Middle Back Pain
What is a Middle Back Pain?
Middle back pain refers to discomfort or pain felt in the thoracic spine, which is the region of the spine that runs from the base of the neck down to the lower back. This area of the spine is made up of 12 vertebrae and is responsible for supporting the upper body and protecting the spinal cord.
Middle back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, muscle strain, spinal problems such as herniated discs or degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, or even stress and anxiety. The pain may be dull or sharp and may be accompanied by stiffness, muscle spasms, or difficulty moving.
It’s important to seek medical attention if middle back pain is severe or persistent, or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, numbness or tingling, or difficulty breathing. Treatment for middle back pain may include medication, physical therapy, chiropractic care, or in some cases, surgery.
What is the middle back?
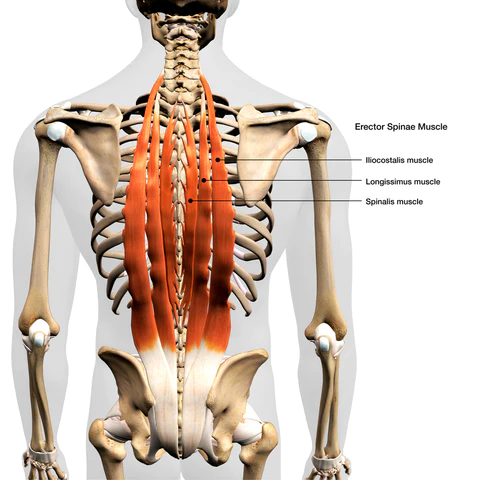
- The middle back contains the thoracic spine which consists of 12 vertebrae.
- These all vertebrae are united to the ribs and the rib cage space between the neck and the diaphragm muscle.
- The thoracic erector spine group of muscles is around the thoracic spine.
- The thoracic erector spine group of muscles contains the Iliocostalis, Longissimus, and Spinalis the main extensor backward flexing muscle of the thoracic spine which is situated on either side of the thoracic vertebral column.
- The erector spine muscle is huge in the thoracic and lumbar regions.
Which are the causes of middle back pain?
- Poor posture: If your posture is involved recited stress on the spine which causes middle back muscle pain. Because the muscles and ligaments of the back work hard to maintain you balanced when you slump. So the overuse of these muscles which is caused aching and spasm of the middle back muscles.
- Obesity: Heavyweight and lower back pain have a positive correlation with obesity and back pain. So when your weight boosts, that increase the risk of middle back pain.
- Muscle sprain or strain: Sprains represent the pulling and stretching of ligaments. Strains represent the pulling and stretching of muscles and tendons. When you are regularly lifting heavy weights inappropriately it is cause a sprain or strain of the middle back. Sprains and strains also happen after an awkward and sudden jerk during movement.
- Fall or another injury: This middle back pain causes very less because of injury than the lumbar spine and cervical spine pain. These fall injuries contain:
- A car accident
- Blunt force trauma
- Sports accident
- A strong fall for example down the stairs and from a height
- A thoracic spine injury occurs to anyone, but aged people are at a higher risk than younger.
When you sense middle back pain after the incident consult your doctor instantly.
- Herniated vertebral disk: A herniated vertebral disk happens when the internal gel-like seat of a vertebral disk in your middle back presses against the outer round of cartilage, which is spread to place pressure on a nerve. This sickness is normally called slipped vertebral disk or ruptured vertebral disk (PIVD). This force is caused nerve pain, tingling, and numbness in the middle back region which also spread to the nerve in the leg region.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis – OA is a degenerative disease of bone that happens when the cartilage surrounding joints break down, which leads to bones rubbing together.
- Aging: Middle back pain mainly happens in 30-50-year old people. Some age-associated procedures which are inherently frayed the body, involve thinning bones, a decrease of synovial fluid between joints in the spine, and a decrease in muscle mass all things are created in middle back pain.
- Fractures: Vertebral fractures usually happen because of trauma for example fall, car accident, and sports injury. These fractures also happen in people with a decreased bone density for example people with OA. Fractures are developed into intense middle back muscle pain which is evolved worse while the movement. Because of the fracture, you also sense incontinence, tingling, and numbness this fracture is occasionally impacting the spinal cord.
- Kidney problems: Kidney problems generate pain in the middle back which survives under the rib cage on either side of the spine.
- Lifestyle factors: When you don’t exercise daily it conducts to weak muscles, which is donating to pain. If you do wrong lifting it causes middle back muscle pain.
- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis this sickness is a type of bone degenerative disease that is shown to result in breakable bones. It happens when the body doesn’t produce sufficiently new bone to return the raw bone loss.
- Mental health conditions: When you are undergoing depression and anxiety it leads to boosts the risk of growing middle back muscle pain.
- Scoliosis: Scoliosis indicates the spine curve evolves sideways which shows the uneven allocation of weight throughout the back and creates middle back pain.
- Tumor: If ensure to a tumor is evolving in the middle back, it may implicate the spinal alignment which is operated to pressure the surrounding structures(nerves, muscles, and ligaments).
Which are the symptoms of middle back injury?
- You experience several different signs of middle back pain
- Your symptoms rely on the reason for the pain.
- You experience muscle aches and a dull type of pain.
- You also experience too sharp and stabbing pain.
- This type of pain is occasionally a burning-like sensation
- You are sensing tightness and stiffness(spams) in the muscle.
- Occasionally you experience tingling and numbness in the arms, legs, or chest.
- Also sensing muscles weakness in the legs or arms
- Occasionally loss of control in the bowel and bladder.
- You experience trigger and tender points in the middle back region.
- You are marked swellings and spasms around the affected region.
