Muscle pain in the upper arm
Upper Arm pain is defined as discomfort and pain experienced anywhere throughout the arm.
This pain is located between the elbow and the shoulder joints. This arm pain occurs due to many reasons. The most common causes of muscle pain are injury & overuse. This pain is reduced by pain medication, the RICE principle, and physiotherapy treatment.
What is the upper arm?
The upper arm is situated between the shoulder joint and elbow joint.
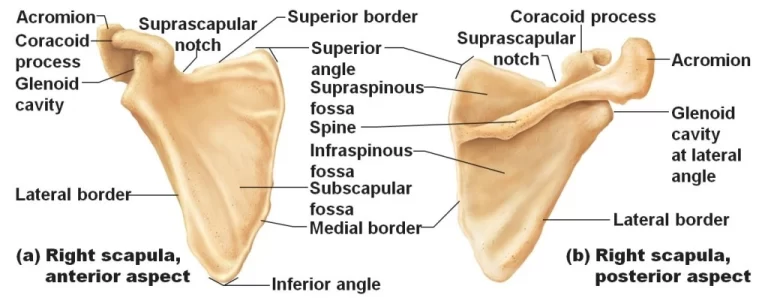
It includes 4 muscles- 3 in the anterior compartment ( biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis ), and one in the posterior compartment ( triceps brachii ).
Causes of the upper arm muscle pain
Pinched nerves:
These Pinched nerves happen when a nerve is too much pressure on the nerve due to surrounding tendons, bones, cartilage, and muscle
Sprains:
Sprain means occurs to stretching and tearing of the ligaments and tendons.
This is a common injury.
Tendonitis:
Tendonitis means arises from inflammation in the tendon.
This tendonitis commonly occurs in the shoulders, elbows, and wrist joints.
Tendonitis is differ from mild to severe.
Rotator cuff injury:
These occur when people perform overhead movements in daily life, like painters and baseball players.
Broken bones:
Broken and fractured bones produce immense, sharp pain in the arm.
Rheumatoid arthritis:
It is a chronic condition that is occurred by to inflammation that primarily involves the joints.
Angina:
It is chest pain that arises when the heart is not getting enough oxygen.
It produces pain in the arm and shoulder as well as produces pressure in the chest, neck, and back. Angina generally indicates an underlying heart difficulty.
Heart attack:
It occurs when the blood can’t get to the heart due to a blockage that is cutting off the heart’s oxygen supply.
Symptoms of the upper arm muscle pain
- The symptoms of this muscle depend on the cause of the pain.
- Seen to have redness and swelling in the arm.
- Also feeling stiffness in the muscle.
- Tingling and numbness are also felt in the muscle pain.
- The patient presents the visible deformity
- Feel shortness of breath and dizziness.
- Also feel chest pain and pressure.
- You also feel weakness and stiffness in the arm.
- In the place of pain, some tender points mean tenderness is also present.
Diagnosis of the upper arm muscle pain
- First, the doctor requires to diagnose the underlying cause of the pain which is to treat it.
- It is first to conduct a history and physical exam, asking them about the activity, potential injuries, and symptoms.
- Based on the symptoms, they do y ctor is to do the following tests which are helpful to the doctor make to a diagnosis.
- The doctor asks about the arms and does other simple movements which are used to evaluate the ROM ( range of motion ).
- This is useful to doctors for identifying the location and cause of potential injuries and pain.
Some diagnostic tests for diagnosis:
Blood tests :
This examination helps them to doctor for identifying some conditions which are produced arm pain, like diabetes and certain disorders which produce inflammation of the joints.
X-rays :
This examination helps the doctor diagnose broken or fractured bones.
If the doctor thinks the arm pain is associated with potential heart complications, they are ordered some tests to consider how to heart is working and evaluate the blood flow via the heart.
Ultrasounds :
This examination is used for high-frequency sound waves which get an image of the inside of the body.
This test benefits to doctor detect problems with joints, ligaments, and tendons.
In some cause, the doctor orders MRI and CT scans which get a more detailed image of soft tissue and bones.
It helps them detect problems.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging [ MRI ]:
This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves which are created to detailed images of places of the body.
Nerve Conduction Study :
This testing process measures the nerve impulses when a small amount of the electrical current is applied so that it is detected in damaged nerves.
Electromyography [ EMG ]:
This test includes inserting a needle electrode into muscles which is measure electrical activity, which is help to detect the damage to the nerves conducting to muscles.
In which condition need an emergency?
- Most of the time arm pain is not a symptom of a medical emergency.
- In many cases, you can treat arm pain with home treatments.
- But you should get to emergency medicine in some cases.
- You must call 911 immediately if you suspect a heart attack or another heart condition that is produced by arm pain.
- Contact the doctor when you feel the pain that occurs with exertion and is relieved by rest it is indicated to reduce blood flow to the heart.
- If you feel severe pain and swelling.
- When occur to any sudden injury
- If you feel difficulty in moving or rotating the arm.
Which condition occurs with arm muscle pain?
Carpal tunnel syndrome :
A common condition that is caused by repetitive activities in the hands, wrists, and fingers.
This condition is lead to tingling, numbness, and weakness in the arms, palms, and fingers.
Tennis elbow:
It is also known as lateral epicondylitis.
It is a typical condition that is produced by repetitive activities in the arms, elbows, and mostly the wrists.
Which is cause pain and weakness in the elbow joint or forearm, along with tenderness on the outside of the elbow joint.
Frozen shoulder
It is also known as adhesive capsulitis, and it is a less common condition that tends to impact adults ages 40-60.
Which is produced in pain and limited ROM ( range of motion ) when the connective tissue around the shoulder joint becomes too thickened and inflamed.
Deep vein thrombosis:
When a form of blood clot forms in a deep vein in the arm, which is produce swelling and extreme pain in the arm.
Treatment for upper arm muscle pain
RICE principle :
In the starting stage of muscle, a pain doctor is a suggestion to you RICE principle as a home remedy and primary treatment.
R [ Rest ]: When you feel pain, all the body requires to rest so that the rest of the area in pain avoids strenuous exercise or movement.
I [ Ice ]: When you use ice on injuries it helps you decrease the swelling and inflammation when using an ice pack always covered them in a towel, for 15 to 20 minutes at a time on the painful region, and wait for at least an hour between the ice packs.
C [ Compression ]: Wrapping the area where you’re experiencing pain with an elastic bandage and brace which helps you decrease the swelling and prevent you from extending a joint too far and encouraging recovery.
E [ Elevation ]: Must keep the arm elevated to help reduce the swelling and pain.

