What is the Cause of the Joint Pain?
Joints are essential parts of the body that assist limbs to move. If a person feels pain in the joints, called arthralgia, it can be irritated and affect their ability to participate in activities of daily living.
What is joint pain?
Joint pain is common and Mostly felt in the hands, feet, hips, knees, or spine. Pain may be continuous or it can come and go. Occasionally the joint can feel stuffy, achy, or sore. Some patients complain of a burning, beating, or “grating” sensation. In addition, the joint can feel stiff in the early morning but loosen up and feel better with exercise and movement. However, excessive activity could exacerbate the pain exacerbated.
Joint pain may involve the function of the joint and can alter a person’s ability to do necessary tasks. Severe joint pain can impact the quality of life. Therapy should concentrate not only on pain but also on the affected movements and functions.
Who is more likely to experience joint pain?
Joint pain tends to affect those who:
- Have had past injuries to a joint
- Frequently use and/or overuse a muscle
- Suffering from arthritis or other chronic medical illnesses
- Suffer from depression, anxiety, and/or stress
- overweight
- Suffer from poor health
Getting older is another factor in tight and painful joints. After years of use, and wear and tear on joints, difficulties may arise in middle-aged or older adults.
What causes joint pain?
These are the primary causes of chronic joint pain:
Joint pain is very common, especially as you grow up. In one national survey, about one-third of grown-ups conveyed having joint pain within the past thirty days. Knee pain was the most typical complaint, followed by shoulder and hip pain. But joint pain can involve any part of your body, from your ankles and feet to your shoulders and hands.
Osteoarthritis
This typical type of arthritis occurs over time when the cartilage, the protecting cushion in between the bones, wears away. The joints become aching and rigid. Osteoarthritis grows gradually and usually happens during middle age.
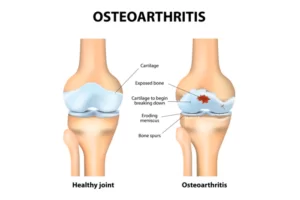
- wrists
- hands
- hips
- knees
Joint pain due to OA effects from a breakdown of the cartilage that serves as a cushion and shock absorber for the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis
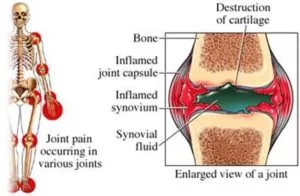
This is a chronic condition that induces swelling and pain in the joints. Mostly the joints become impaired (usually appearing in the fingers and wrists).
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that can involve more than just your joints. In some individuals, the condition can harm a wide variety of body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
An autoimmune disorder, rheumatoid arthritis happens when your immune system poorly attacks your own body’s tissues.
Unlike the wear-and-tear injury of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis involves the lining of your joints, generating a painful swelling that can ultimately result in bone erosion and joint deformation.
The inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis is what can hurt other parts of the body as well. While new types of medications have enhanced treatment choices dramatically, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still generate physical disabilities.
Gout
This is a painful disease where crystals from the body accumulate in the joint, forcing extreme pain and swelling. This usually happens in the big toe.
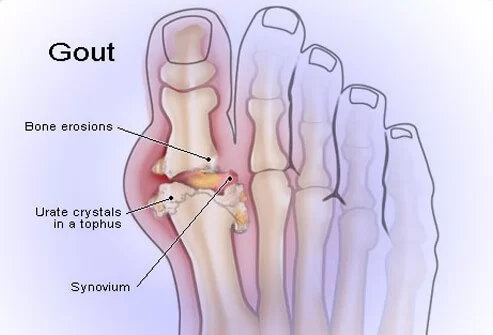
Gout is a condition of inflammatory arthritis that generates pain and swelling in your joints. Gout occurs when there’s a buildup of uric acid in your body. Gout most typically affects your big toe joint. But it can involve other joints, including your:
- Knees.
- Ankles.
- Feet.
- Hands and wrists.
- Elbows.
