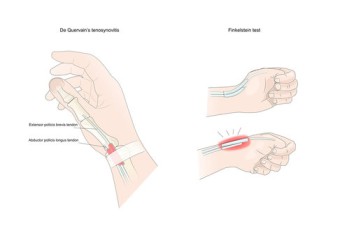
Finkelstein Test
- This Finkelstein’s test is the clinical provocative test for diagnosis & checking De Quervain’s disease.
- This test is described by Finkelstein who has hypothesized the entry of the muscle which is bellies of the abductor pollicis longus = APL & extensor pollicis brevis = EPB.
- Tendons which stay into the first extensor compartment are responsible for the findings observed in the now eponymous test.
Purpose of the Finkelstein Test:
- This Finkelstein test is used to diagnose De Quervain’s syndrome.
- In the fact implies tenosynovitis & tenovaginitis of the extensor pollicis Brevis muscle = EPB & Muscle of abductor pollicis longus = APL.
- Finkelstein test manoeuvre is a helpful test to check & diagnose De Quervain’s Tendonitis/first dorsal compartment tendonitis which is named after the Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain.
- This is the main condition that is brought on by the irritation/inflammation of the wrist joint tendons at the base of the thumb.
- Causes of the inflammation are the compartment means a tunnel/sheath around the tendon of the wrist joint which swells & enlarges to make thumb & wrist joint movement painful.
- This test is also used to determine the Hoffmann disease & paratenonitis in the thumb.
Testing Position of the patient for Finkelstein test:
- Sitting /standing.
Technique of performance of the Finkelstein test:
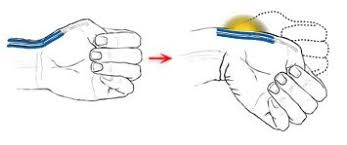
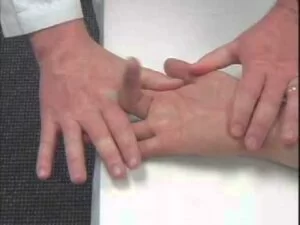
- The patient makes a fist with the thumb inside the fingers.
- The examiner [ therapist ] stabilizes the forearm & deviates the wrist joint toward the ulnar side.
Result of the Finkelstein test
- A positive test is indicated by pain over the abductor pollicis longus = APL & extensor pollicis brevis muscle = EPB tendons at the wrist joint.
- It is also indicative of the paratenonitis of these two tendons.
- Because of this test patients can complain of some discomfort in normal individuals, the examiner should compare the pain caused on the affected side with that of the normal side.
- Only if the patient’s symptoms are produced in the test considered positive.
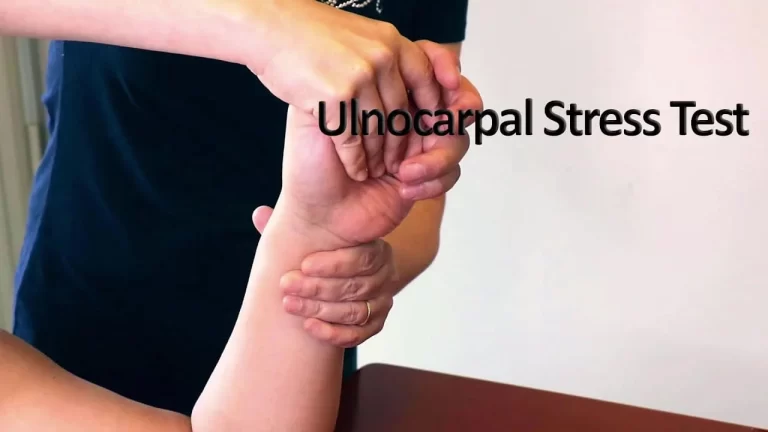
Modification of the Finkelstein test:
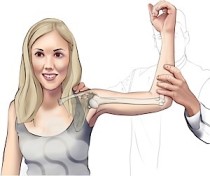
- For the modification, the patient is sitting comfortably & relaxed on the examination table.
- The patient is must behold the affected hand in the air, while the help of the other hand is resting against the body. The examiner [ therapist ] grasps the affected hand of the patient & rotates it in the ulnar deviation at the wrist joint.
- The examiner pulls the patient’s thumb across the palm of the patient hand.
- This is the cause of the give to additional stress on the extensor tendons of the thumb.
- Then the therapist instructs the patient to do active/active assistive flexes of the thumb maximally & wrap the fingers over the thumb & make a fist.
- The patient then ulnarly deviates from the wrist joint which stretches the muscles of the 1st extensor tendon compartment.
- This test is positive if the patient is complaining of pain over the 1st extensor muscle compartment of the wrist joint.
Interpretation of the Finkelstein test:
- The negative result of the Finkelstein test: if The patient does not feel any pain which is radiating up the inside of the patient’s arm from the thumb.
- The positive result of the Finkelstein test: if the patient feels the pain that is radiating up the inside of the patient’s arm from the thumb.
- If the patient reports noticeable pain then, then Finkelstein’s test is positive, which is indicates De Quervain’s syndrome.
Importance of Test of the Finkelstein test:
- The muscles that cross the wrist joint are separated into compartments by the extensor retinaculum.
- In the first compartment of the wrist joint, the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis = EPB & abductor pollicis longus APL pass through which is to attach the distally.
- According to Neumann, EPB = the extensor pollicis brevis which is attached distally to the dorsal side of the proximal phalanx & mechanism of the extensor of the thumb, while the abductor pollicis longus attaches to the distally of
- to the radial-dorsal side of the 1st metacarpal of the hand.
- The combination of the maximum finger flexion & ulnar deviation of the wrist joint elongates these tendons & produces pain in symptomatic individuals.
Reliability of Test of the Finkelstein test:
- Investigation into the validity of the tests is important to know whether our tests are reliable & not.
- Studies that test the reliability of the Finkelstein test the very limited.
- One research showed that the Finkelstein test is highly reliable, but further research is still required.


3 Comments