Extensor Tendonitis
What is Extensor Tendonitis?
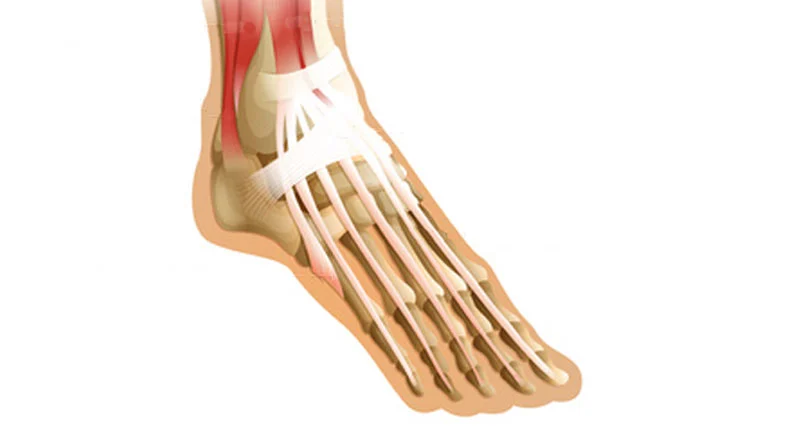
Extensor tendonitis, also known as extensor tendinopathy or tenosynovitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the extensor tendons in the body. These tendons are responsible for facilitating the movement of our joints, enabling us to extend our limbs and digits. Extensor tendonitis most commonly affects the tendons located in the hands, wrists, and feet, but it can occur in other parts of the body as well.
Extensor tendinitis is typically caused by repetitive actions that, over time, irritate your tendons and put too much strain or weight on them. The most frequent reasons are using your hands or feet while working, as well as participating in activities for prolonged periods of time such as typing, playing musical instruments, or participating in sports like tennis and golf, are at a higher risk of developing extensor tendonitis.
These are the two primary toe extensor tendons:
- The long extensor of the hallux elevates the big toe.
- The muscle in the thumb that extends to raise the other four toes
Causes of Extensor Tendonitis
Extensor tendonitis in the foot can occur for a variety of reasons, including the following:
- Friction
- Activity
- Calf Tightness
- Abnormal Foot Arches
- Injury
Friction: Extensor tendinopathy maximum generally happens because of the foot rubbing towards a good shoe, both from the shoe being too small or being laced up too tightly.
Activity: People who spend a lot of time on their feet, especially those who walk or run on uneven ground or up and down hills, are more likely to suffer from it.
Calf Tightness: In the lower leg muscles put the extensor muscles under more noteworthy strain making tendonitis bound to create.
Abnormal Foot Arches: Individuals with high foot curves are bound to have tension on the highest point of their foot, and individuals with level feet track down their extensor ligaments under more strain, the two of which build the possibility of creating tendonitis.
Injury: Extensor Tendonitis can likewise happen after a physical issue, for example, in the event that you have dropped something weighty onto the highest point of your foot.
Symptoms of Extensor Tendonitis
The hallmark symptoms of extensor tendonitis include pain, tenderness, and swelling around the affected tendon. In some cases, individuals may experience weakness or a limited range of motion in the affected joint. The pain is often exacerbated during movements that involve extending the affected joint or when pressure is applied to the affected tendon.
Extensor tendinopathy typically affects the top of the foot, though it may occasionally affect the arch of the foot:
- Top of Foot Pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
Top of Foot Pain: tends to get better with rest and worse with activity. Shoes may be uncomfortable to wear because the top of the foot may be tender to the touch.
Swelling: There might be some noticeable expansion or potential swelling across the highest point of the foot or a knock on top of the foot
Bruising: You might see some gentle swelling across the highest point of your foot
Try drawing your toes up toward you while resisting the movement with your hand as a simple test for extensor tendinopathy. Assuming that reproduces your aggravation on top of your foot, you presumably have the condition. Extensor tendonitis is one of the most well-known reasons for top-of-foot torment.
