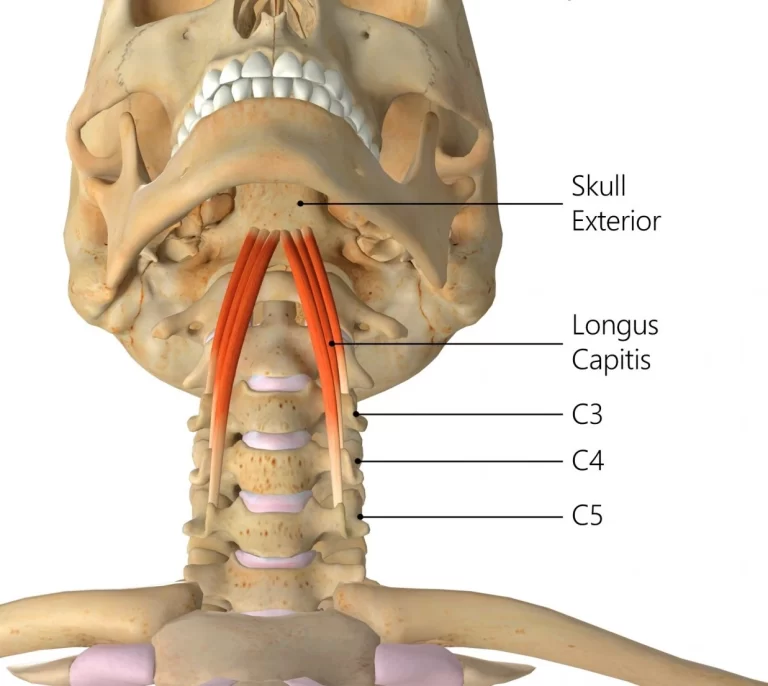
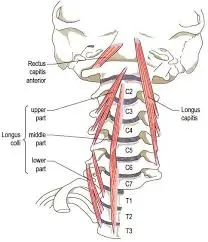
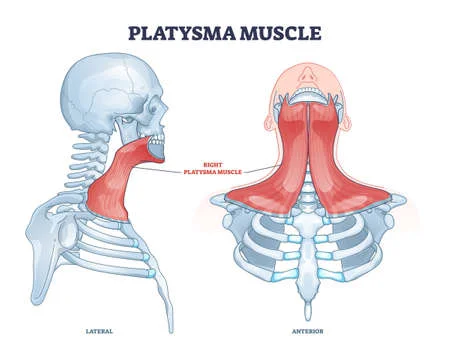
Coracobrachialis muscle
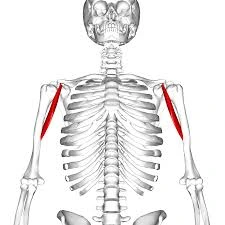
What is Coracobrachialis? The coracobrachialis is a long and thin muscle in the arm’s anterior compartment. It runs from the coracoid process of the scapula to the shaft of the humerus, as the term implies. The coracobrachialis muscle’s main function is to generate arm flexion and adduction at the shoulder joint. The musculocutaneous nerve innervates…