Hemiplegia left side : Physiotherapy Treatment and Exercise :
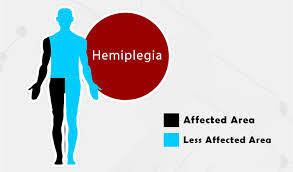
Left Hemiplegia define :
Left Hemiplegia is a condition where left side of the body is paralyzed. Left Hemiplegia is caused by damage to the brain of right side or after a stroke. Symptoms include loss of sensation, lack of coordination, lack of balance, and the inability to properly use the muscles on left side of the body. Left Hemiplegia often impacts a person’s ability to walk, talk, speak, eat, and drink.
Left Hemiplegia is more common as compared to right Hemiplegia mainly due to non-dominant side of Body, Non-dominant side is less active and higher chances of clot and hemorrhage due to High Blood Pressure.
Causes of Left Hemiplegia :
Stroke:
It is the most common cause of hemiplegia.
The stroke may be caused by:
- A Blood clot formed within the artery that goes to brain, blocking the blood supply, known as a thrombus.
- A thrombus breaks away from its site of origin and forms a block everywhere in the blood circulation, known as emboli.
- A sudden blood loss from a blood vessel supplying the brain known as hemorrhage stroke, mainly due to sudden increase of high blood pressure.
Brain infections :
An infection in brain can cause damage to the area of the brain. Mostly infections in brain are caused by bacteria, viral or fungal.
Head Injury (Brain trauma) :
Head injury on right side of Head can cause brain damage. If the trauma only affects ride side of your brain, left hemiplegia can develop. Common causes of Head injury are Bike and car accidents, sports injury, and assaults.
Brain tumors :
Brain tumors on right side can lead to a variety of physical problems including left hemiplegia. Symptoms of Left hemiplegia may get increases as the tumor grows.
Genetics :
A highly rare mutation of the ATP1A3 genetics can cause a condition known as alternating hemiplegia in children. It causes temporary hemiplegia symptoms that come and go. This disorder affects about 1 in 10 lakh people.
Brain Diseases
Diseases that affect brain that cause demyelination of the brain area, for example multiple sclerosis and some other autoimmune diseases. There are many brain diseases that may affect in right side of brain may cause brain lesions or other issues that lead to left hemiplegia or left hemiparesis.
Symptoms of Left Hemiplegia :
Symptoms are vary depending upon area of brain involved, following are few most common symptoms are :
- Difficulty moving, or the inability to move left side of the body.
- Difficulty or loss of bowel – bladder control.
- Altered or loss in sensation on one side of the body.
- Keeping left hand in a fist position.
- Increase muscle tome (Spasticity)
- Loss of Balance
- Difficulty in Walking and performing day to day activity.
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unable to use left Hands.
- Loss of coordination
- Weak fine motor skills
- Slurred speech.
- Bed-sore in Back and left heel region due to long Bed-ridden position.
- Higher function also affected in severe form brain injury – Left side vision difficulty, Hearing problem and memory problems.
- Trouble concentrating with disturbed sleep.
- Pusher syndrome is a disorder occurs after right brain damage(Left Hemiplegia) in which patients actively push their weight away from the nonhemiparetic side to the hemiparetic side.
- Behavior changes such as Depression
- Seizures
- Breathing difficulties rarely affected.
Diagnosis :
Left Hemiplegia is identified by clinical examination by a physiotherapist or Neaurologist/Physician. Radiological imaging like a CT scan or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain should be used to confirm injury in the right brain area and spinal cord, but alone cannot be used to diagnosis of hemiplegia.
Left Hemiplegia patients usually have typical gait. The left leg is extended and internally rotated and is swing in a wide, lateral arc rather than lifted in order to move it forward. The upper limb on the same side is also adducted at the shoulder, flexed at the elbow, and pronated at the wrist with the thumb tucked into the palm and the fingers curled around it, This kind of gait pattern called Hemiplegia gait.
There are a variety of standardized assessment scales mostly used by physiotherapists and neaurologist for assessment / evaluation of the status of left hemiplegia. The use of this assessment scales may help physiotherapists and Doctors to check progression of their treatment plant.
Manual Muscle Testing and Voluntary control grade are help to decide exercise plan and Modified ashworth scale are used to measure spasticity scale and this scale help to decide which muscle required stretching exercise.
This assessment may help :
- Assessment may help recovery pattern (treatment interventions) based on specific identifiable motor and sensory deficits.
- Create appropriate short- and long-term goals for treatment plan based on the scales, and assessment.
- Evaluate the potential cost of care and monitor any changes depends on either improving – declining scores.
Treatment of Left Hemiplegia :
Treatment of Left hemiplegia depend on the symptoms and cause of left Hemiplegia. Left hemiplegia often require multidisciplinary rehab team such as Physiotherapy treatment, Occupational therapy, Physician, Speech therapist and mental health professionals.
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatment are depends on assessment of the Left Hemiplegia carried out by Physiotherapist. Physiotherapist helps to you to improve balance, improve strength of left side weak muscles, and also improve co-ordination of movement and also helps to improve flexibility with the help of Stretching exercise of tight/spastic muscles.
Physiotherapist are using various Neauromuscular Developmental technique also called NDT to improve mobility and function of Left Hemiplegic side. These technique helps you to faster recovery and able to get movement control and also helps in reducing spasticity.
Neurofacilitatory Techniques:
Bobath Approach :

Bobath approach develop by Berta & Karel Bobath – focuses to control responses from damaged postural reflex mechanism. Emphasis is placed on affected inputs facilitation and normal movement patterns
Rood’s Approach use of activities in developmental sequences, sensation stimulation and muscle work classification. Various sensory stimuli such as icing, tapping and brushing are used to facilitate activities.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) :
Developed by Knott and Voss, they recommend the use of peripheral inputs as stretch and resisted movement to reinforce existing motor response.
Total patterns of movement are used in treatment and are followed in a developmental sequence. It was shown that the commutative effect of PNF is beneficial to left Hemiplegia patient.
However, Comparing the effectiveness of PNF, Bobath approach, Rood’s approach and other traditional exercise, demonstrated that no one approach is better as compared to others.