How to diagnose middle back pain?
You must consult your doctor when the signs evolve too extreme so that obey the diagnosis to try to know the reason for the middle back pain.
The doctor is operating the following steps for diagnosis:
Physical exam:
While the physical exam, the doctor estimates your spine, head, pelvis, abdomen, arms, and legs.
When happening in an accident as an emergency responder you put a neckband around your neck while the examination stabilizes the cervical spine.
Testing:
Your doctor is recommended to do some tests which are useful to diagnose these tests involving neurological examination and imaging tests.
A neurological test explores the function of the brain and spinal cord.
This test shows the situation of the spinal cord and nerve endings.
Imaging tests are useful to detect any injury in bones.
These tests reveal fractures, bone degeneration, and other causes of middle back pain.
The imaging tests contain:
- MRI scan
- X-ray
- CT scan
- ultrasound
These imaging tests let your body do any damage to your spine and determine a proper protocol of treatment.
What is the treatment for middle back pain?
RICE protocol:
When you experience pain in the middle back region doctor is recommended the RICE protocol as home management or primary treatment.
- R–rest: When you experience muscle pain doctor recommends rest for sometimes form activities for reducing muscle pain.
- I-ice: The doctor recommends ice on the painful area for 20 minutes, It will reduce swelling and muscle pain but always used ice with the use of a towel between the skin and ice to control ice burn, can also be used for an ice pack and frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C-compression: The doctor recommends also applying compression bandages to reduce muscle pain and swelling.
- E-elevation: When you experience pain in the middle back region you must be used the pillow under the knee to reduce the swellings and pressure over the back region also take care in the sleeping position.
Pain medication:
In some cases of muscle pain, the doctor specifies anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant drugs.
When a doctor suspects this muscle pain is because of depression then the doctor is recommended an anti-depressant drug but doesn’t take it for a longer period.
An opioid is recommended for extreme pain but this drug is also not recommended for a long duration– 7 to 10 days.
You can also use pain-relieving gel and spray for example move gel and spray on the painful area to reduce muscle pain and swelling.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for middle back pain?
When the pain isn’t alleviated after the home treatment and pain medication then the doctor recommends physiotherapy treatment to reduce muscle pain and improve flexibility and strength of the back.
Physiotherapy treatment assists you to alleviate pain, swelling, spasm, and tightness of the muscle.
Physiotherapy management contains massage, electrotherapy treatment, and exercise therapy.
Massage:
When the trigger and tender points are present in the affected area physiotherapist is recommended to massage therapy for relieving pain and muscle spasms in the affected region.
Massage is used after 2-3 days of following the RICE protocol when you experience reduced pain.
Massage is used with the help of the oil and applied for 10-20 minutes.
Massage is used 3 times/a day at home or the clinic.
Electrotherapy:
After the RICE protocol, pain medication, and massage if the pain isn’t reduced then used electrotherapy for reducing pain.
To reduce the swellings, spasms, and pain physiotherapist suggested electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the physiotherapist has used machines that are useful to alleviate the pain.
When the trigger and tender points are present physiotherapists are instructed to implicate ultrasound therapy(US) for the reduction of pain.
This treatment is used with the help of ultrasonic gel and applied for 10-15 minutes on the affected area.
For alleviating pain physiotherapists used short wave diathermy(SWD), Interferential Therapy(IFT), and Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation(TENS) on the area of pain.
- SWD(short-wave diathermy) is deep heat therapy to reduce muscle spasms and pain in painful regions.
- IFT(Interferential Therapy) and TENS(Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) are applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of pain.
- Electrotherapy is used for 10-15 minutes on the affected area.
Exercise therapy:
After obeying the RICE protocol for 2-3 days at home and primary treatment and the help of pain medication, you experience reduced pain.
When you experience too relaxed and release from your pain then the physiotherapist is recommended to you exercise therapy to improve flexibility and strengthen muscle and ROM.
Exercise therapy for muscle pain contains stretching and strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to reduce muscle tightness and strengthening exercise assists you to reduce muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
This stretching is involved when your pain is reduced and when you perceive comfort.
- Cat-Cow
- Passive backbend
- Seated twist
- Cobra Pose
- Child’s pose
- Latissimus dorsi stretch
1. Cat-Cow:
- Begin this stretching on all fours with your wrists straight under your shoulder and knees under your hip.
- Experience to free for your knee on a blanket when you sense discomfort.
- Extend your fingers wide and distribute to weight evenly throughout your hand.
- Push your palms and fingers into the floor to avoid leaving weight on the wrist.
- Then take a deep breath and kindly move your pelvis upward your heart forward and drop your belly downward and face upward.
- Try to make an arch in your back like a cat, rounding your back region.
- Try to fold in your pelvis and let your head hang flexibly.
- Repeat this 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

