Clonixin
Description
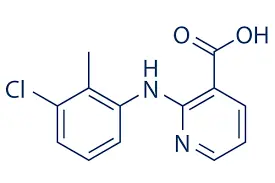
Clonixin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It also has analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory movements. It is utilized primarily in the treatment of chronic arthritic diseases and certain soft tissue disorders associated with pain and inflammation. Clonixin is a pyridine monocarboxylic acid that is nicotinic acid superseded at position 2 by a (2-methyl-3-chlorophenyl)amino group. Utilized (as its lysine salt) for therapy of renal colic, muscular pain, and moderately severe migraine attacks.
It has a position as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a non-narcotic analgesic, an antipyretic, a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a vasodilator mechanism, an EC (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase) inhibitor, and a lipoxygenase inhibitor. It is a pyridine monocarboxylic acid, an aminopyridine, and an organochlorine combination. It is functionally related to nicotinic acid. It is a conjugate acid of clonixin drug.
Clonixin is a nonsteroidal agent. It is an aniline-nicotinic acid derivative. It is a drug of anti-inflammatory antipyretic and analgesic exercise that produces minor digestive side effects. At high attention, clonixin inhibited PGE2 formed by COX-2 and somewhat by COX-1 activity.
The remedy is indicated for the relief of headaches, muscle aches, and also joint, dental, ear, dysmenorrhea, and also post-traumatic, post-surgical, and/or gynecological. Adverse effects are occasionally nausea, dizziness, and somnolence, which were mild and transient. On infrequent occasions, and administering high doses, it is possible the appearance of dry mouth and/or constipation. Concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs is to be avoided by the possibility that they enhance their effects atropine.
- Molar mass: 262.69 g/mol
- ChemSpider ID: 26711
- Type – Small Molecule
- Groups – Experimental
- Chemical Formula – C13H11ClN2O2
- Synonyms – Clonixin, clonidine
What is Clonixin?
Clonixin drug is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) structurally homologous to Diclofenac with vasodilator and analgesic consequences. The drug is prepared in the form of soft gels or film-coated tablets with the strength of 125mg and 250mg. Clonixin therapy is demonstrated in the restorative of headaches, muscle aches, joints, teeth, ears, and also menstrual pain, after trauma, after surgery, and in gynecology. The unfavorable effects were nausea, dizziness, and somnolence, which were mild and transient. In infrequent cases of high doses, patients may develop dry mouth or constipation.
Absorption of Clonixin: Clonixin is rapidly absorbed after oral management. Extreme plasma concentrations are achieved 1 hour after dosing. The half-life of clonixin in mortal plasma is about 1.75 + 0.10 hours. Concentrations in milk are about 7 to 10% of plasma concentrations.
Diffusion of the drug Clonixin: Clonixin is widely distributed in numerous body liquids and tissues. The speed of binding to plasma proteins varies from 96 to 98%. The primary clonixin combination is found in the blood around 6 hours after taking the drug. The importance of distribution is 0.112 L/kg body weight.
Pill metabolism Clonixin: The clonixin drug is metabolized to 5 -OH Clonixin and/or 4 -OH Clonixin.
Elimination of the drug Clonixin: Within 24 hours of handling the medication, a vocalized dose of 500mg is passed in the urine at about 62%, mainly in the state of metabolites 4-OH Clonixin and 5-OH Clonixin. More accessories diminutive than 1% of the remaining clonixin drug are excreted in the feces. After 120 hours of dosing, the portion of the drug eliminated in urine and feces is about 86%.
Mechanism of action of Clonixin
The mechanism of Clonixin does not arise to be studied at the molecular level. At expanded engagements, clonixin is thought to act similarly to other NSAIDs by acting especially on the enzyme that catalyzes the production of prostaglandins responsible for inflammation (cyclooxygenase-2 or COX-2), with a more nominal impact. On the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of prostaglandins in the gastric and renal mucosa (cyclooxygenase-1 or COX-1), prostaglandins have a defensive role at this site.
