascular endurance since it needs no equipment. One could do this activity anywhere, anytime, and it could get one’s heart rate up in a very short period. One could do it anytime, be it early in the morning after waking up or while waiting for lunch to get ready. If you are looking for a full-body workout, then jumping jacks are your go-to exercise. This is a classic exercise that would get the heart rate revved up while working on the entire body. Here are a few guidelines to get you started:
- Put your arms at the sides and make sure you are standing with the legs together.
- Bend the knees moderately, then jump while spreading the legs. It is important to note that the legs should be wider than the shoulder width during these movements. Also, you should lift your arms over the head.
- Finally, jump to the center and repeat.
Speed Skaters
As the name suggests, Speed skaters’ exercise is all about imitating how skaters move. You can add a jump when you move to the sides for a few more challenges. Here the point is how you can get begun:
- Your starting position should be a curtsy lunge. That means that both knees should be bent and the right leg positioned diagonally behind you. You should also bend the right arm and keep the left arm straightened.
- Next, push the left leg and move the right leg forward. Follow this by switching arms while bringing the left leg diagonally behind you.
- Continue alternating these movements between the right sides and left sides for the needed number of reps.
Crab Walks
If you want to have fun while getting the blood flowing, then this is it. Also, crab walks will work on your back, core, and legs while strengthening your upper arms. To do a crab walk:
- Bend the knees and put the feet flat while sitting on the floor. Next, put the hands on the floor, under the shoulder, with the fingers pointing forward.
- Carry the hips off the floor. Start “walking” backward using the arms and legs. Make sure the weight is evenly distributed between the legs and the arms.
- Walk backward for the target distance. Simple, right?
Oblique Crunch
Oblique Crunch is one of the most ideal low-impact cardio exercises for beginners. If you are a novice and you are wondering what exercises can assist with cardiovascular endurance, then you should try this workout.
When you lift the knees, you engage the core muscles of the sides. Here are a few steps that steps you should follow:
- Your starting position should be lying on the back with the knees bent. Put the hand on the back of the head, making sure the elbows are pointing outward.
- Bending to the right, move the right elbow down and the right knee up.
- Go back to the starting position and repeat the process on the left side.
Lateral Shuffles
Lateral shuffles are a few of the best exercises to enhance cardiovascular endurance for both beginners and pros. They are a sure way of raising the heart rate and improving your side-to-side coordination. To do lateral shuffles:
- Get into the starting position- feet hip-width apart with the knee and the hips bent. Next, brace the core while leaning forward slightly.
- You should then lift the right foot while pushing off the left foot. Follow this by moving right while maintaining the form.
- Place the feet together while shuffling to the right.
- Repeat these steps to the left side for the needed number of reps.
- It is also important to note that you should aim to work both(or bilateral)sides evenly. To do this, shuffle the right side and left side for the same amount of space.
With time, you would build up endurance and strength. When this occurs, try adding these intermediate moves to bump up the intensity of the workouts.
Lunge Jumps
Lunge jumps are a few of the best aerobic exercises to improve cardiovascular endurance for intermediate trainees. These routines are a combination of jumps and standard lunges that would get the heart pumping. Here is how you do them:
- Bend both knees to 90 degrees to get you into the starting lung position. and Make sure the feet are pointing forward.
- Pull the shoulders down while bracing the core and swinging the arms back.
- Next, jump and swing the arms upward while simultaneously switching the legs.
- Land in a lung and repeat for the needed number of reps.
Standing Alternating Toe Touches
This is an excellent full-body cardio routine that will work the arms, core, and legs. Here is how you get started:
- Get into the starting position- feet shoulder-width apart and arms at the sides. Next, brace the core.
- Lift the right leg up and concurrently raise the left hand, reaching for the right toes.
- Repeat this on the left leg and is suitable for the needed number of reps.
Squat Jumps
Squat jumps are high up a cardiovascular endurance exercises list and for a good reason too. When you do a regular squat, you are performing a bodyweight exercise that targets the lower body. Adding a jump to the routine creates an explosive cardio workout that gets the heart pumping hard and fast. Here is how you start doing the squat jump:
- Get into the starting position- feet shoulder-width apart. Next, bend the knees and lower yourself into a squat.
