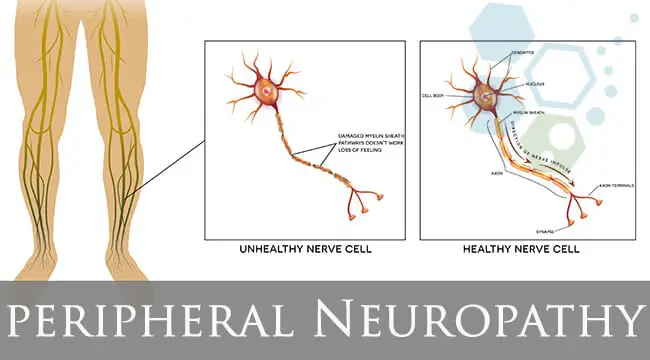
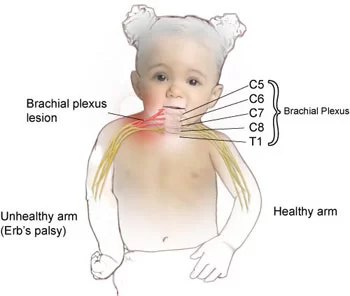
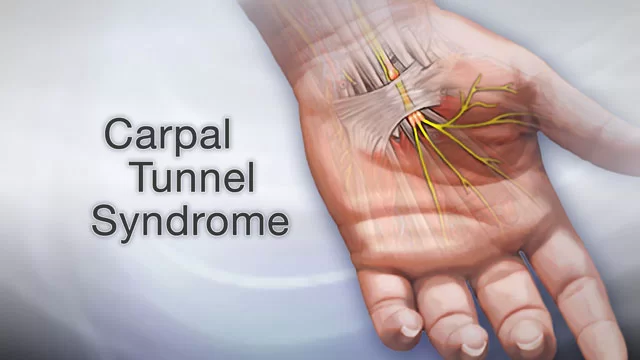
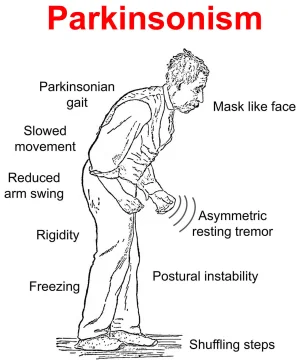
Peripheral Neuropathy: Physiotherapy Treatment, Exercise
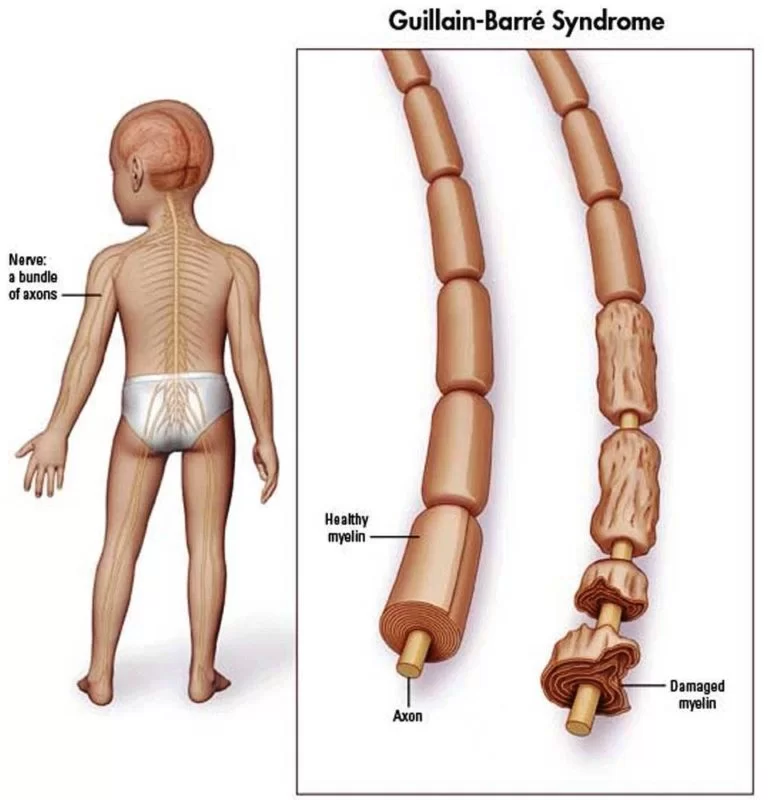
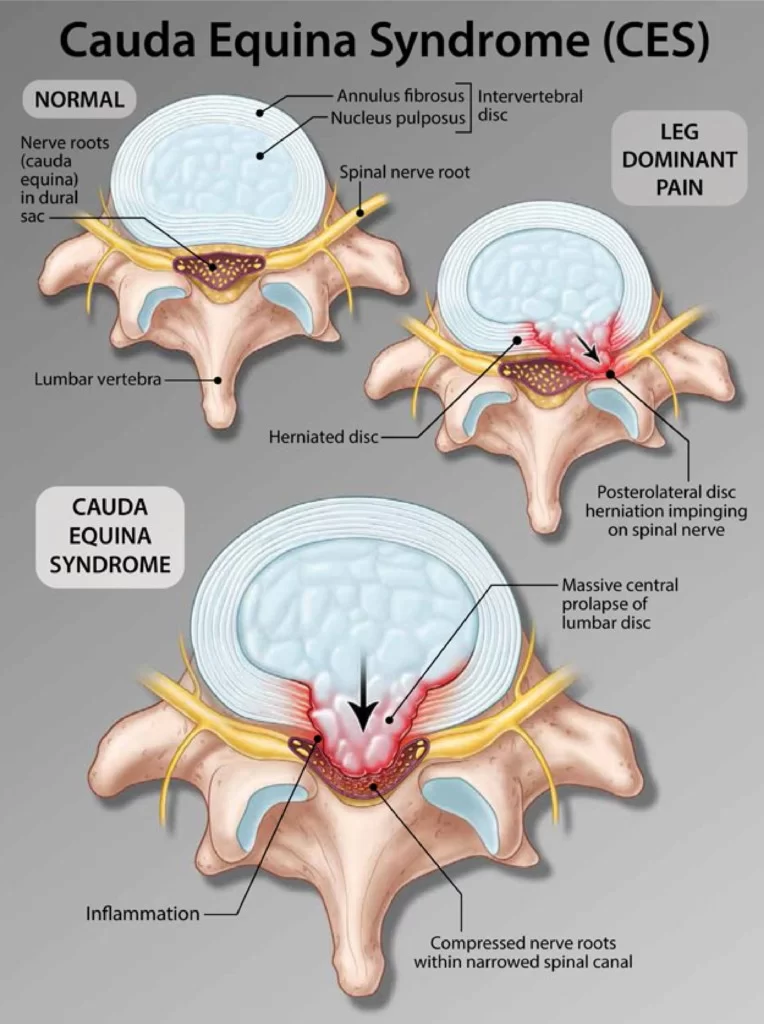
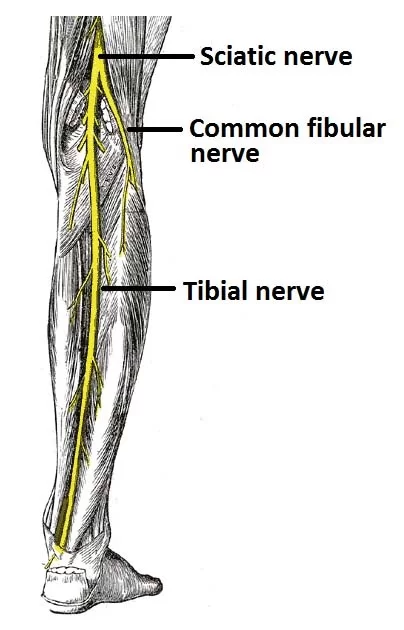
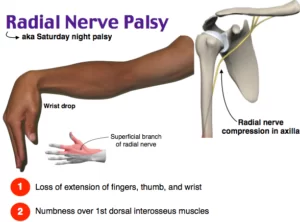
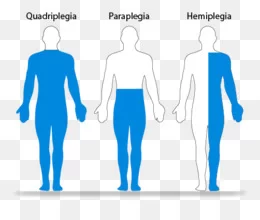
Peripheral: Beyond (in this case, beyond the brain and the spinal cord.)Neuro-: Related to the nerves-pathy: Disease Peripheral neuropathy refers to the conditions that result when nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord from and to the rest of the body are damaged or diseased. The peripheral nerves make up…