Clonixin is a non-steroidal agent, it is an aniline-nicotinic acid derivative and is structurally similar to flufenamic acid. Clonixin is a drug with an antipyretic and analgesic activity that causes mild gastrointestinal side effects. The mechanism of clonixin does not seem to have been researched on a molecular level. It is supposed to function similarly to other NSAIDs by inhibiting cycloxygenase enzymes 1 and 2 resulting in a decrease in prostaglandin production.
A Clonixin drug is revealed for the control of aches and spasms of smooth muscle, realized in any piece of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary, and liver. Its major signs are Gastrointestinal: spastic syndrome of the esophagus, pylorus, bowel or colon, and also irritable colon. Urinary system: renal colic, ureteral and bladder spasms, cystitis and also seminal vesicle inflammation, kidney or ureteral stones. It is also utilized when one has to perform a specific investigation of the urinary tract. Female genital tract: dysmenorrhea, premenstrual tension, tubal spasms, painful adnexal processes, and/or also spasticity in the postpartum duration.
- Pharmacodynamics – Clonixin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) equivalent in structure to Diclofenac. It produces vasodilation and analgesia.
- Absorption – Not Available
- The volume of distribution – Not Available
- Protein binding – Not Available
- Metabolism – Not Available
- Route of elimination – Not Available
- Half-life – Not Available
- Clearance – Not Available
- Toxicity – Not Available
- Pathways – Not Available
- Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs – Not Available
Drug Interactions
Concomitant utilization of anticholinergics should be evaded because they potentiate the effects of atropine. Concomitant clonixin with other anti-inflammatory analgesics, including low-dose aspirin, increases the risk of undesirable effects, especially on the gastrointestinal tract. Concurrent usage of clonixin and warfarin may increase the chance of gastrointestinal bleeding. Clonixin works by inducing arteriolar constriction to the glomeruli, which may increase nephrotoxicity as well as reduce the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors. ). Co-administration of furosemide and thiazides with clonixin also decreases the effect of this category of diuretics. Concomitant usage of clonixin with lithium salts can also lead to increased plasma concentrations of lithium salts, which can cause serious, life-threatening toxicity. If clonixin and methotrexate drugs are to be employed, they should be taken at least 24 hours separated, as clonixin can improve plasma concentrations of methotrexate.
Side effects of the drug Clonixin
On the digestive system: Using Clonixin for a long time can cause side effects on the gastrointestinal tract, especially can cause peptic ulcer, gastric perforation, and more serious gastrointestinal bleeding. In this case, the patient should stop taking the drug and notify the doctor immediately. Other undesirable effects: Occasionally, the drug can cause nausea, vomiting, somnolence, dizziness, headache, sweating, and mania.
A Clonixin drug is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) structurally equivalent to Diclofenac. The drug is indicated for the medicine of aches in some pathological symptoms. To ensure the effectiveness of treatment and avoid side effects, patients need to take medicine according to prescription or consult a doctor, or pharmacist for advice.
How to use Clonixin
Employing clonixin by mouth should take the medication with filtered water and after meals. The typical adult dose is 1 to 2 tablets at a time, with different doses possible after 8 hours. The dose utilized is not identical for all patients and will be adjusted on a case-by-case basis.
A course of therapy can also last from 7 to 10 days or maybe longer depending on the medical condition of each person.
Indication of the drug Clonixin
Indicated for usage in the management of chronic arthritic disorders and certain soft tissue disorders associated with pain and inflammation. An indication is a term utilized for the list of diseases or symptoms or illnesses for which the medicine is prescribed or used by the patient. For instance, acetaminophen or paracetamol is employed for fever by the patient, or the medic prescribes it for a headache or body pains. Currently, fever, headache, and body aches are indications of paracetamol. A patient should be mindful of the indications of medications used for common conditions because they can also be taken over the counter in the pharmacy meaning without a prescription by the Physician. It is indicated for the management of aches and spasms of smooth muscle, encountered in any piece of the digestive tract, genitourinary and hepatolenticular level. Its main indications are:
Gastrointestinal: esophagus painful spastic syndrome, pyloric, intestinal or colon, and also irritable colon.
Urinary system: renal colic, ureteral and also bladder spasm, cystitis and cistopielitis, kidney and/or ureteral pebbles. It is also utilized when one must make an instrumental examination of the urinary tract.
