Dumbbell Back Exercises to Improve Your Strength and Posture
When it comes to improving strength and posture, incorporating dumbbell back exercises into your workout routine can be highly beneficial. The back muscles play a crucial role in supporting the spine, maintaining proper posture, and facilitating movements of the upper body. By targeting these muscles with dumbbell exercises, you can strengthen them, enhance your overall back strength, and promote better posture.
Your back muscle strength can also help you feel and look better. Studies have shown that people prefer to view those with good posture as more attractive than those who do not. As if that weren’t enough, research demonstrates that sitting up straight, which you can only do if your back is strong, is also linked to better attitudes, more stress durability, and higher levels of self-esteem. Your health is impacted by bad posture just as much as how you arrive. Aches and pains like persistent low back discomfort are frequently related to poor posture.
Introduction:
There have many benefits to working your back supporting your back muscles is necessary because it helps improve muscle inequalities and posture. Particularly when we consume lots of time sitting, our back muscles tend to be weak. This lack of proper tension in your muscles can make a rounding of your shoulders or a hunched work more likely.
Weak back muscles associated with lots of sitting can also damage the flexibility in your upper back, making it difficult to move your shoulder blades. A bunch of times people will begin to get shoulder injuries from that. They do not have good mobility and strength in the upper back, and when they do any kind of activities that target the ‘moving’ muscles, like the shoulder or chest muscles, that is when we get into trouble.” (While your rear deltoids are technically part of your shoulders, they are also small-but-important back-of-the-body muscles to focus on supporting for this reason, too).
It is essential to note that your lower back muscles are also considered part of your core, and there are tons of advantages to maintaining both. Maintaining your back and your core muscles to keep your spine supported, and involves everything from standing posture to gait, balance, and even joint health. That is because good alignment takes the pressure off your joints, and that provides major injury precluding.
Performing the back muscles exercise have great benefits. A strong back will help in spine alignment and stabilization. This will give support and power to the rest of the body to achieve not only exercises but also daily activities.” For example, when you pull a heavy door shut or pull a lawnmower to start, those are your back muscles shooting.
The Importance of Back Strength and Posture:
The latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboids are just a few of the various muscles that make up the back. These muscles stretch from your neck down to your waist and play an essential role in your daily activities. Unfortunately, prolonged sitting and crouching over a computer can generate these important muscles to weaken. Strengthening your back is better than just reducing discomfort; it is about enhancing your posture, mobility, and overall quality of life. Powerful back muscles can offset the tendency to round your shoulders and hunch over, assisting you maintain a straight and healthy posture. In the next section, we will analyze some straightforward dumbbell exercises that you can incorporate into your routine to assist create a stronger back, enhance your posture, and reverse the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle.
Improve posture. strengthening your back lowers your chance of injury by enhancing posture. If you begin to walk anatomically incorrectly, you will be hurt. Think chin parallel to the base, neutral spine, shoulders rolled back, and hips even.
Prevent injury. The back is the powerhouse of the human body and can help control neck, hip, and shoulder pain. If you do not have a strong back, you get injured. research indicates working your back muscles also helps relieve back pain.
Secure stability. The anatomy of your back is difficult, but the muscles around your spine are especially crucial to strengthen and stabilize. When you work [your back], all the other muscle fibers around your spine support and tighten, so they are not loose. Strengthening the muscles around your spine can relieve chronic back pain, and make daily tasks like selecting up kids or carrying groceries a little stressful on your body.
Here we describe different types of dumbbell exercises to improve back strength and posture:
Good mornings with dumbbells

- To initiate this exercise you have to stand width apart and hold a dumbbell in both hands, your palm facing inward on your shoulder.
- Slightly flex your knees, holding your back straight and core contracted as you hinge at the hips.
- Push your hips back until your trunk is parallel to the ground.
- Return to the initial position, then repeat ten times.