2. Passive backend:

- First, roll up a towel or yoga mat.
- Place the roll on the ground.
- You must want to roll only part of it when you use a yoga mat. Relying on your middle back flexibility and the mat’s thickness.
- A bigger role needs more flexibility and a smaller one offers a more peaceful release.
- You are lying on the roll so that it relaxes against the base of your shoulder blades, near the middle of your back.
- For this backend, if you use the yoga blocks, put one block under your shoulder and a second block beneath your head.
- Then elevate your head as much as essential so that your neck feels supported.
- Must stay calm in your posture and put a second blanket under your head for example a pillow.
- Maintain your breath long and deep.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.
3. Seated twist:
- You are sitting cross-legged if possible if not then seat in a chair.
- You sit up elevated and put your right hand behind you carrying your left hand to your right knee joint.
- Try to softly twist your heart to the right.
- Extend through the back and sense the twist squeezing out the tension in the middle of the back.
- Don’t over-twist by dragging on your knee and twisting too strongly.
- Try to stare over your right shoulder just as far as your neck permits.
- Maintain for 10-15 seconds and release to center.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

4. Cobra Pose:

- Begins with lying in a prone position, body extended, jaw on the mat, or face down towards the floor.
- Put your hands beneath your shoulder.
- Try to make a curl by your chest off the floor and engage your middle back.
- Then raise your hands off the floor for a moment and engage through the middle back.
- Try to push lightly into your hands to stronger the stretch.
- Maintain for 10-20 seconds and release to center.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.
5. Child’s pose:
- Start with a kneeling position, with the hip and buttocks resting on the feet(seat on the heel)
- Spread your knee apart to a relaxing point.
- Tuck the body forward and bring the chest down towards the knee.
- If possible bring the forehead to the ground with the arms extended out toward the front.
- The palms should be softly resting on the bottom and must be holding the arms straight.
- Maintain for 10-20 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