Diagnosis of Extensor Tendonitis
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to prevent the condition from worsening and to promote a full recovery.
It’s possible that you have mild inflammation if you have pain in the top of your foot but it goes away after a few days of rest. You should see a doctor if the pain persists for days and gets worse when you exercise or wear certain shoes.
Extensor tendonitis is a genuinely normal condition, so your essential consideration doctor or a specialist at a stroll-in center might have the option to analyze your concern. You may likewise have to see a specialist who has practical experience in feet, or an orthopedist, a specialist who has some expertise in foot and lower leg wounds. The Healthline FindCare device can give choices in your space in the event that you don’t as of now have a specialist.
Your doctor will examine your body and inquire about your symptoms during the appointment. To make sure there aren’t any fractures causing your pain, an X-ray may be taken. In serious cases, other imaging devices might be utilized. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are two examples, both of which offer in-depth views of tendons, muscles, and other soft tissue. These additional screenings can be helpful in determining whether or not additional tendons or muscles have been injured and which parts of the foot may require medical attention.
Assessment of Extensor Tendonitis
To aid in the diagnosis of extensor tendonitis, a professional therapist uses the resisted dorsiflexion test.
This includes inspiring you to lift your foot and toes up while they delicately oppose the development. In the event that this is difficult, the test is positive, accordingly demonstrating potential extensor ligament injury.
Complications of Extensor Tendonitis
Tragically, not all instances of extensor tendonitis can be treated with ice, rest, and other harmless means. In these cases, where the ligaments are so severely harmed or they simply don’t answer different medicines, medical procedures might be fundamental
Like any activity, a ligament medical procedure conveys the dangers of contamination, draining, and entanglements from sedation. The surgery, on the other hand, is successful in restoring the tendons’ strength and range of motion and is generally well tolerated. The recuperating time can require as long as half a month prior to you can begin to continue typical exercises with the harmed hand or foot. Following this kind of surgery, physical therapy is typically required.
Treatment of Extensor Tendonitis
Treatment typically involves rest, avoiding activities that worsen the symptoms, application of ice packs, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy and exercises may be prescribed to strengthen the affected tendons and improve flexibility.
Rest: It is genuinely critical to try not to exasperate exercises for adequate opportunity to permit the ligament to mend. Rest until the aggravation has gone. If you keep training when your foot hurts, it will only worsen the injury and take longer to heal.
Healing will take much longer if your injury becomes chronic or the tendon degenerates.
Ice: Utilizing ice consistently diminishes aggravation and irritation. Visit the Ice Treatment area to figure out how to securely and successfully use ice. Apply ice or cold treatment and pressure wrap for 10 minutes consistently at first, decreasing the recurrence as your side effects work on throughout the following 48 hours.
Try not to apply ice straightforwardly to the skin as it might cause ice consumption.
Use a cold therapy and compression wrap or wrap ice in a wet tea towel.
Medication: To alleviate pain and inflammation on the top of the foot, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like naproxen and ibuprofen are frequently utilized. Extensor tendonitis may be treated with ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory medication. In any case, don’t take ibuprofen assuming you have asthma.
Shoe Laces: The least difficult method for treating and forestalling extensor tendonitis is to change the way in which you ribbon your shoes. Tie your knot at the side, or you’ll miss one of the lacing holes over the area that hurts the most. It may appear straightforward, but it actually makes a significant difference.
Exercises: Reinforcing practices for the extensor muscles help to further develop strength and perseverance. Calf stretches can likewise help as having tight calves overwhelms the extensor ligaments.
Orthotics: Shoe insoles and supplements can be utilized to give cushioning and back the foot, taking any unjustifiable pressure off the ligaments.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, more invasive interventions, such as corticosteroid injections or surgery, may be considered.
Physical Therapy:
As well as a recovery program with you, an actual specialist might utilize electrotherapy, for example, Ultrasound treatment to assist with advancing mending.