Upright row
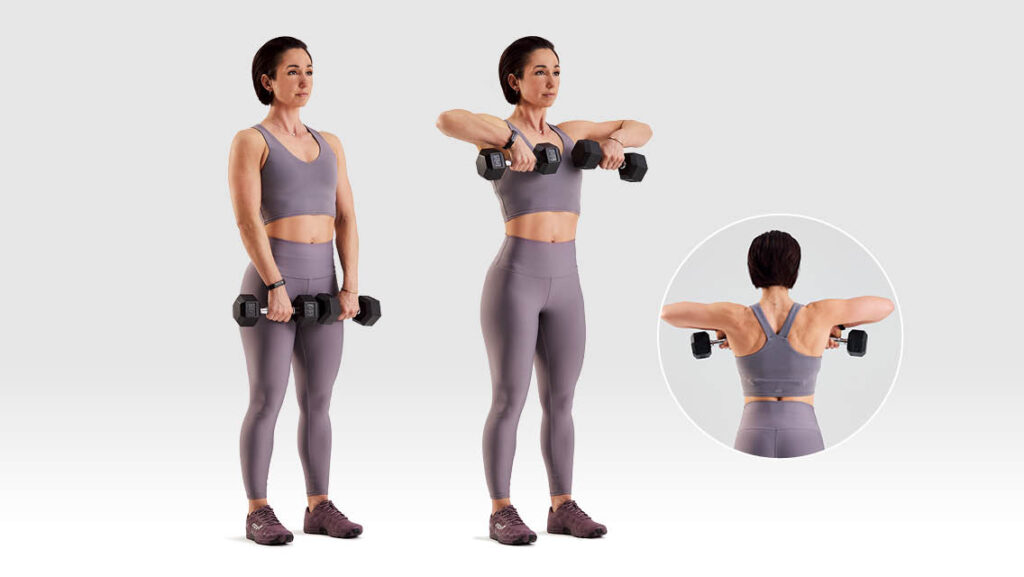

- Stand straight with your feet hip-width apart, hold a dumbbell in both hands, and carry them with palms facing you.
- With your core contracted and your chest up, lift the dumbbells toward your chin by raising the elbows to the top. Lower to the initial position.
- Repeat for ten repetitions.
Romanian Deadlift
- stand straight with feet hip-width apart, just flex your knees. grab a dumbbell in both hands and push your hips back to hinge forward. Think of attempting to push your buttocks against a wall after you or shut a door with your buttocks.
- Maintain and contract core. push your feet into the floor as you allow the dumbbells to touch down your legs stopping around your shins.
- Each individual is different, but the plan is to continue moving down your legs until your hips can not push back any distance and you feel a stretch in the hamstrings. hold, then return to the initial position by engaging the hamstrings. Repeat ten times.
T-raises
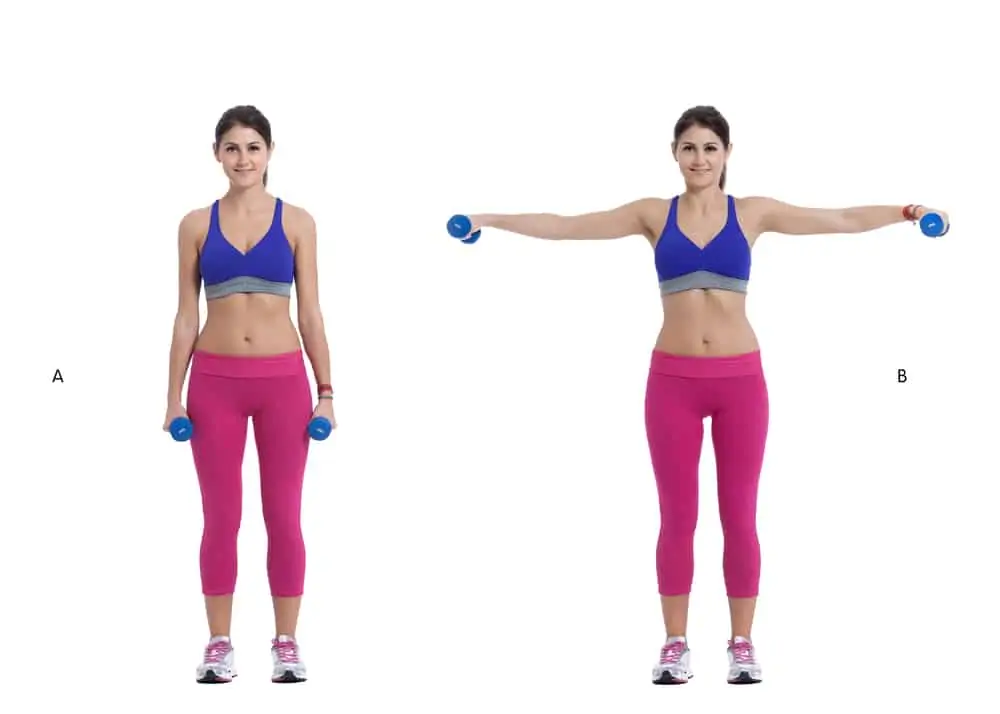

- Stand with feet hip-width apart carrying a dumbbell in both hands. Little flex the knees and hinge at the waist until the trunk is almost parallel to the floor.