Pain medication
In some cases, pain in the arm is severe enough that the doctor prescribes a pain drug.
You can take to anti-inflammatory drugs mainly Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(NSAIDs) release to muscle pain.
If the pain occurs due to inflammation take to anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids which help you decrease the underlying cause and the subsequent pain.
These anti-inflammatory medications are available as oral medications, injections, and intravenous medications.
Surgery
In many cases of arm pain, surgery is necessary.
Examples include torn ligaments and broken bones.
In carpal tunnel syndrome, the benefit is from surgery which reduces pressure on the median nerve by cutting the ligament which is pressed against both.
Tendinitis benefit from surgical and nonsurgical procedures, including minimally invasive which is ones designed to stimulate healing and remove scar tissue, as well as do the direct surgical restoration of a tendon injury.
Physiotherapy treatment for upper arm muscle pain
The physiotherapy treatment contains massage, electrotherapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises are included.
Massage
If the patient presents tender points and trigger points of muscle pain, the therapist is recommended to massage the patient.
Massage is given with the help of oil on the trigger points for 5-10 minutes.
Massage is given in a circular movement.
Massage is decrease swelling and tender muscle pain.
Electrotherapy treatment :
The electrotherapy treatment includes SWD, TENS, IFT, and US machines for the release of muscle pain and swelling.
When the present to any muscle tender points of muscle pain use US ( ultrasound ) therapy for 5-10 minutes release to the muscle pain and swellings.
For release to pain and swellings therapist is recommended to you Short wave diathermy (SWD), Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), & Interferential therapy (IFT) machines for 10 to 15 minutes on the pain area.
Strengthening exercise
Exercise helps you reduce muscle pain and muscle weakness.
- Neck release
- Chest expansion
- Eagle arms spinal rolls
- Shoulder circles
- Downward Dog Pose
- Child’s Pose
- Thread the needle
- Arm circles
- Eagle Pose
Neck release:
The patient’s position is in a sitting or standing position and ower the chin toward the chest.
Then feel a stretch along the back of the neck, and gently tilt the head to the left to stretch the right shoulder.
Maintain this exercise for up to 1 minute, and then repeat this exercise on the other side.
Perform this exercise on both sides 10 times every day.
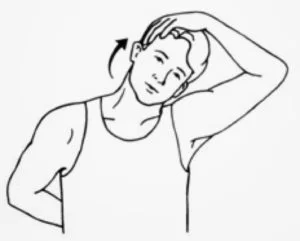
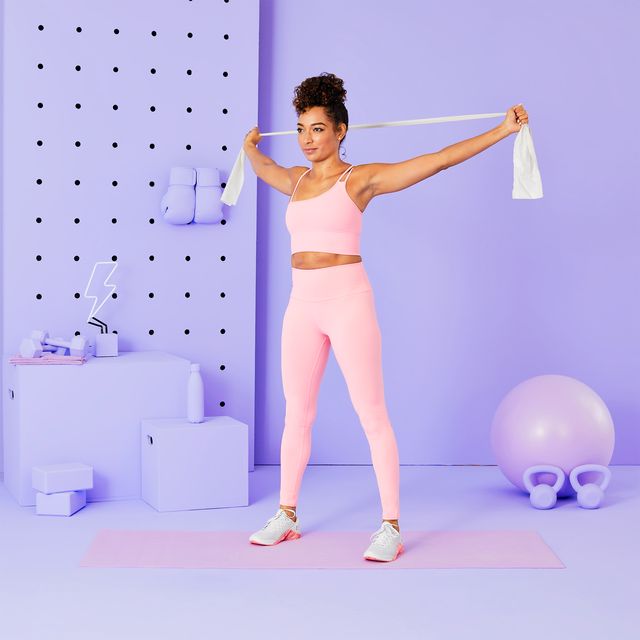
Chest expansion:
The patient’s position is standing position and holds an exercise band, strap, and towel behind the back with both hands.
Broaden across the chest as they move the shoulder blades toward each other, lift the chin and look up toward the roof.
Maintain this exercise position for up to 15 to 30 seconds, and then repeat this exercise 10 times.
For the deep stretch, put the hands closer together along with the towel and strap.