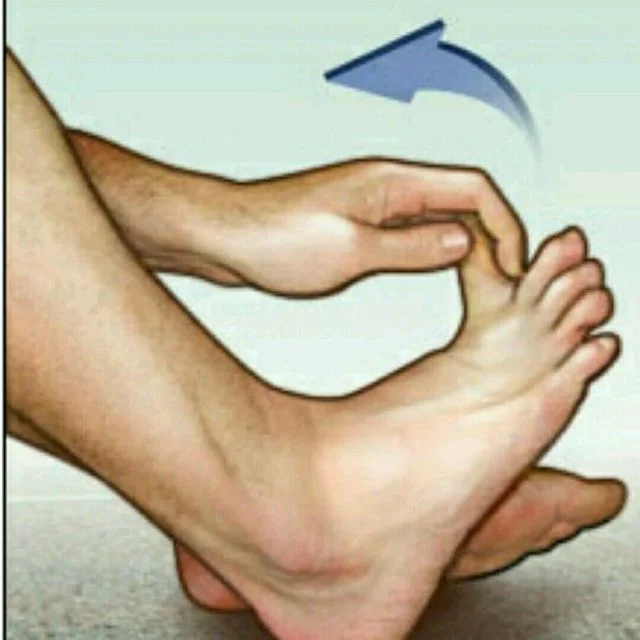
Big toe stretch:
The big toe stretch is a straightforward exercise meant to stretch the toes and alleviate pain.
To do this exercise;
Sit in a seat with your feet flat on the floor and your back straight. Take your left foot up and put it easily on the thigh of your right leg. Then, utilize your fingers to tenderly stretch the huge toe up, down, and to the sides. Keep on doing this for 10 seconds and rehash multiple times. Change to the next foot by putting your right foot on the thigh of your left leg. Follow a similar everyday practice for your right foot.
Toe curls:
This exercise develops the flexor muscles of the toes and feet. It works on the general strength of the toes and feet.
To do this exercise;
Sit up straight in a seat and put your feet level on the floor. Lay a little towel on the floor before you. On one side of the towel, place one of your feet. Have a go at holding the towel with your large toe and the subsequent toe. Pull the towel toward you as you hold onto it. Hold for roughly five seconds. Rehash the normal multiple times and afterward change to the next foot. For the opposite foot, perform the same steps.

Steroid Injections: In the event that the aggravation neglects to settle, a steroid infusion can be given to assist with lessening the irritation. Care should be taken as it really does briefly debilitate the extensor ligament.
Heat: When the underlying difficult intense stage has passed, applying intensity might be more viable. In the beginning, phases when you in all probability have intense irritation, ice will assist with decreasing this.
Heat, on the other hand, may be more appropriate for more persistent injuries where acute inflammatory cells are unlikely to be present.
Summary:
Extensor tendinitis is typically brought on by repetitive actions that, over time, irritate your tendons and put too much strain or weight on them. The most frequent reasons are using your hands or feet while working, as well as participating in a sport or other activity often.
It is crucial to seek timely medical attention if you suspect extensor tendonitis to ensure a proper diagnosis and to receive appropriate treatment to regain full functionality and alleviate discomfort. With proper care and attention, most individuals with extensor tendonitis can recover successfully and return to their normal activities.
FAQs
What does extensor tendonitis torment feel like?
The fundamental side effect of extensor tendonitis in the foot is tormented on the highest point of the foot. It is much of the time right where your shoestrings are. This aggravation might be felt while running or strolling.
Might extensor tendonitis at any point be relieved?
The majority of people begin to feel better as soon as they take a break from activities that irritate their extensor tendons and rest their hands or foot. The normalization of your tendons can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months.
Does tendonitis improve on its own?
The good news is that the tendon will heal on its own, eliminating the need for invasive procedures. Active recuperation and rest could be sufficient to mend the impacted region.
What amount of time does it require for extensor tendonitis to recuperate?
Most people with Extensor Tendinopathy experience relief from their symptoms within three months of following the advice provided; however, in some cases, relief from their symptoms can take up to one year. During your recovery, you may also experience periods of increased pain or flare-ups.

One Comment