Gout signs come and go (recur) in attacks called flares or gout attacks. A healthcare provider will recommend medications and modifications to your diet that will reduce your uric acid levels and underestimate how often you undergo gout attacks in the future.
Bursitis
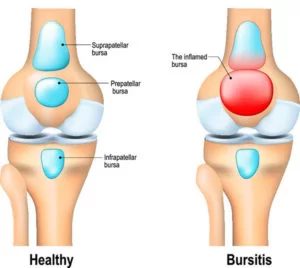
This is induced by overuse. It is typically noticed in the hip, knee, elbow, or shoulder. Bursitis is a painful condition that involves the small, fluid-filled sacs known as bursae that buffer the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints. Bursitis is induced when bursae become inflamed.
Shoulder, elbow, and hip bursitis are the most typical locations for this condition. But you can have bursitis by your knee, heel, and the bottom of your big toe. Bursitis usually occurs near joints that serve regular repetitive movement. Treatment typically involves relaxing the affected joint and protecting it from further concussion. In most cases, bursitis pain goes away within a few weeks with proper therapy, but recurrent flare-ups of bursitis are expected. Joint movement may hurt when there is a viral infection, rash, or fever.
Injuries, such as injured bones or sprains
Tendinitis
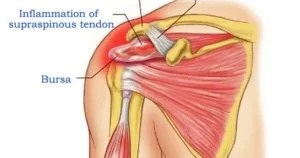
This is an inflammation of the tendons or the elastic bands that connect bone and muscle. It is commonly seen in the elbow, heel, or shoulder and is usually caused by overuse.
Other causes
Joint pain can be caused by:
Lupus
several contagious illnesses, such as the flu, the mumps, and hepatitis; chondromalacia of the patella, or degradation of the cartilage of the kneecap;
An infection of the bone or joint
Osteomyelitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, epidural abscess, and diabetic foot osteomyelitis are among the joint infections caused by septic arthritis, prosthetic joint infections, osteomyelitis, and spinal disorders. The acute medical take may reveal any of these.
Overuse of a joint
Powerful damage to a joint, such as the knee, can afterward result in osteoarthritis. Injury may also result from repeated overuse or misuse over some time.
Cancer
Typically, bone cancer-related pain starts as a feeling of soreness in the damaged bone. This progressively worsens into a constant aching or throbbing pain that persists through sleep and rest. Any bone can be impacted, but long bones like those in the legs or upper arms are where bone cancer typically manifests itself. In adults, the pain may occasionally be mistaken for arthritis, and in kids and teenagers, it may be confused for growing pains.
Fibromyalgia
A chronic (long-lasting) illness called fibromyalgia causes widespread pain and discomfort as well as exhaustion and trouble sleeping. People with the condition have increased pain sensitivity, yet scientists are not entirely sure what causes it.
Osteoporosis
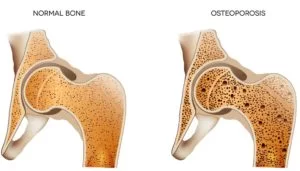
Osteoporosis is a bone disorder that forms when bone mineral density and bone mass reduce, or when the quality or structure of bone modifications. This can lead to a reduction in bone strength that can raise the risk of broken bones (fractures). Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Bone Health.
Sarcoidosis
The expansion of teeny inflammation cell clusters in various bodily regions. Lung, lymph nodes, eye, and skin growths are the most typical locations for these lesions. Symptoms vary, depending on the organs affected. Sarcoidosis often goes away on its own. Minimal treatment is required in most cases. For some people, it may persist for years, harming their organs.