Eagle arms spinal rolls:
The patient’s position is sitting position, extend the arms out to the sides, and cross the elbow joint in front of the body with the right arm on top.
Flex the elbow joint and place the backs of the forearms and hands together.
Reach the right hand around to bring the palms together, and maintain this position for up to 15 to 30 seconds.
On an exhale time, roll the spine and draw the elbow joint in toward the chest.
On an inhale, open the chest and lift the arms, and continue this exercise for 1 minute.
Then repeat on the other side.
Shoulder circles:
The patient’s position is to stand with the left hand on the back of a chair.
Then allow the right hand to hang down, and circle this right hand 5 times in each direction.
Repeat this exercise on the other side.
Perform this exercise 2 to 3 times every day.

Downward Dog Pose:
The patient’s starting position with the hands and knees, and press into the hands to lift the hip joint toward the roof.
Then maintain a slight bend in the knee joint patient press the weight evenly into your hands and feet.
Must keep the spine straight, and bring the head toward the feet so that the shoulders are flexed overhead.
Maintain this exercise position for up to 1 minute, and repeat it many times in the day.

Child’s Pose:
The patient’s position is dog pose, bringing the big toes together and knees slightly wider than the hip joint, sinking the hips back onto the heels, and extending the arms in front of the body.
Then allow the chest to fall heavy toward the ground, relaxing the spine and shoulders.
Must stay in this exercise for up to 5 – 10 minutes.