- Get the weights together in front of the chest and turn the palms to face forward. Raise the weights straight out to the sides up to shoulder height, holding the arms straight.
- Then lower them back down.
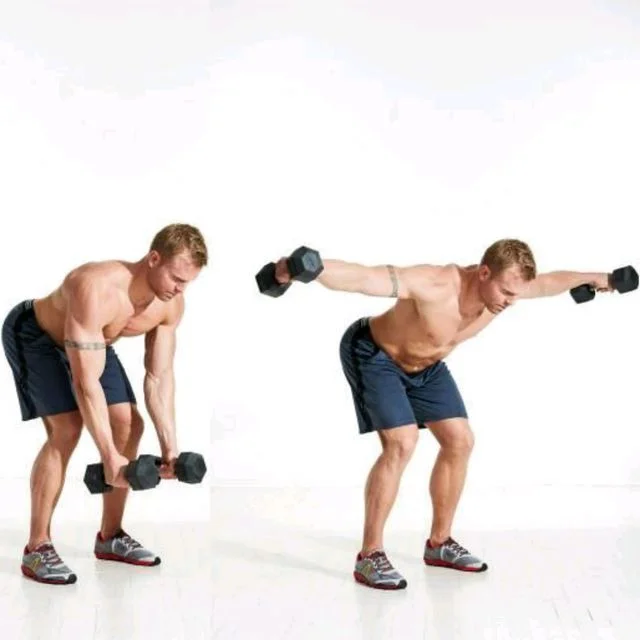

Rear delt fly
- Stand with your feet as much as your hips and grab a dumbbell in both hands. Get your arms toward the ground as you hinge forward at the hips, leaning your trunk forward on a diagonal.
- Then raise your arms out to the sides as much as the shoulders.
- Contract your shoulder blades together and then relax down to the beginning position.
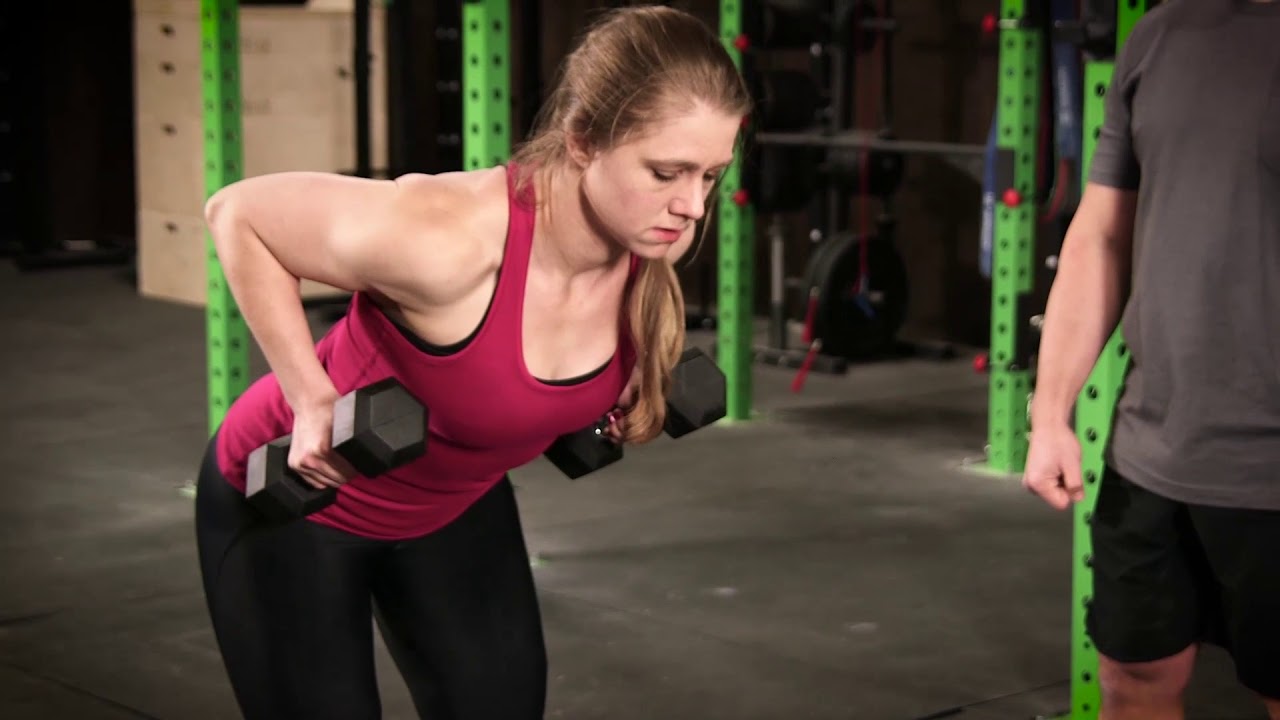
Single-arm bent-over dumbbell rows
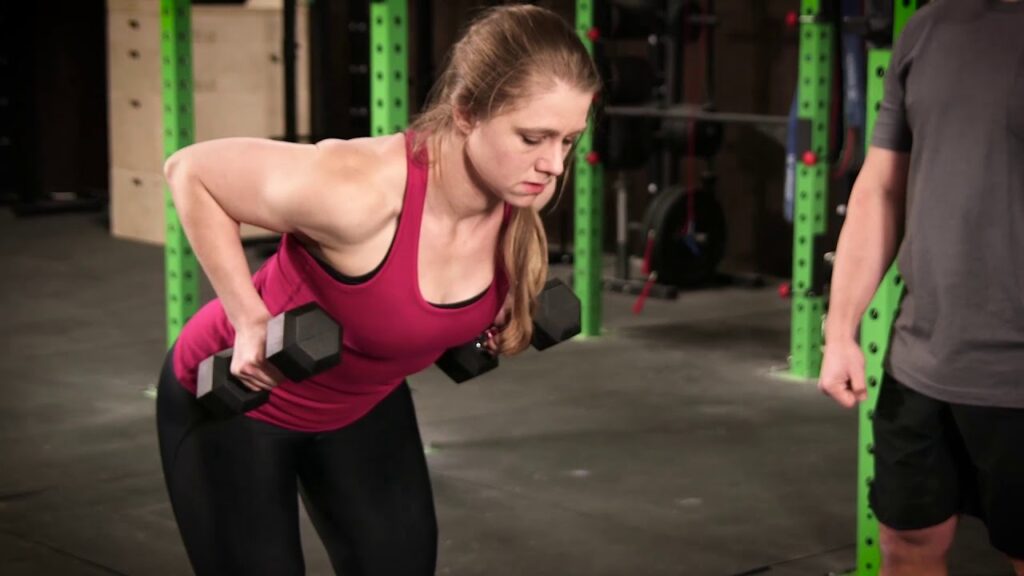

- Hold a single dumbbell. Most recommend a 4 or 5-pound weight for beginners.
- Step one leg back into a staggered posture with your feet hip-width apart. With a slight flex in your knees, press your hips back and allow your trunk to lower, making sure to hold a straight back and healthy, contract core. For the move, think of starting up a mower. Using a neutral grip, engage your lats and drive your elbow up toward the ceiling, pulling the weight in toward your body.
- Then, slowly lower the weight back to the starting point and repeat 10 times.10 reps should be done on the opposing side.
Bent over row
- Start by standing with your feet hip-width apart. Pull your abs in as you lean forward at the waist. Reach your torso diagonally, bending your knees just a bit.
- Allow the weights to hang down by your sides, then draw them up towards your chest while tucking your elbows close to your sides. Tighten your upper back and the area between your shoulder blades.
- Next, lower your arms while maintaining your elbows close to your sides.
