Apprehension test :
What is Apprehension Test?
What is Apprehension Test?
This test is mostly used to test the stability of the glenohumeral joint capsule, or to examine glenohumeral instability in an anterior direction in Shoulder Dislocation related condition.
- It is also known as the crank test .
What doe a positive Apprehension test?
If you have positive test is usually susceptible to a labral lesion and/or bony lesion at the anterior inferior rim of the glenoid in the shoulder.
Purpose of this test :
- This test is generally used for the integrity of the glenohumeral joint capsule / to the assess of the glenohumeral instability into the anterior direction.
- It is also used for the check the shoulder dislocation .
Part of this test :

- This test is perform in 4 part :
- Normal crank test
- Anterior translations means fulcrum test
- Posterior translation means relocation test
- Surprise test
How to perform the test?
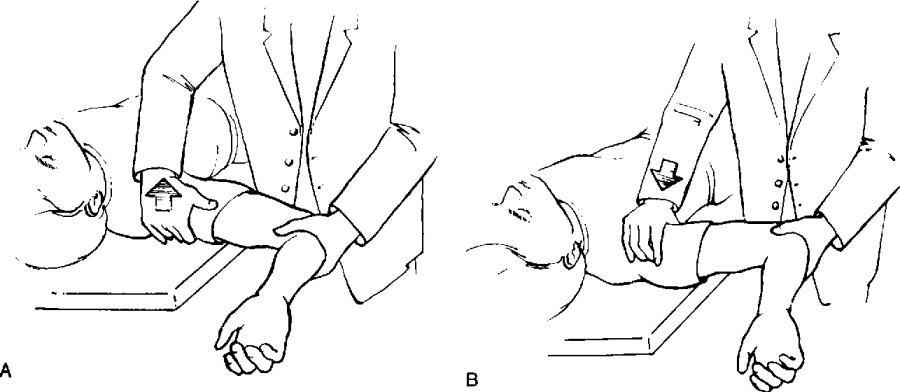
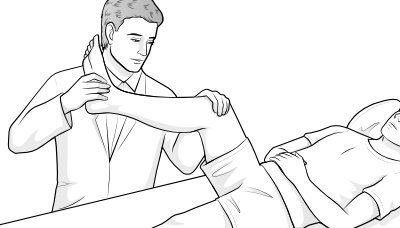
- Test position is the supine position.
- Therapist is flex to the patient’s elbow up to 90 degrees & abducts the patient’s shoulder up to 90 degrees & maintaining the neutral rotation.
- Then examiner does the slowly apply to the external rotation force on the arm at the 90 degrees & carefully monitoring to the patient.
- Patient is feel to the apprehension from the maneuver / not up to the pain, it is considered a positive test.
- Pain with to the maneuver, but not to the apprehension; it is indicate to the pathology other than of the instability,
- Like as posterior impingement of the rotator cuff.

Test Item of the Cluster:
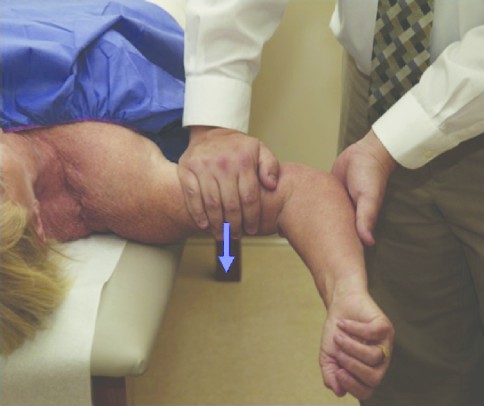
- When the test is positive, this test is perform combined with the Jobes Relocation test.
- This job relocation test is known as the fowler sign.
- In this test position is supine.
- In the supine position scapula is supported by the edge of the examine table.
- Then the arm is positioned into the 90 ° of abduction &external rotation.
- After that increasing to the external rotation & examiner watches for the apprehension of the patient.
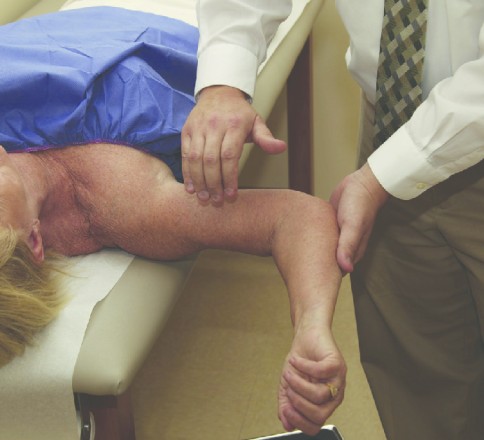
- Test is also perform in the sitting position.
- After this position the examiner place hand which is known as the fulcrum & apply the anterior translation force with to the thumb which is placed to the posterity on to the humerus.
- If the patient feel apprehension not the pain so that the test is positive for the posterior instability.
- Then examiner applies the posterior translations or stress on the head of humerus & try to Relocation of the joint.
- If the pain is decrease or apprehension is also decrease so that positive of the test foe the shoulder dislocation.
- In the last stage when the examiner leave the posterior stress patient is give in normal position & produce the crank sound / return of the pain & apprehension .
- This part of the test is known as the surprise test or anterior release test.
Evidence of the test :
- Sensitivity of this test = 0.53
- Specificity of this test = 0.99
- Positive Likelihood Ratio [+LR ] = 53.0
- Negative Likelihood Ratio [ -LR ] = 0.47
Importance of this Test:
- Patient who have suffer form the shoulder instability so that in the patient increase the risk of the shoulder dislocation and injury.
- Causes of the shoulder instability is traumatic, genetic or micro traumatic.
- Mechanism of the injury is patients have problem with the muscle length discrepancies /other connective tissue problems & lengthened of the joint capsules.
- Mostly with the anterior apprehension, most common injury is to the Bankart lesion.
- So that this test important for the apprehension sign because dislocated shoulder is damage of to the surrounding nerves & vascular supply.



3 Comments