Thread the needle:
The patient’s starting position is on the hands and knees, and lift the right hand toward the roof with the palm facing away from the body, and then lower the arm to get it under the chest and over to the left side of the body with the palm facing up.
Then activate the right shoulder and arm to avoid collapsing into this region.
Must keep the left hand on the ground for support and lift the hand toward the roof or bring it around to the inside of the right thigh.
Maintain this exercise for up to 15 to 30 seconds, and then relax in the child’s pose before repeating this stretch on the left side.
Arm circles:
The patient’s position is standing up straight with the feet hip-width apart.
Then lift the arms and extend them to the side and create a T shape with the body, and try to make small circular movements with the arms.
Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times and switch the direction of rotation.

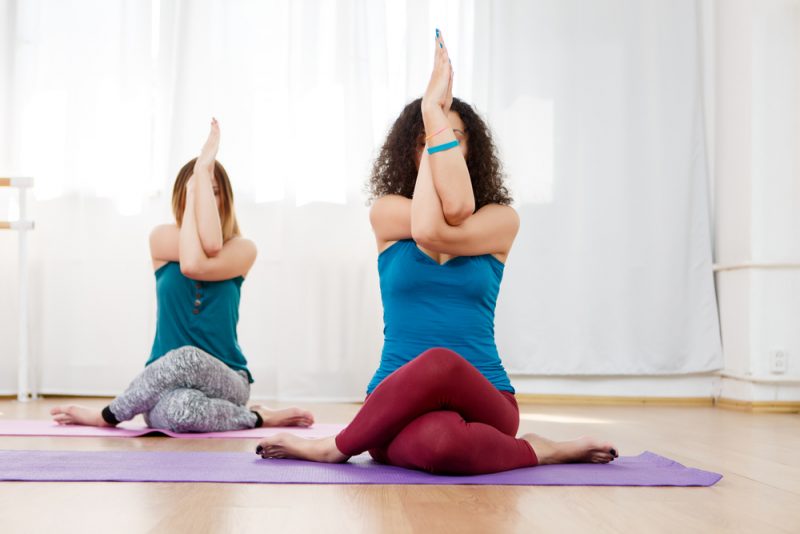
Eagle Pose:
The patient’s position is standing and sitting position then extends the arms to the sides, and then crosses the arms in front of the body, with the right arm over the left.
Flex both arms at the elbows, twist the right forearm behind the left forearm, and bring the palms together.
Then gently raise the arms upward to stretch the shoulders, and maintain this position for up to 15 to 30 seconds.
Then lower the arms and gently release the position.

Stretching Exercise
Stretching is very helpful to you for releasing muscle tightness and muscle pain.
- Shoulder stretching
- Triceps stretching
- Neck stretching
- Across-the-chest stretch
- Doorway shoulder stretch
- Seated twist
Shoulder stretching:
The patient’s position is in a sitting and standing position, cup the elbow joint with the opposite hand.
Raise the elbow joint and pull it across the chest without rotating the body, and maintain this stretching exercise for 15 to 30 seconds, feeling the tension in the shoulder joint.
Then remove the hold and relax, after that repeat this stretching with the next arm, and continue this stretching in 3 repetitions with each arm.
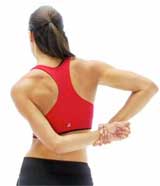
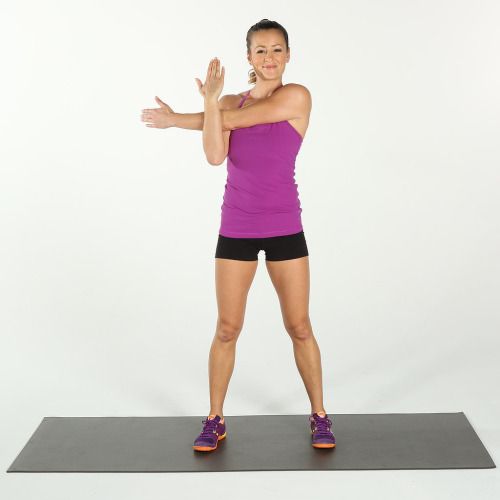
Triceps stretching :
The patient’s position is in a sitting and standing position, lift one arm above the head and flex it so that reaches towards the back, behind the head.
With the help of the other hand, gently push back against the bent elbow joint, maintain this stretching for 15 to 30 seconds and feel the stretch in the tricep.
Remove the hold and relax, then repeat this stretching exercise with the other arm.
Continue this stretching exercise for 3 repetitions in each arm.
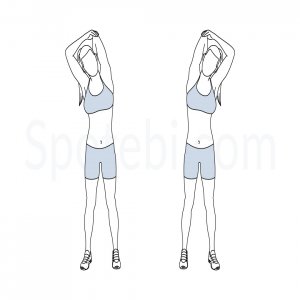
Neck stretching:
The patient’s position is in a sitting and standing position, but the back up nice and straight, facing forward, and then tilting the head to one side, as if they going to place the ear on the shoulder, but don’t move the shoulder joint, and must be kept joint relaxed.
Maintain this stretching for 15 – 30 seconds.
Remove the hold and relax, then repeat this stretching exercise on the other side.
Continue this stretching exercise for 3 repetitions, on both sides.
Across-the-chest stretch:
The patient’s position is in a sitting or standing position, and bring the right arm across the chest.
Then put the arm in the crease of the left elbow joint and use the left hand to support the arm.
Maintain this stretching position for up to 1 minute. Then repeat this stretching exercise on the other side.
This stretches exercise on each side 3 times.
To deepen the stretch, raise the arm to shoulder height.