Bent-over rows with an underhand grip
- Grab a dumbbell in both hands.
- Stand erect with feet hip-width apart, and slightly flex your knees before hinging forward by pushing your hips back.
- Keep a straight back and strong, contracted core. While holding dumbbells, extend your arms downward with your palms facing away. Before bringing both elbows back towards your hips, tighten your back and core. hold to create muscle tension, then gradually lower to the initial position.
- Repeat ten times.
Plank with lateral arm raise
- Begin in a plank position, carrying a dumbbell in each hand. contract your abdominals and keep your hips stable as you raise your right arm out to the right up to shoulder height.
- Return to the base, and then perform with the opposite side.
Single-arm plank row
- Starting in a plank position, place one dumbbell beneath your left hand, and place your right palm on the floor.
- Pulling the dumbbell towards your chest while raising your left elbow. contract your shoulder blades together and try to keep the left hip level with the right. Then lower the dumbbell and tap it on the ground before doing the next rep.
- Do 10 reps on the left side before switching to the right.
Pullover
- This training only needs one dumbbell. Take a supine lying position on a flat surface and hold your dumbbell with each hand, think of cupping one end of the dumbbell for an optimal holding position.
- flexed your knees and put your feet flat on the ground. elevate the dumbbell so it is over your chest. gradually let the dumbbell move after your head, holding your arms straight, until it creates forty five-degrees with the ground.
- Return to the initial position. Repeat ten times.
Superman with dumbbells

- Take a prone lying position and reach your arms back alongside your body and grab a dumbbell in both hands (with the palms facing up).
- Tense your core, pull your abdominals in, and raise your legs off of the floor, contracting the glutes. gradually raise your head and look a few inches in front of you to support your neck in proper alignment as you press the back to raise your upper body off the floor.
- Then reach the arms up toward the roof. contract your shoulder blades together and maintain for a moment at the top, then lower back down.
Reverse Fly
- stand straight with your feet hip-width apart, grab a weight in both hands with your arms by your sides, palms facing in, and elbows slightly flexed.
- To ensure that your back is parallel to the ground, bend forward at the hips while keeping your core tight. You should also slide your buttocks back and slightly flex your knees. Stare at the floor a few inches in front of your feet to support your neck in a comfortable position.
- Maintaining your back flat, core tight, and elbows flexed, extend your arms out to the sides until they are in line with your shoulders. Wait for a second, and then lower your arms back down to the initial position. This is one repetition.
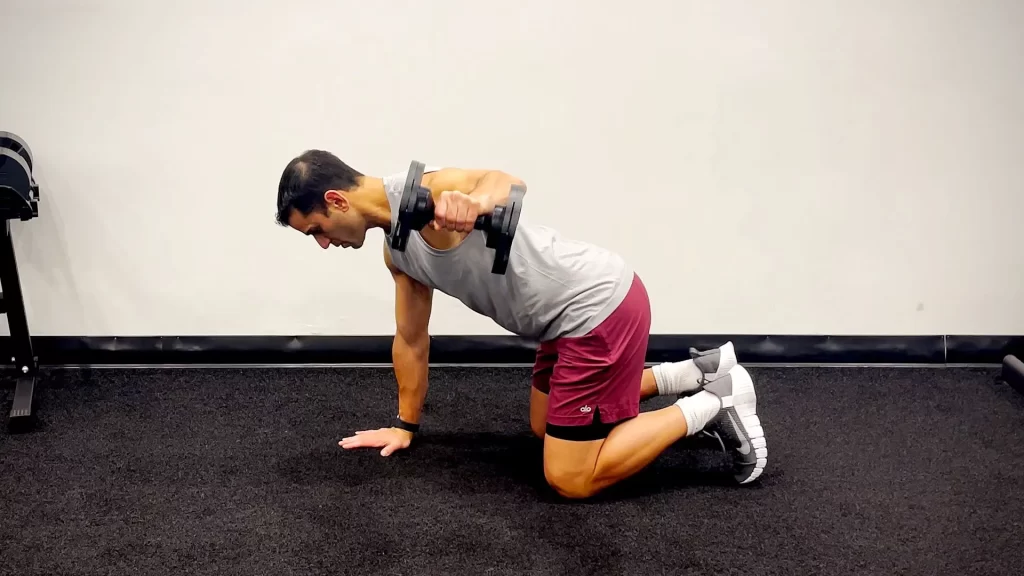

Quadruped Single-Arm Rear-Delt Raise
- To begin this exercise take a quadruped position On a mat, begin in an all-fours position with your knees under your hips and palms underneath your shoulders. In your left hand, take a dumbbell.