6. Latissimus dorsi stretch:
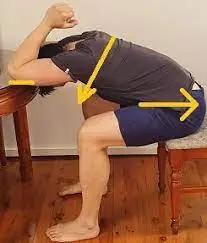
- Start with a standing or sitting position.
- Try to lift the right hand directly upward, over the head level.
- Flex the elbow, so that the right-hand falls toward the middle back.
- Must put the left hand on the right elbow and kindly draw the right arm to the left arm.
- While pulling the right elbow and flex the body in a straight to the left side.
- Make sure not to rely on forward or backward.
- Maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds, then do repeat on the other side.
- Do repeat this exercise 3 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow of electrotherapy and massage for 2-3 days to remove muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the physiotherapist recommended strengthening exercises for improving muscle strength.
This strengthening exercise is always recommended when you experience releasing pain and when you feel comfortable while doing exercises without any kind of pain.
These strengthening exercises will help to reduce muscle weakness and pain.
- Bridge Pose
- Opposite arm/leg raise
- Passive backbend
- Resistance band pulls
- Dumbbell row
1. Bridge Pose:
- Start with a supine position, flex your knees, and put your feet flat on the mat or bed a few inches out from your buttocks.
- Compress your shoulder into the bed and gently fold them to your middle back so that your chest huffs out slightly forward.
- Push into your foot and move your hip up toward the ceiling.
- Grab your hands under you, pushing into your arms and foot to raise your hips kindly toward the roof.
- Get attention to your middle back behind your heart level and intentionally move your chest toward the wall after you.
- This pose is beneficial to bring the backbend out of the middle back region.
- Maintain for 5 seconds before gradually lowering down and unclasping the palms and reaching them to rest beside you.
- Do repeat this exercise 10 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

2. Opposite arm/leg raise:

- Start on your hands and knee(like a cat or cow).
- Must maintain your back straight, with your hands straight under your shoulder and your knees aligned straight under your hips.
- Try to gradually reach out with one arm and extend the leg on the opposite side.
- Must be maintained at both straight levels.
- Keep for 5-10 seconds, then slowly lower your arm and leg and return to starting position.
- Do repeat this exercise 10 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.
3. Passive backend:
- Start with the place of the roll on the ground.
- You are lying on the roll so that it is rest under the shoulder blades, near the middle of the back region.
- Try to put something beneath your head if demands elevation.
- Begin with arms out from the body and resting at a 45-degree angle.
- Maintain this position for 1–2 minutes.
- Do repeat this exercise 10 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

4. Resistance band pulls:
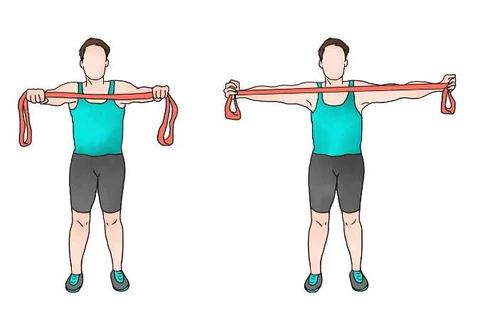
- You are standing with your foot parallel and your hip distance separated.
- Then carry a resistance band and raise your arms out in front of you at shoulder level.
- Must maintain your navel engaged and stand elevated.
- Try to squeeze your shoulder and scapula together as your hands separate and slowly release them back to the center.
- Maintain the exercise for 10-20 seconds.
- Do repeat this exercise 10 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.
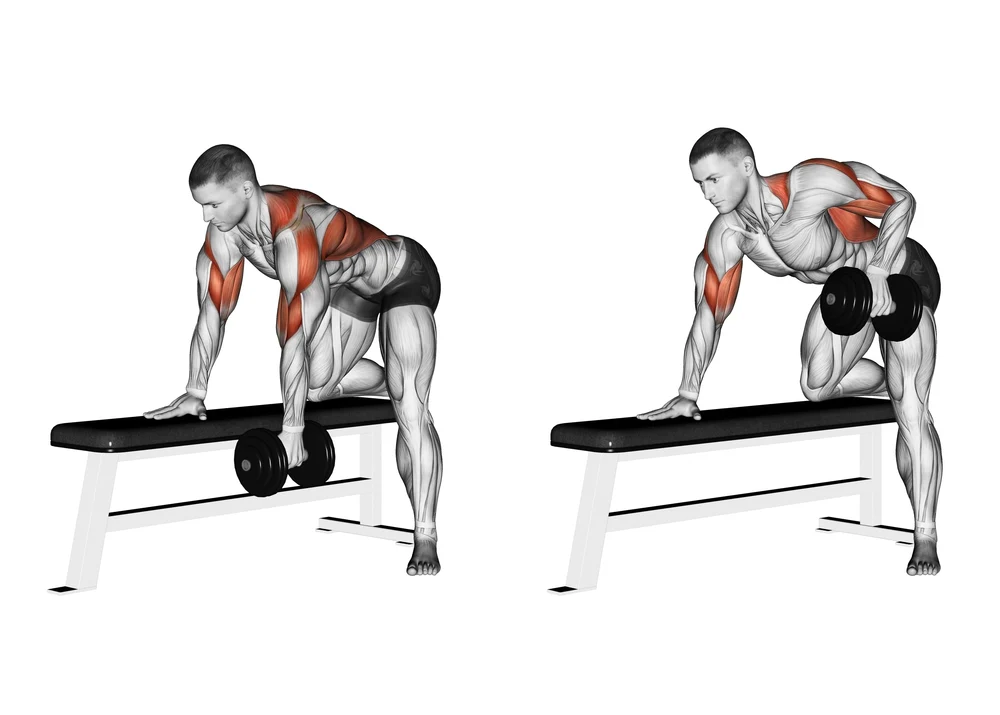
5. Dumbbell row:
- This exercise is conducted on all fours and with the help of a bench or a chair.
- Begin this exercise with a dumbbell in both hands.
- Try to engage your navel to maintain your lower back sustained.
- Gradually extend your elbow to bring the dumbbell in your right hand to your axilla.
- Must hold your arm clasped close to your body.
- When you use a bench for this exercise, your left knee and hand are placed on the bench.
- Your right leg remains on the floor as you row on the right side of your body.
- Maintain the exercise for 10 seconds.
- Do repeat this exercise 10 times/session and perform 3 sessions/day.