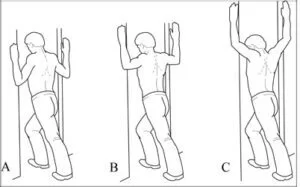
Doorway shoulder stretch:
The patient’s position is to stand in a doorway with the elbow joint and arms forming a 90-degree angle.
Step the right foot forward as the patient presses the palms into the sides of the door frame.
Lean forward and engage the core, maintain this stretching exercise for up to 15 to 30 seconds, and then repeat the stretching exercise with the left foot forward.
Perform this stretching exercise on each side 2 to 3 times every day.
Seated twist:
The patient’s position is sitting in a chair with the ankles directly under the knees.
Twist the upper body to the right, bringing the back of the left hand to the thigh, and then place the right hand down because it is comfortable.
Maintain this stretching exercise for up to 15 to 30 seconds, and then repeat this stretching exercise on the left side.
perform this stretching exercise on each side 3 to 5 times every day.

Complications of upper arm muscle pain
- When you feel aches and pains in the arm, shoulder, and wrist joints it becomes difficult to write, type, talk on the phone, or go about your daily actions.
- If left undiagnosed and untreated, some kinds of injuries and inflammation may cause serious tissue damage that needs surgery or other extensive treatment.
Prevention of upper arm muscle pain
In many cases, arm pain arises due to a preventable injury and condition.
So that you can follow to prevent injury and arm pain:
- You must stretch regularly, particularly before the exercise.
- Always do the correct form for the exercises which are performed to prevent injury.
- Always wear a protective kit while playing sports.
- Lift the heavy things carefully.
FAQ
Why does the muscle in the upper arm hurt?
Overuse, weak muscles, improper or poor technique, & overly strenuous training all can cause upper arm pain; that said, overuse is considered to be the most typical cause of upper arm pain and issues like shoulder bursitis, bicep tendonitis, & impingement.
What causes arm muscle pain without injury?
Common arm pains that are not caused by a specific injury, such as a blow or fall, include the following: Overuse or repetitive motion injuries occur when you “overdo” an activity or repeat the same activity. Repeated movement may stress joints or other tissues and cause pain & swelling.
When should be concerned about upper arm muscle pain?
Arm, shoulder, or back pain that comes on suddenly, is unusually severe, or is accompanied by pressure, fullness, or squeezing in your chest, an obvious deformity, or protruding bone in your arm or wrist, specifically, if you have bleeding or other injuries.
What doctor treats arm muscle pain?
Orthopedic doctors are experts who treat shoulder and elbow pain. An orthopedic expert can analyze the shoulder or elbow and order imaging studies like X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds. He/she will determine what kind of pain you are experiencing, as well as what remedies will help.
Can stress cause upper arm muscle pain?
Anxiety can cause muscles in the arm to become tense, & that tension could cause pain. Although muscle tension-sometimes the result of anxiety is the most likely origin of arm pain, it is not the only possible cause. Heart attack, angina, & injury are other possible causes of upper arm muscle pain.



3 Comments