Extensor indicis muscle
What is Extensor indicis muscle?
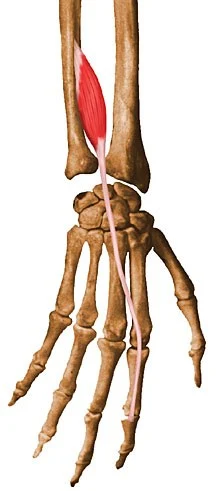
The extensor indicis is a long, narrow muscle in the forearm’s posterior compartment. It has a place with the profound extensors of the lower arm, along with the supinator, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, and extensor pollicis brevis muscles. By applying deep pressure with the index finger extended over the lower part of the ulna, the extensor indicis can be felt.
The main function of this muscle is to extend the index finger at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. One of the few fingers with its extensor muscle, the index finger can extend independently of other fingers. Furthermore, the extensor indicis muscle delivers a feeble expansion of the wrist.
Origin of Extensor indicis muscle
It starts from the back surface of the distal third of the ulna and interosseous layer.
Insertion
It fits into the index finger’s extensor expansion.
Relations
The extensor indicis is located in the forearm’s deep extensor compartment, medially adjacent to the extensor pollicis longus, lateral to the extensor carpi ulnaris, and deep to the extensor digitorum.
The extensor indicis tendon is located in the fourth dorsal (extensor) compartment of the wrist, deep into the extensor retinaculum. It sits medially to the tendons of the extensor digitorum muscle in this compartment, which it shares with them in their common tendinous sheath. The tendinous sheath of the extensor digiti minimi (the fifth extensor compartment) is laterally located, while the sheath of the extensor pollicis longus (the third extensor compartment) is located midway between them. Additionally, the extensor indicis and extensor digitorum share a deep passageway with the posterior interosseous nerve.
Innervation
A posterior interosseous nerve, a branch of the radial nerve that originates from the spinal roots C7 and C8, supplies the extensor indicis with its nerve supply. The same nerve supplies the muscle-covered skin, whose fibers originate from the spinal roots C6 and C7.
Blood supply
The posterior interosseous branch of the ulnar artery supplies the extensor indices’ superficial surface with arterial blood, while the anterior interosseous artery’s perforating branches supply the deep surface with blood.
Function of Extensor indicis muscle
The index finger is extended by the extensor indicis at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. The index finger, in contrast to the majority of the other fingers on the hand, has its extensor, allowing it to extend independently of the other fingers. What’s more, as it crosses the wrist, this muscle delivers a feeble expansion of this joint.
Related pathology
Tenosynovitis is the most common condition that affects the Extensor Indicis Propius.
Extensor indicis muscle stretching
With your affected elbow bent roughly 90 degrees, place it at your side. Then, with your palm facing down, make a fist.
Slowly straighten your elbow until your arm is down by your side, keeping your wrist bent.
Maintain for at least fifteen to thirty seconds.
Two to four times.
Extensor indicis muscle strengthening exercise
Resisted Isometric Finger Extension
Place your affected arm on a table with your palm facing down and fingers flat on the table to begin. Sit down.
Hold your middle, ring, and little fingers bent with your thumb or the table, keeping your index finger straight.
To prevent the index finger from rising toward the ceiling, use your opposite hand.
During the exercise, try to keep your forearm and wrist on the table.
Recount this exercise 5-10 times.

FAQ
Where can I find extensor indicis?
The extensor indicis [proprius] is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle that is located in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm. It is parallel to and medial to the extensor pollicis longus in human anatomy. It extends from its tendon, which connects it to the index finger.
Which muscles help the index finger stretch?
The extensor digitorum (ED), which has separate tendons for each finger and multiple compartments, is the primary extrinsic muscle that extends the fingers. The extensor indicis (EI) and extensor digiti minimi (EDM) muscles extend the index and little fingers, respectively, as additional extrinsic extensor muscles.
What is the pain in the extensor indicis tendon on the hand?
Repetitive movements that over time cause irritation in the tendons and overload them with more weight or tension are typically the root cause of extensor tendinitis. Working with your hands or feet, participating in a sport, or engaging in a regular activity are the most common causes.
Extensor indicis is what nerve?
Extensor indicis accepts its apprehensive stock from a back interosseous nerve, a part of the outspread nerve got from spinal roots C7 and C8. The same nerve supplies the muscle-covered skin, whose fibers originate from the spinal roots C6 and C7.
What does the extensor indicis do?
Function. The extension of the second digit at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints is the Extensor Indicis Propius’s primary function. It may help you extend your wrist. It makes it easier to kidnap the index finger.