- Swing the arms back and follow this with a quick upward swing of the arms and the jump.
- Gently land back into a squat and repeat for the needed number of reps.
Box Jumps
You have been doing cardio exercises for a while now, and things are getting monotonous. You are now wondering what exercises enhance cardiovascular endurance for intermediate trainees. You require the extra challenge. Well, box jumps can assist you to achieve this.
This exercise primarily targets the lower body muscles. This includes the glute, the thigh, the calf, and the shin muscles. To do a box jump:
- Stand in front of the knee-high platform or box. Next, place the arms at the sides and the feet hip-width apart. Ensure that you are engaging a core.
- Hinge forward (or ahead) at the hips while bending the knees. the back should be flat during this process. Swing the arms up while jumping explosively onto the box.
- Land gently and slightly lean forward. Jump back off the box and repeat for the needed number of reps.
Planks Jacks
Have you ever thought of what a horizontal jumping jack will look like? Hint: Plank jacks. This routine forces the arms to support the body weight as you rapidly move the legs. Here is how to safely do the plank jack:
- Get into a plank position- hands under the shoulder while keeping the body straight. Next, bring the feet together.
- Now jump while spreading the legs wider than the shoulder width.
- Jump back into a plank and repeat for the needed number of reps.
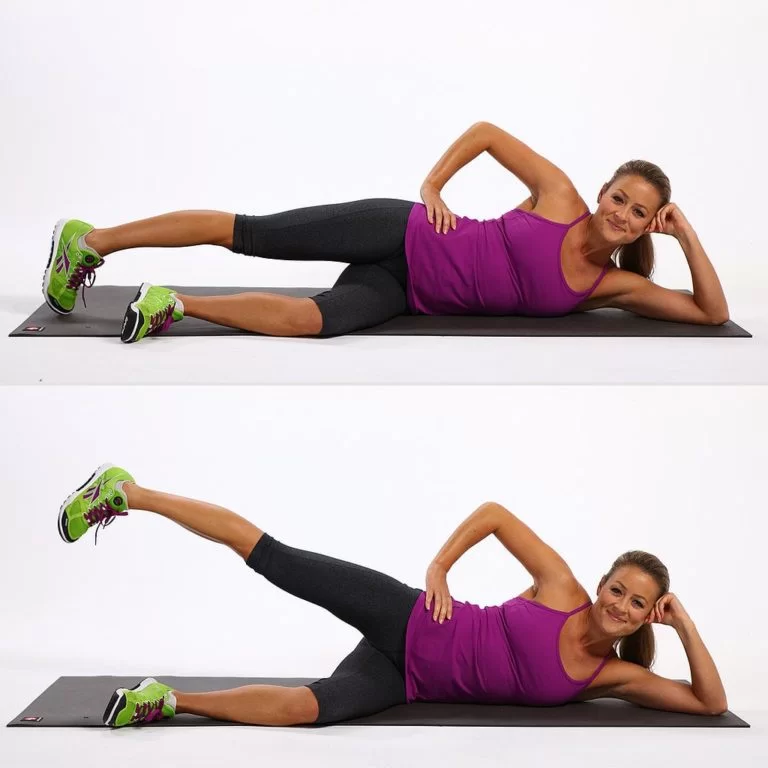
Best Cardiovascular Endurance Exercises for Women
Finding the exercise you enjoy is essential to sticking with any training routine. With a few enjoyable cardio activities or workouts, think outside the box, and give something new a try. Women can improve their cardiovascular endurance with these five workouts:
Jumping Jack
One can do jumping jacks essentially anywhere to strengthen cardiovascular endurance. Jumping jacks are another great home exercise for cardiovascular endurance since it needs no equipment. One could do this activity anywhere, anytime, and it could get one’s heart rate up in a very short period. One could do it anytime, be it early in the morning after waking up or while waiting for lunch to get ready. If you are looking for a full-body workout, then jumping jacks are your go-to exercise. This is a classic exercise that would get the heart rate revved up while working on the entire body. Here are a few guidelines to get you started.
Here is how to do it:
- Put your arms at the sides and make sure you are standing with the legs together.