Rickets
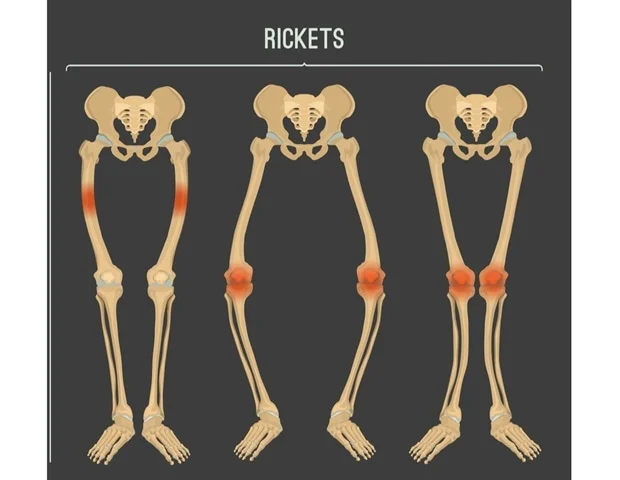
A softening and weakening of children’s bones is typically brought on by insufficient vitamin D. Calcium and phosphorus absorption are reduced when vitamin D deficiency is present. Rickets can be brought on by problems keeping the right levels of calcium and phosphorus in the bones.
Delay in growth, bow legs, weakness, and pain in the spine, pelvis, and legs are some symptoms. Sunlight exposure, a vitamin D and calcium-rich diet, dietary supplements, prescription drugs, and even surgery are all part of the treatment.
Osteomyelitis
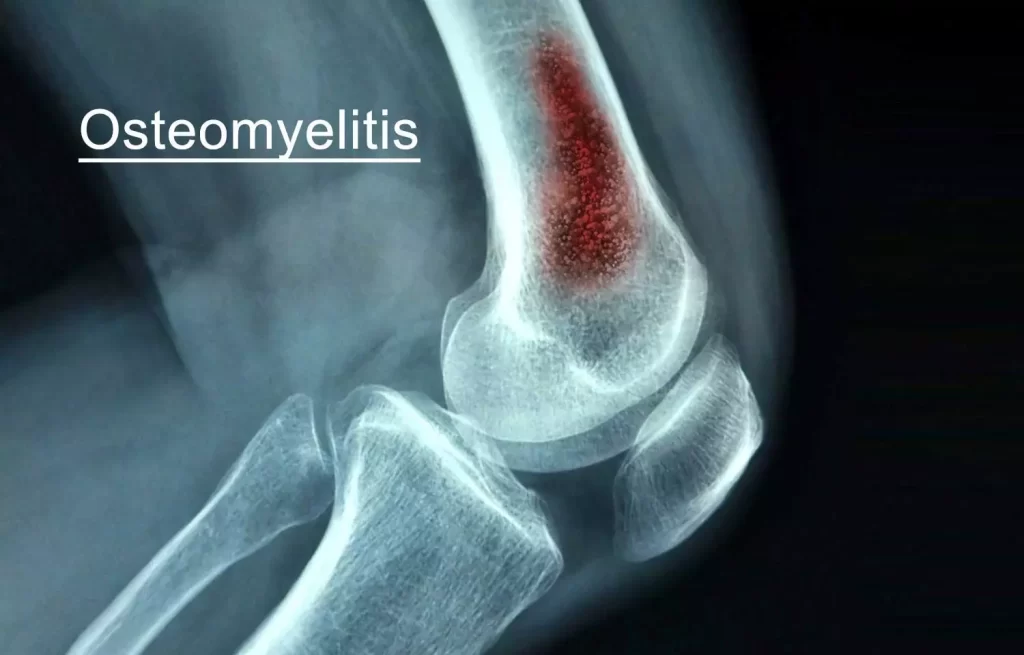
This is a serious condition of the bone that can be either critical or chronic. It is an inflammatory process involving the bone and it is induced by pyogenic organisms that circulate through the bloodstream, fractures, or surgery.
Bone and joint TB
Bone and joint TB contains a group of serious infectious diseases whose incidence has grown in the past two decades, particularly in underdeveloped nations, in part due to the AIDS epidemic. Tuberculous spinal conditions should be suspected in patients with an insidious, developed history of back pain and people from an endemic area, especially when the thoracic vertebrae are involved and a pattern of bone destruction with proximate disc preservation and paravertebral and epidural soft tissue masses are observed. Atypical tuberculous osteoarticular representations involving the extraspinal skeleton, a prosthetic joint, or the trochanteric area, and nontuberculous mycobacterial infections should be considered in clear epidemiological contexts. Surgery connected with prolonged specific antituberculous chemotherapy is particularly marked in patients with neurological presentations or deformities and provides adequate results in most cases.