- Raise your left arm to the side, feeling the work in the back of your shoulder. contract your core, keep your back straight, and try not to turn to the side.
- Drop your dumbbell back on the floor. That is one repetition. complete ten repetitions on each side.
Prone Y Extension
- Utilizing a bench or exercise ball, lie on your belly facing the floor, and grab a dumbbell in both hands, palms facing in.
- Completely extend your arms out in front of you in the shape of a Y.
- Contract your core and squeeze your shoulder blades together as you raise your arms as much as you can over your head.
- Wait for 2 to 3 seconds at the top.
- Gradually lower back down to the initial position.
- do more 5 times.
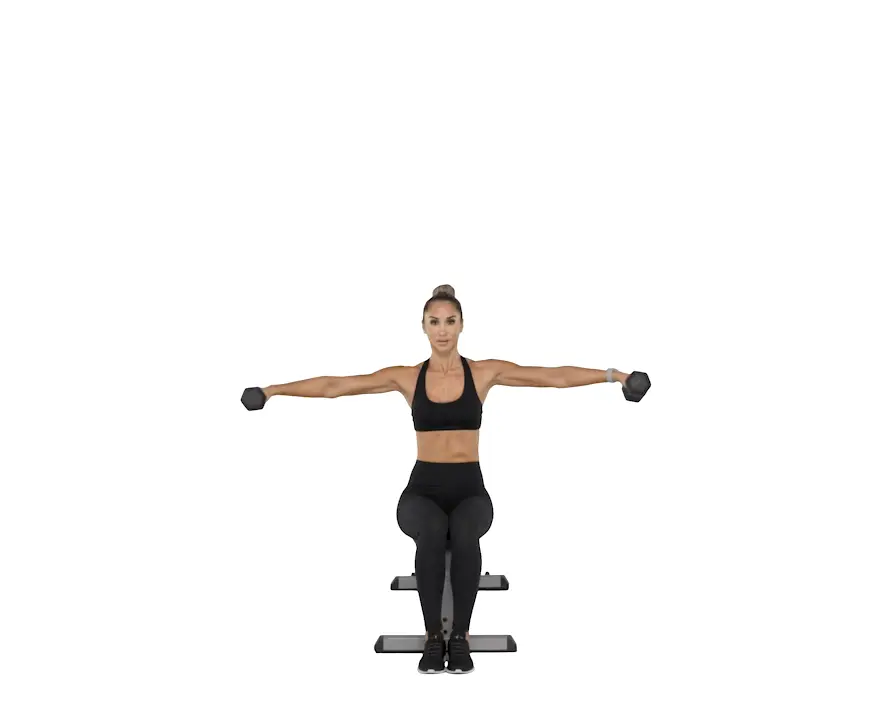

Seated T-Spine Openers
- Start sitting on a bench, hands behind your neck and elbows in close to each other. raise your chest and elbows toward the top, moving from your upper back. do not arch from your lower back.
- That is one rep. Do 3 sets of 8-10 repetitions.
Farmer’s Carry

- Another traditional training, and a move that man’s been doing since the onset of time, the farmer’s carry has you choosing up heavy dumbbells and walking with them, typically either for time or distance.
- In any case, you develop a bigger, stronger back (and a more durable body overall) as you concentrate on pulling in your shoulder blades and tightening your abdominals.