- Bend the knees moderately, then jump while spreading the legs. It is important to note that the legs should be wider than the shoulder width during these movements. Also, you should lift your arms over the head.
- Finally, jump to the center and repeat.
Squat Jump
Squat jumps are an effective way to up cardiovascular endurance while exercising the glutes, the quads, the hamstrings, and the calves.
Here is how to do it:
- Stand with the arms at the sides and the feet hip-width apart. To squat, bend at the knees. Jump into the air while even in the squat stance, extending the hips till the body is straight. Rolling backward to absorb the stress in the heels, lightly land on the balls of the feet. To alter the difficulty, repeat utilizing different arm motions.
Screamer Lunge
Screamer lunges work up cardiovascular endurance while strengthening your legs.
Here’s how to do it:
- Keep your legs hip-width apart when you stand. Keep the right leg extended (or raised) back into a lunge. Lifting the right side of the knee to a hip height while jumping through the air, push it off with the right foot. Complete 10 lunges on one side, commencing with a right foot in the starting posture. Continue with the left leg.
Mountain Climber
Mountain climbing is a challenging exercise that targets the entire body, particularly the bottom part, and builds up your cardiovascular endurance.
Here’s how to do it:
- Start with the push-up position, extending the right leg back and placing the left leg close to the chest with the toes on the floor. Quickly change the leg position while maintaining the hands on the floor and hips level. Repeat by alternating sides.
Inchworm
A full-body exercise, the inchworm promotes mobility, improves cardiovascular endurance, and boosts shoulder strength.
Here’s how to do it:
- In starting with a standing posture, briefly touch the toes before walking the arms out to a push-up position. Performing a push-up, move the feet towards the hands, and lift the hips like you would in the downward dog position. To recover to the push-up posture, walk the hands out as near the feet as you could while still keeping balance.
How Does Exercising Help Relieve Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
A sedentary lifestyle, along with other risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, and abnormal values for blood lipids, is a major contributor to low cardiovascular endurance. Thus, if one does not take the necessary steps to decrease these factors, the chances of having a heart attack or any other cardiac event like a stroke can improve. Regular exercise, although, has shown favorable effects on established risk factors for these diseases.
For example, cardiovascular fitness exercise helps decrease blood pressure and promotes weight reduction. It can also decrease bad cholesterol levels in the blood, raise good cholesterol levels and impact total cholesterol levels.
Patients who have diabetes should regularly exercise as it favorably affects the body’s ability to control glucose levels in the blood by using insulin properly. however, the effect of exercise is small on a single risk, the effect of moderate and continued exercise is impactful on overall cardiovascular health. Apart from that, one also requires to make necessary lifestyle modifications such as decreasing smoking, proper medication uses, and proper nutrition to improve cardiovascular endurance to the maximum.
Which Exercises to Avoid for Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
To enhance cardiovascular endurance, one should also know about the exercises which negatively impact it. People who are already suffering from any existing heart condition should follow certain safety precautions. They should not begin any new exercise program without a doctor’s consultation.
Moreover, they should start with short-duration and low-intensity exercises to see how much they can do. Overdoing any exercise would be harmful to one’s health and could lead to serious medical hazards. If one feels any discomfort, shortness of breath, chest heaviness, or giddiness, one should immediately (or instantly) stop exercising and consult a doctor instead.
What are Precautions to Be Taken While Exercising With Low Cardiovascular Endurance?
The precautions that one should be taken while exercising with low cardiovascular endurance are-
- One should wait for at least ninety minutes after eating the meals and then start or participate in aerobic exercise.
- Focusing on warm-up and cool-down is important.
- One must remember to take enough rest while doing exercise. Although laying down after the exercises might decrease one’s tolerance. Thus, it is best to rest by sitting.
- People having low cardiovascular endurance should not overdo any exercise. They should remember to gradually improve their exercise levels with time at a steady pace.
- One should not exercise if people are sick. Instead, the person should wait for it to heal and then return to the exercise routine.
- People should schedule exercise as a part of their daily routine. One can try planning to exercise at a similar time every day and build a habit of exercising.
- In conclusion, these are all about exercises for cardiovascular endurance. Along with a proper exercise routine, a maintained lifestyle, and good food habits, one can strengthen his or her cardiovascular endurance. Though, those who are already having low endurance should first consult a doctor before starting any routine.