Sprains
A joint capsule stabilizes joints, while ligaments, tough bands of connective tissue, support joints. The synovial membrane that surrounds the entire joint is filled with lubricating synovial fluid, which helps to hydrate the joint and adds further shock absorption. A sprain is an injury in which one or both of the ligaments or the joint capsule have torn. Sprains frequently occur in the thumb, ankle, and knee.
Strains
A strain is an injury to the tendons or the muscles themselves, which are commonly found in the calf, groin, and hamstring. Tendons are the connective tissue that ties muscles to joints.
What indications of joint pain need attention?
The symptoms of joint pain can range from mild to incapacitating. Bones move together directly against one another in the absence of cartilage. Symptoms can include:
- Swelling
- Stiff or enlarged joint
- Numbness
- The Joint can generate grinding and cracking sounds.
- Painful movement
- Difficulty bending or straightening the joint
- Loss of motion
- A red, heated, and swollen joint
Treatment
Therapy for joint pain will differ depending on the underlying cause.
Generally, a doctor may prescribe pain medicine to reduce pain. For example, for arthritis, they may recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
If the joint pain is due to an infection, a doctor will prescribe antibiotics or antivirals to loosen and control the symptoms.
If the pain is due to an injury or arthritis, a doctor may guide people to a physical therapist for rehabilitation. In more extreme cases, or if the pain continues, a doctor may advise undergoing surgery.
FAQ
Which defect induces joint pain?
Joint pain can be induced by various defects and conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. One common defect that leads to joint pain is arthritis, a group of inflammatory disorders that affect the joints. Osteoarthritis, caused by the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, both result in joint pain and stiffness.
Which foods induce joint pain?
Pasta: Wheat-based foods like pasta, bread, crackers, and bagels, particularly if you have rheumatoid arthritis, might be bad for your joints.
Butter and Margarine.
Hamburgers.
Tomatoes.
Sugary Drinks.
Can stress induce joint pain?
These hormones tell our bodies to go into a fight-or-flight reaction, removing pro-inflammatory molecules and causing inflammation. The body makes cytokine molecules due to long-term stress, resulting in joint swelling and pain.
Can a deficient diet induce joint pain?
Poor dietary and nutritious choices can also improve your pain by improving your waistline. Excessive consumption of fatty, sugary, starchy, or rich meals might make you gain weight, especially if you lead a sedentary lifestyle. This increased weight can hasten joint deterioration and aggravate arthritis symptoms.
Is arthritis curable?
Arthritis has no prescribed therapy. While preserving joint function, treatment tries to lessen pain and inflammation. In addition to drugs, there are other treatments like weight loss, exercise, and surgery.
What relieves joint pain the best?
Ice: To reduce discomfort and swelling in your joints, apply ice to them. Apply 15 minutes of ice to the joint multiple times per day. Heat: To treat any muscular spasms near the joint after a day or so, try using a heating pad. Rest: Take it easy on the joint the first day and stay away from any painful activities.
Can a weak immune system lead to joint pain?
Some CVID patients who might not be getting the best immunoglobulin replacement therapy might also experience painful joint inflammation. Polyarthritis is the name of this condition. The joint fluid is typically devoid of germs in these instances.
References
- Arthritis. (2023, August 21). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthritis
- Todd DJ. Bursitis: An overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed June 27, 2017.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Orth Info. Osteoarthritis. (https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/osteoarthritis/) Accessed 3/30/2018.
- American Academy of Family Physicians. What You Should Know About Osteoarthritis. (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0101/p57.html) Accessed 3/30/2018.
- Merck Manual. Joint Pain: Many Joints (Polyarticular Joint Pain). (https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/bone,-joint,-and-muscle-disorders/symptoms-of-musculoskeletal-disorders/joint-pain-many-joints) Accessed 3/30/2018.