What is a surgical treatment for middle back pain?
After the medical treatment and physiotherapy treatment pain isn’t alleviated then the doctor is recommended surgical treatment.
Surgery for middle back pain is very irregular.
Some probable surgeries for middle back pain contain:
- Laminectomy: In this surgery extracts the entire lamina and the back wall of a vertebra which relaxes the compressed spinal cord or nerve.
- Laminotomy: In this process extracts part of the lamina which helps to release a pinched nerve.
- Diskectomy: In this surgery extracts part of a vertebral disk which relieves a pinched nerve.
What are home cures for this middle back pain?
- You use ice on the affected area and subsequently apply heat.
- It is one of the common procedures which is provided quick relief.
- You are taken to consider taking to painkillers like ibuprofen and naproxen to decrease the swelling and pain.
- Stretch and strengthen the middle back muscles by accomplishing exercises for example yoga.
- You must be enhanced your posture to alleviate middle back pain. Use some steps contain to :
- Must maintain your shoulder back while standing position.
- Avoid slumping posture.
- Take breaks in prolonged sitting or standing.
- If you do a desk job must be modifying your chair and computer monitor level, keyboard and mouse positioning which is beneficial to your good posture.
How to Prevent middle back pain?
- You change your sleeping position on a daily routine because If you sleep on your back it is raised the chance of misaligning your backbone which leads to middle back pain.
- There are some positions conveyed which are controlling back pain, try this position: Try to sleep on your side with a pillow between your knees and sleep in the fetal position.
- Try to modify your posture: Preserve good posture which is to provide your middle back muscles a break and allow them to strengthen.
- Your standing and sitting position must be straightforward for that declining the chair level so that your feet remain flat on the floor then moving the computer screens at eye level and using a standing desk for all techniques to enhance your posture.
- If you experience weakness in muscles then consult with a physiotherapist who helps you for enhancing your core strength, posture, spinal mobility, and endurance.
- Always hold a healthy weight because living overweight and obese puts extra pressure on the middle back muscles.
FAQs
When should I worry about middle back pain?
Back pain will reduce in 6-7 days, but if you have been undergoing pain for more than a week, then it is time to consult a doctor. Your doctor will conduct examinations and tests needed to assist get to the origin of your pain before it could evolve into a bigger situation.
Is middle back pain common?
Middle back pain isn’t as common as lower back pain because the spine isn’t as flexible in this region. The thoracic spine contains 12 vertebrae, that divide the bones from each other and immerse shock, and muscles and ligaments that maintain the spine together.
Is middle back pain related to the kidney?
Back pain generally impacts the middle of your back, over your spine, and considerably commonly in the lower back. Spine-associated problems can also force back pain to occasionally ray down your limbs. In comparison, kidney pain is generally located higher on your back and it usually feels sharp.
How to diagnose muscular back pain?
Pain that brings more harm when you move, particularly when flexing and stretching. Difficulty in prolonged standing up straight. swelling in a localized area.
Why is back pain worse at night?
While sleeping, inflammatory chemicals collect in your joints, which is exacerbating pain and stiffness. That’s why people with inflammatory back pain can wake up suffering at the midnight and experience tight and achy first thing in the morning.

5 Comments