Conclusion
Maintaining cardiovascular endurance is essential, no matter where you are in the fitness journey. Building it and tracking the progress can be done by yourself or with the assistance of a professional. Aside from lowering the risk of certain diseases, exercise also assists improve the heart and lungs. As a result, improving endurance will improve the effectiveness of your exercise regimen and keep your body in good condition.
Working out is an important aspect of leading a healthy or good lifestyle. Although, in modern life, each one always seems to be running on a tight schedule. This has, in turn, necessitated the requirement for a more flexible and convenient approach to working out.
Cardio exercises are great for your health- both on a mental level and a physical level. Although, you do not always have to hit the gym or go outdoors to get a little cardio. All you require is a bit of creativity to begin working out in the comfort of the house. and so make sure you try out these workouts today.
DISCLAIMER
This article is intended or purposeful for your general informational purposes only and does not address particular circumstances. it is not a substitute for professional advice(or guidance) or help( or assistance) and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. A few or any actions you take upon the information presented in this article are strictly at your own risk and responsibility.
FAQs
What is the meaning of cardiovascular endurance?
Cardiovascular endurance is a measure of how well you can do exercises that involve the whole body at moderate to high intensity for an extended time. Enhancing cardiovascular endurance can make it easier for you to carry out your daily tasks.
Which is for cardiovascular endurance?
Cardiovascular endurance is the ability to exercise without becoming overly tired because the heart, the lungs, and the blood vessels are healthy. Exercise eg, includes walking, jogging, cycling, dancing, running, and bike riding. Distance swimming is also a better cardiovascular endurance exercise.
What are 4 examples of cardiovascular endurance?
Forms of exercise that depend on cardiorespiratory endurance include vigorous or strong distance running, cycling, and swimming. This fitness component also affects a person’s ability to perform or act, without undue fatigue, less intense, sustained whole-body activities, such as brisk walking, stair climbing, and home chores.
What is called cardiovascular?
The heart pumps blood to the body via a network of arteries and veins (blood vessels). The circulatory system could also be defined as the cardiovascular system. Cardio means a heart, and vascular refers to blood vessels. The circulatory system supplies blood to all the body’s tissues so they can function.
Why is cardiovascular endurance important?
Endurance activity maintains the heart, lungs, and circulatory system healthy and improves overall fitness. As a result, individuals who get the recommended regular physical activity can decrease the risk of many diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Is cardiovascular endurance a fitness?
What Are the Components of Physical Fitness? : The 5 components of physical fitness are cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition, according to Fit Day.
What are the types of endurance?
What types of endurance are there? The types of endurance are anaerobic endurance, aerobic endurance, speed endurance, and strength endurance. The sound basis of aerobic endurance is essential for all events.
What are the benefits of endurance?
Endurance activities often referred to as aerobic, improve your breathing and heart rates. These activities help keep you healthy, improve your fitness, and assist you to perform the tasks you require to do every day. Endurance exercises enhance the health of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system.
How can I improve my cardiovascular?
Aerobic Exercise
What it does: Aerobic exercise enhances circulation, which results in lowered blood pressure and heart rate, Stewart says. …
How much: Ideally, at least 30 minutes a day, at least five days per week.
Eg, Brisk walking, running, swimming, cycling, playing tennis, and jumping rope.
Is cardiovascular endurance stamina?
When people talk about stamina, they usually use it to refer to the feeling of being peppy or energetic while doing an activity. Endurance refers to the body’s physical capability to sustain (or maintain) an exercise for an extended period. It is made up of 2 components: the cardiovascular endurance and muscular endurance.
Why is it called cardiovascular exercise?
“Aerobic” means “needs oxygen.” Aerobic exercise utilizes a continuous supply of oxygen during exercise while burning both fat and carbohydrates for energy. It gets the heart rate up for longer periods. That is why it is commonly called “cardio.”
What are the two types of cardiovascular endurance?
Cardio training improves the function, capacity, and health of the heart and the lungs. There are two types of cardio training: aerobic and anaerobic.
What are the 5 activities for cardiovascular endurance?