Female genital tract: functional dysmenorrhoea, premenstrual tension, spasm of the tubes, adnexal processes painful and/or spastic pains in the puerperium.
Associated Conditions – Migraine
Associated Therapies – Analgesia
Contraindications of the drug Clonixin
Hypersensitivity to any component. – Must be employed with caution in patients with a record of coronary disease, peripheral vascular disease, severe hypertension, advanced hepatic or renal.- It is contraindicated in patients with active peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding. No corresponding with macrolide antibiotics or beta-blockers
Patients with allergies and hypersensitivity to any element of Clonixin Pregnant and lactating women should not utilize it because there are no formal studies on this subject. The patient has a gastric ulcer and duodenal bulb. Do not use in children under 12 years of age Use with caution in patients with a history of coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, severe hypertension, or progressive liver or kidney failure.
Notes when using Clonixin
Clonixin only treats symptoms (mainly relieves pain), and does not work to solve the root cause of the pain. Before establishing Clonixin in the treatment of chronic disorders, it is necessary to perform clinical tests (liver or kidney function, blood count, urine.) and regularly monitor the patient’s essentials to maintain up with Timely detection of unwanted effects and convenient discontinuation of the drug. Utilizing clonixin as monotherapy for pain and inflammation in an infection may also cause the infection to spread to other tissues. Therefore, appropriate antibiotics must be used concurrently. Minimize the combination of Clonixin with other anti-inflammatory drugs, unless it is necessary. As with other systemic NSAIDs (except aspirin), clonixin use may increase the frequency of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which may lead to death. This chance increases with the growing dose and length of use. Therefore, before prescribing Clonixin for long-term use, patients must be evaluated for the risk of cardiovascular events, as well as regularly monitored during treatment. To minimize this danger, the most inferior effective daily dose of clonixin must be employed for the shortest possible duration.
The drug can cause vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, and headache. Consequently, do not conduct or operate machinery while taking this medicine. Clonixin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) structurally comparable to the Diclofenac drug. The drug is indicated as the remedy for pain in some pathological symptoms. To ensure the effectiveness of treatment and avoid side effects, patients need to take medicine according to prescription or consult a doctor, or pharmacist for advice.
FAQ
What is Clonixin lysine Pargeverine hydrochloride?
Sertal is a medication that consists of clonixin lysine, and pargeverine hydrochloride. It is used as an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory remedy.
Does Lysine clonixinate help period pain?
Lysine clonidine is a nutritional supplement that has been utilized to treat aches such as migraines and menstrual cramps.
Does Lysine clonixinate help migraine?
Lysine clonixinate (LC) is the anthranilic by-product of nicotinic acid that compares the chemical structure of flufenamic acid. Several prevented and open-label trials support the usage of Lysine clonixinate for acute migraine treatment.
What is clonixina in English?
Clonixin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It likewise has analgesic, antipyretic, and also platelet-inhibitory activities. It is used primarily in the treatment of chronic arthritic disorders and certain soft tissue disorders associated with pain and inflammation.
What is Clonixin lysine Pargeverine hydrochloride?
Sertal is a medication that consists of clonixin lysine, and pargeverine hydrochloride. It is employed as an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory medication.
Why take muscle relaxers at bedtime?
Muscle relaxants are ideally prescribed for acute preferably than chronic pain. They may also be an option if the ache is preventing you from getting enough sleep. Because muscle relaxants cause drowsiness, they can also help you get rest when you take them at night.
What is the best anti-inflammatory for headaches?
NSAIDS and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the favored sequence of restorative when it comes to migraines. These include ibuprofen, which is known by the brand names Motrin and Advil; and naproxen, which is known as Aleve.
Does cyclobenzaprine help you relax?
Primary effects when handling cyclobenzaprine recreationally enclose drowsiness and a feeling of relaxation. The Flexeril delight could also incorporate a pleasant feeling of muscle relaxation and a feeling of floating as well.
Can I take lysine Clonixinate with paracetamol?
Termination: The analgesia of the integrated medicine of paracetamol analogous with clonixinate of lysine is remarkable to that constructed by the standard dose of ibuprofen and paracetamol in the cure of post-operation ache of simple extractions.