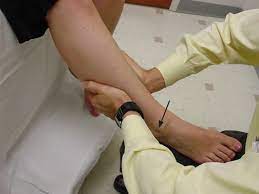
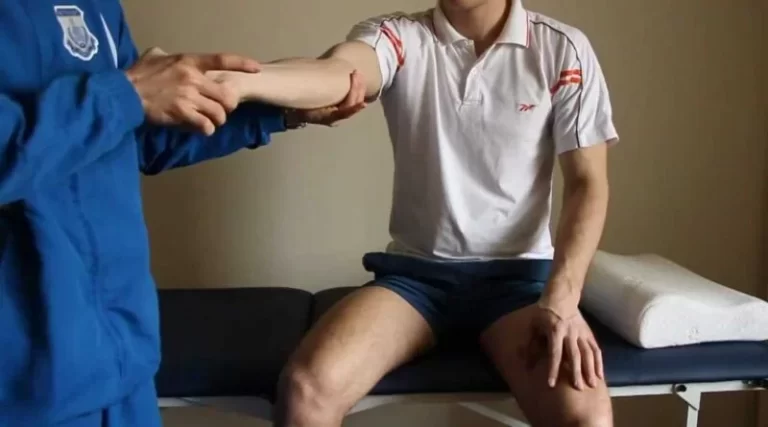
Cotton test of Ankle
- It is also known as the lateral stress test.
- It is a clinical test that is used to check the ligaments instability of the ankle.
- It is applied in the clinic by the therapist when the patient is doing complaints about ankle pain.
- Other test for check the syndesmosis is crossed leg test.
What is the purpose of the Cotton test of the ankle?
- This test is used to assess for syndesmosis instability caused by the separation of the tibia & fibula means diastasis.
- Normally, the two bones of ankle are held together by the help of four ligaments.
- into fore ligaments includes:
- the tibiofibular interosseous ligament
- anteroinferior tibilofibular ligament
- posteriorinferior tibilofibular ligament
- transverse tibilofibular ligament
How do you perform the Cotton test of the ankle?
- The examiner stabilizes the distal tibia & fibula with the help of one hand.
- After that applies a lateral translation force but not an eversion force with the help of the other hand of the examiner to the foot.
What is the result of the Cotton test of the ankle?
- Any lateral translation that means more than 3 to 5 mm/clunk indicates syndesmotic instability.
- Stoffel, et al felt this test was better than the lateral rotation stress test for determining syndesmotic instability on stress x-ray.
- If the examiner applies a medial translation force, the test is called the medial subtalar glide test.
Crossed leg test :

- This test is another test that is used to check the syndesmosis instability of the ankle.
How do you perform the crossed leg test?
- The starting position for the test is the sitting position.
- The patient sits in a chair with the affected leg crossed over the opposite knee so the midpoint of the fibula is resting on the opposite knee.
- The examiner then applies a gentle force to the medial aspect of the knee of the injured leg.
What is the result of the crossed leg test?
- If the patient experiences pain in the area of the distal syndesmosis, it indicates a positive test.