Kickstand Deadlift
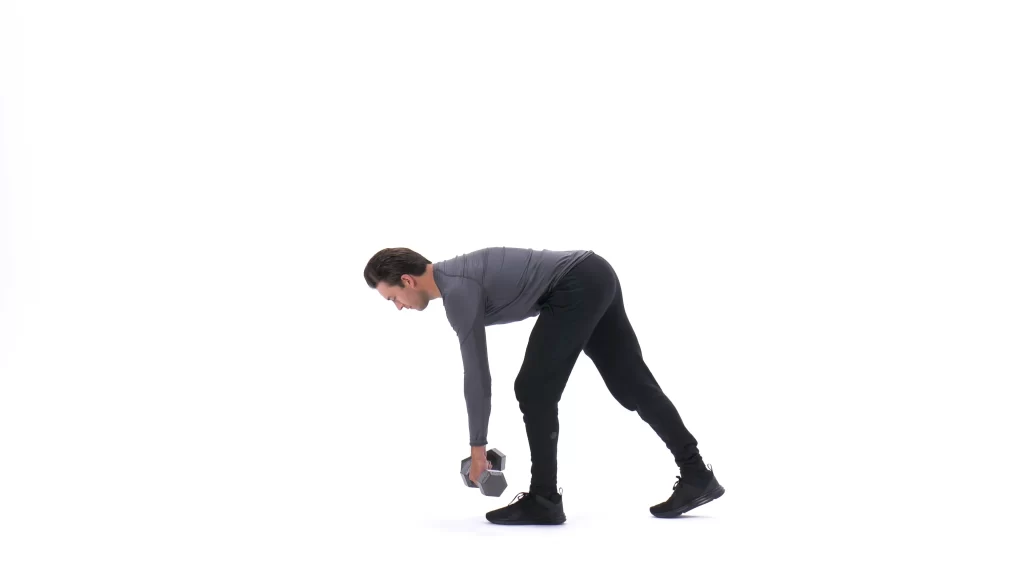

- Stand straight with your feet hip-width apart, and grab a dumbbell in both hands.
- Put one foot a foot-length behind the other, heel raised, so your stance is staggered. You will be working your anterior leg.
- Hinge at your hips to drop your body. Push your buttock far back and support your back flat. The bottom of your trunk should be nearly parallel to the ground.
- Holding your core tight, push via your front heel to stand up straight. The weights should remain close to your shins as you pull up.
- Stay at the top and press your butt. That is 1 repetition, Complete 2 to 3 sets of 10 to 12 repetitions.
Renegade Row
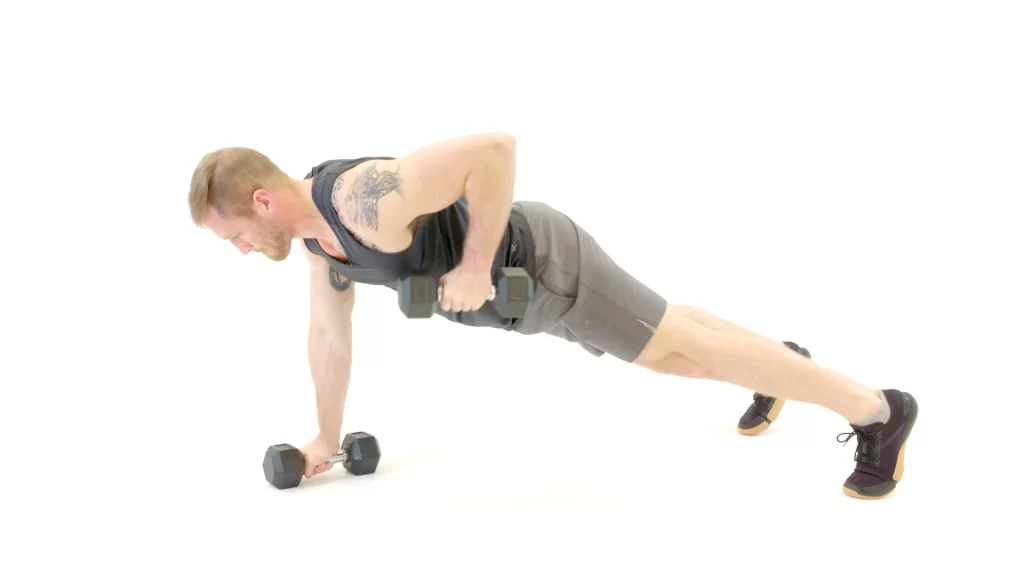

- Begin in a high plank, grab a dumbbell in both hands on the ground, hands shoulder-width apart, shoulders stacked straight above your wrists, legs extended behind you wider than hip-width apart, and your core and glutes committed. This is the initial position.
