Hallux Valgus Deformity: Physiotherapy Treatment & Exercise
What is the Hallux Valgus Deformity?
Hallux valgus is a progressive foot deformity in which the great toe deviated towards the 2nd finger (first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint) is affected and is often accompanied by significant functional disability and foot pain, tenderness, and swelling around the joint.
There is a lateral deviation of the great toe and a medial deviation of the first metatarsal bone while the phalanges are adducted. The continuous pain, inflammation, and swelling of the joint leads to bony prominence on the medial side is also called bunion.
The Hallux valgus treatment mostly is a non-operative symptomatic medical treatment with a combination of corrective splint-insoles and physiotherapy exercises that mostly relieve the pain and symptoms and also correct the deformity. If conservative treatment fails then corrective surgery is also recommended by your doctors.
In this article, we discuss the what are causes, and symptoms, How to diagnose the condition, what is the best treatment option for you, which splint you can choose to correct the deformity and possible surgical options.
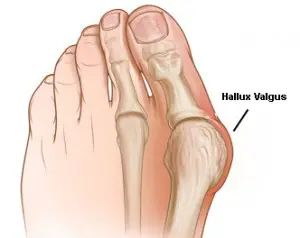
What are the causes of Hallux Valgus deformity?
• Bunions are a widespread foot ailment that can be caused by a number of factors such as
- Genetics – Congenital Hallux valgus is also seen in childhood
- Excess weight gain: Obese people with weak foot muscles create extra strain on the foot to develop initial pain and the pain cycle follows inflammation and swelling over the joint.
- Poor fitness -Activity level
Ill-fitting shoes.
• Other less common causes of bunions include trauma to the
- MTP joint (sprains, fractures, and nerve injuries),
- Neuromuscular disorders, such as Paralysis, foot drop, flat foot
- Limb-length discrepancies.
Few studies report that bunions tend to occur ten times more frequently in women than in men, primarily as the result of wearing narrow, pointy, tight-fitting, and/or high-heeled shoes over a significant period of time. Repetitive stresses to the foot can also cause bunions.
Hallux Valgus Deformity Symptoms:
• Your big toe points toward your second toe, or your second toe overlaps your big toe
• A prominent bump on the inside of the MTP or big toe joint
• Pain on the inside of your foot at the big toe joint when wearing any kind of shoe
• Pain each time the big toe flexes when walking
• Redness, swelling, or thickening of the skin on the inside of the big toe joint
Diagnosis:
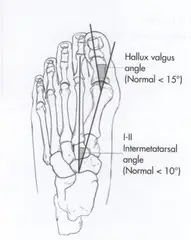
• Radiographic examination shows the angle formed between longitudinal bisection of the 1st Metatarsal and proximal phalanx.
• A big toe position with an angle of up to 10° is still considered normal.
• A minor hallux valgus defect is 16-20°.
• A moderate hallux valgus deformity has a deviation of 16-40°.
• A severe hallux valgus deformity has a deviation of over 40°.
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) will detect cartilage damage, trapped soft tissue, and bone damage.
What is the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformity?
Treatment of Hallux valgus deformity depends upon cause, symptoms, and pain. Mostly Doctor prescribes you pain relieving medicine Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly prescribed medicine worldwide.
Pain relieving gel and patches also help to reduce pain and swelling over the joint.
Corrective splint is the best option to correct the deformity. Splint you can wear it initially few hours because it is painful but as you improve you can wear more and more time to maintain the correction position of the big toe.
Physiotherapy treatment is the best option for you for permanent resolution of the deformity.
Physiotherapy treatment of Hallux Valgus:

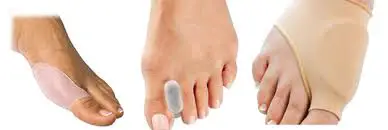
• Adjusted footwear with wider and deeper tip
• Increase extension of MTP joint
• Relieve weight-bearing stresses (orthosis)
• Sesamoid Mobilization: The physiotherapist performs grade III joint mobilizations on the medial and lateral sesamoid of the affected first MPJ. One thumb is placed on the proximal aspect of the sesamoid and is used to apply a force from proximal to distal that causes the sesamoid to reach the end range of motion (distal glides). These are performed with large amplitude rhythmic oscillations. No greater than 20° of movement of the MPJ should be allowed during the technique.
• Strengthening of peroneus longus
• Electrotherapy Modalities – Ultrasound, ice, electrical stimulation, MTJ mobilizations, and exercises. This is more effective than physical therapy alone. The combination will result in an increase in ROM of the MTP joint, strength, and function, and also a decrease in pain.
Pain is the main reason that patients seek treatment for a bunion. Inflammation is best eased using ice therapy, techniques (e.g. soft tissue massage, acupuncture, unloading taping techniques), or exercises that unload the inflamed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help. Orthotics can also be used to offload the bunion.
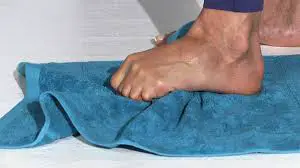
For Restoring the Normal Joint Of Motion –
• Joint mobilization (abduction and flexion) and alignment techniques (between the first and the second metatarsal)
• Massage
• Muscle and joint stretches
• Taping
• Bunion splint or orthotics
• Bunion stretch and soft tissue release.
For Strengthening exercise Of Muscles –
• Towel curls The patient spreads out a small towel on the floor, curling his/her toes around it and pulling the towel towards them.
• The ends of the band are either held by an assistant or secured against an immovable object (e.g. a table leg). The patient then dorsiflexes the ankle, pulling “towards their nose,” working against the resistance of the band.
Surgery for Hallux valgus deformity:
The most commonly used surgical procedures are:
- the modified McBride procedure
- distal metatarsal osteotomies
- metatarsal shaft osteotomies
- the Akin osteotomy, proximal metatarsal osteotomies
- the modified Lapidus fusion
- the hallux joint fusion
After the surgery followed by a corrective splint of the great toe post-operatively to maintain the correct position for a few days. Depending on the surgical procedure, partial or full weight-bearing shoe or cast immobilization is advised for 3 to 4 weeks.
FAQ
What is a hallux valgus deformity?
The great toe (hallux) is malformed or points toward the lesser toes when there is a malformation at the base of the big toe, or metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. Severe forms of the deformity cause the great toe to cross over or under the second toe.
What is the best solution for hallux valgus?
In this instance, the only viable treatment for hallux valgus pain and averting problems in the metatarsophalangeal joint is surgical bunion straightening.
What is another name for hallux valgus?
For people who have been diagnosed with bunions, this information is helpful. Individuals who are exhibiting fresh or persistent symptoms have to get in touch with a medical expert for an evaluation and diagnosis. The deformity known as a bunion (hallux valgus) is brought on by the big toe’s base joint growing laterally.
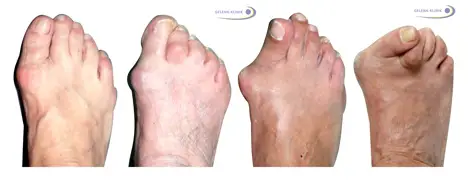
What are the 4 stages of bunions?
the 4 stages of bunions are:
Grade 1 (no deformity)
Grade 2 (mild deformity)
Grade 3 (moderate deformity)
Grade 4 (severe deformity)
Is hallux valgus curable?
There are several ways to treat hallux valgus, from conservative measures to surgery. Approximately 131 distinct surgical methods exist. Nevertheless, there isn’t yet a technique that adequately fixes every hallux valgus deformity.





Nice