Activities like walking, jogging, running, cycling, swimming, aerobics, rowing, stair climbing, hiking, cross-country skiing, and several types of dancing are “pure” aerobic activities. Sports such as soccer, basketball, squash, and tennis may also enhance your cardiovascular fitness.
What are 3 exercises that improve cardiovascular endurance?
Examples: Brisk walking, cycling, running, swimming, playing tennis, and jumping rope. Heart-pumping aerobic exercise is the kind those doctors have in mind when they recommend at least 150 minutes every week of moderate activity.
What are the two types of endurance exercises?
There are mainly two types of endurance training: specific endurance and general endurance. Specific endurance means that you focus on enhancing one particular exercise whereas general endurance means that you improve your overall performance with different types of exercises.
How can I improve my cardio for beginners?
Cardio Workouts for Beginners
Walk and Climb. A few beginner physical activities include walking on the spot while watching TV for 30 minutes, or climbing the stairs to your flat at a moderate pace.
(House)work it Out.
Skipping.
Jumping Jacks.
Jogging on the Spot.
Which cardio burns the fattest?
Running is the winner for the most calories burned each hour. Stationary bicycling, jogging, and swimming are amazing options as well. HIIT exercises are also amazing for burning calories.
Is Plank a cardiovascular exercise?
Planks are known for their core-crushing abilities. Holding one would make anyone’s abs tremble after a while. But a few plank variations have another not-so-obvious superpower: Any moving plank will get your heart rate pumping, letting you sneak some cardio into your abs workout.
What foods increase cardio?
6 foods to help boost your cardio
Apples. It’s crunch time. …
Avocado. The sodium, potassium, and magnesium found in the creamy fruit enhanced lung volume and oxygen flow in a study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology. …
Marmite. …
Champagne. …
Steak.
How much cardio do I need daily?
For most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends these type of exercise guidelines: Aerobic activity. Get at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity per week, or/and a combination of moderate and vigorous activity.
How do you do cardio with a weak heart?
Choose an aerobic activity such as swimming, walking, light jogging, or biking. Do this at least 3 to 4 times per week. Always do 5 minutes of stretching or moving around to warm up the muscles and heart before exercising. Allow time to cool down after exercise or workouts.
Is squats a cardio exercise?
Squats are typically seen as strength training. They are resistance exercise a builds muscle and strength in the lower body. Although depending on how you execute them, they can also emulate the cardiovascular benefits that are typical to cardio, so they can overlap between the two fitness types.
What happens if you do too much cardio?
Too much cardio makes you lose muscle mass and this makes the metabolism slow. As a result, the fat-burning mechanism in the body slows down. Thus, the weight-loss results won’t be as quick as they used to be. This is generally because the body has not recovered from the previous day’s workout involving excess cardio
When should I stop cardio?
8 Signs You’re Doing Too Much Cardio
YOU’RE ALWAYS SORE. …
YOUR JOINTS HURT. …
YOUR ‘EASY’ DAYS ARE BECOMING HARD. …
YOU DO NOT WANT TO WORK OUT ANYMORE. …
YOU’RE NOT SLEEPING WELL AT NIGHT. …
YOU’RE CONSTANTLY FEELING DRAINED OF ENERGY. …
YOU’RE FALLING SICK MORE OFTEN. …
YOU’RE LOSING MUSCLE NOT FAT.
Can too much cardio age you?
After prolonged exercise, such as a 25-mile run, the body changes its metabolism, with a resulting raise in free radicals, atoms that can cause permanent damage to the cells and can also speed up the aging process.
Does cardio burn fat or muscle?
Cardio, an aerobic exercise, is a great tool to use to burn calories. Due to this caloric expenditure, cardio is generally associated with the loss of body fat as well as muscle mass.
Why you should not do cardio every day?
If you only do one kind of exercise, every day, you put the body at risk of overuse injuries. Cardio is a major culprit of this because movements such as running and jumping put so much pressure on the joints. Injuring yourself out of your workout routine will be a setback to your weight-loss goals.
What is an unhealthy amount of cardio?
You should cap the cardio at no more than 3-4 sessions a week and no longer than 20-25 minutes each session, no matter the intensity




6 Comments