- Pull your left elbow back to do a row, increasing the dumbbell toward your chest and holding your elbow close to your trunk. Keep your abdominals and buttocks tight to control your hips from rocking.
- Lower the weight to the initial position. Do the exact thing with your right arm. This is one rep.
Tips and Safety Precautions:
Before you start with these exercises, there are some essential tips and security protection you should bear in mind. While exercising is good for your fitness, accomplishing it incorrectly or without sufficient preparation can lead to damage.
- Warm-up: Start with a light warm-up. This can contain a quick walk, jogging in place, or even some light cardio. It is important to get your blood flowing and muscles warm before beginning your exercise performance.
- Start with lighter weights: If you are new to dumbbell exercises or have not worked out in a while, begin with lighter weights. As you create strength, slowly increase your weight.
- Form and technique: Focus on holding proper form and practice lifting heavy weights. Incorrect forms can lead to damage and less useful workouts.
- Listen to your body: Stop instantly if you feel pain or discomfort during any activity. It is important to listen to your body’s signals to evade injury.
- Incorporate stretching: After your training, take some time to stretch. This will assist prevent muscle stiffness and help recovery.
FAQ
Do dumbbells help with posture?
Dumbbell rows are a great exercise to do while maintaining perfect posture. The lats and traps, two crucial postural muscle groups that resist the slouching pressures of the chest, are strengthened by this straightforward exercise.
Does back strengthening help to better posture?
Stretching and strengthening the muscles in the upper back, chest, and core is essential for correcting bad posture.
Does having a weak back cause improper posture?
Poor posture over time causes deeper supporting muscles to atrophy from lack of use since it necessitates the use of phasic fibers for support. Unused, weak muscles tend to constrict, and this compression of the vertebrae in the spine and the following worsening of posture can result.
What can I do to correct my posture quickly?
Try gently moving your head side to side, front to back, or in little circles. Every day, spend two to three minutes lying flat on the ground. Relax while performing this exercise without any cushions or other supports. Your body will be allowed to return to its natural resting position as a result, which will enhance your posture.
Which muscles are weak in poor posture?
Regularly holding the same posture may shorten the chest muscles and weaken the neck and small upper back muscles that help draw the shoulders back. Due to having to work harder, the major back and neck muscles, like the trapezius and rhomboids, become tight and sore as a result.
What back exercise is the best?
The dead lift is still the best exercise for the back since it works your complete posterior chain while also stabilizing your lats and core. Going heavy is encouraged here, and you’ll see how much more formed your back becomes as your pulls get stronger. Avoid missing deadlift day.
Which muscle is most crucial for proper posture?
The hamstrings and big back muscles, among other muscle groups, play a crucial role in keeping our posture. When they are in good working order, these postural muscles and others stop the forces of gravity from forcing us forward. Our equilibrium while moving is also maintained by our postural muscles.
What four qualities define excellent posture?
Good posture tips:
With your shoulders back, stand tall and straight.
Keep your head in line with your body and level.
Pull your stomach in.
Put a shoulder-width distance between your feet.
Keep your knees from locking.
Put the majority of your weight on the soles of your feet.
Your hands should be free to hang at your sides.
What signs of bad posture are there?
6 Signs You Have Poor Posture:
Tight pecs and rounded shoulders Office workers frequently exhibit bad posture, which is shown by their overly rounded shoulders and tight chest muscles.
Forward head carriage.
Hunched back (kyphosis).
Recurring headaches.
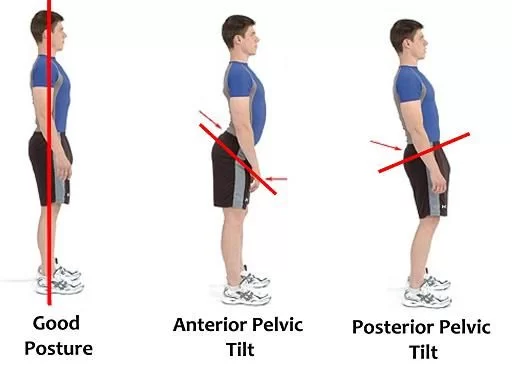
Tilted pelvis.
Back/ neck pain.