Nasalis muscle: Anatomy, Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
INTRODUCTION:
The nasalis is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose whose function is to compress the nasal cartilages.
It is the muscle responsible for “flaring” of the nostrils. Some people can use it to close the nostrils to prevent the entry of water when underwater.
Origin: Maxilla
Insertion: Nasal bone
Nerve: Buccal branch of the facial nerve
Action: Compresses bridge, depresses tip of the nose, elevates corners of nostrils
ANATOMY:
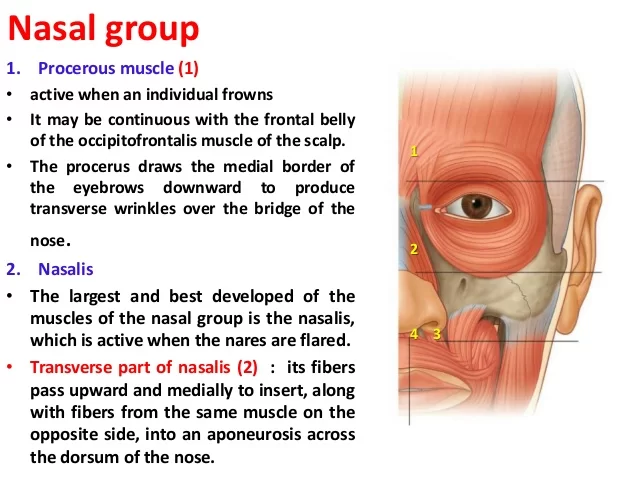
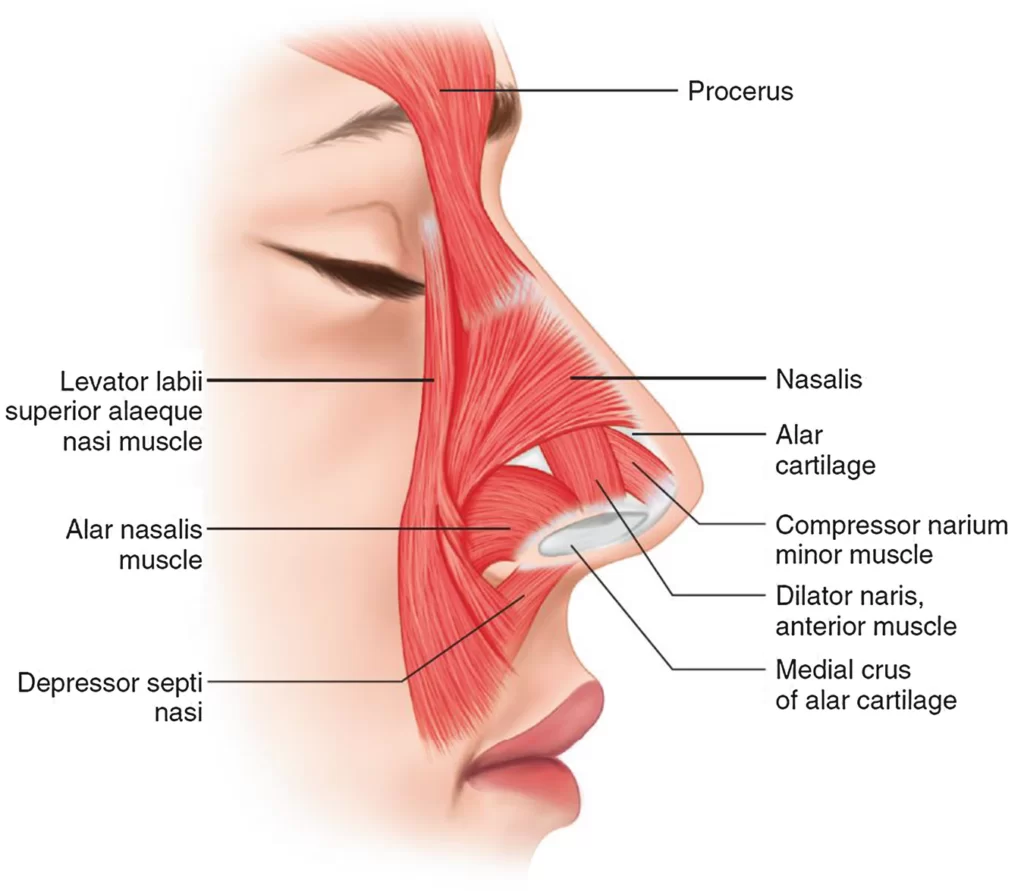
The nasalis muscle, also termed the naris muscle, is divided into two parts:
Compressor nasalis and dilator nasalis. Both are innervated by the buccal branch of the facial nerve.
Compressor nasalis arises from the frontal part of the maxilla just superior to the upper incisors on each side.
It runs roughly medially and transversely to an aponeurosis on the dorsum of the nose. It acts to close the aperture of the nostril.
Dilator nasalis arises from the frontal part of the maxilla at a slightly superior point to compressor nasalis on each side.
It runs medially and slightly inferiorly to insert into the ipsilateral alar cartilages. It acts to open the aperture of the nostril.
The nasalis muscles are used as accessory muscles of respiration during times of respiratory distress; they are partially responsible for ‘nasal flaring’.
The nasalis consists of two parts:
Alar nasalis:
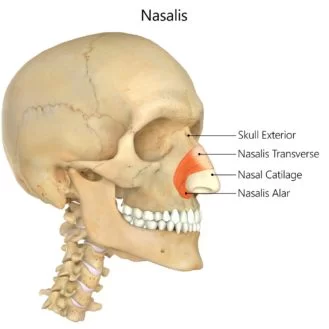
The alar part of the nasalis (also known as alar nasalis, dilator naris, latin: pars alaris musculi nasalis) is a portion of the nasalis muscle that dilates the nostril.
Origin
The alar part of the nasalis originates from the outer surface of the maxilla above the region of the lateral incisor tooth.
Insertion
The alar nasalis inserts into the skin along the posterior circumference of the lateral crura.
Action
The alar nasalis lengthens the nose and dilates the nostrils.
Innervation
The innervation of the alar nasalis is supplied by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Transverse nasalis:
The transverse part of the nasalis (also called transverse nasalis, compressor naris, latin: pars transversa musculi nasalis) is a portion of the nasalis muscle that compresses the nostrils.
Origin
The transverse nasalis arises from the maxilla, its origin site is lateral to the incisive fossa.
Insertion
The transverse nasalis inserts into the aponeurosis of the bridge of the nose.
Action
The transverse part of the nasalis is responsible for compressing and closure the nostril.
Innervation
The nerve supply to the transverse nasalis is provided by the buccal branches of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Description:
- The Nasalis (Compressor naris) consists of two parts, transverse and alar.
- The transverse part arises from the maxilla, above and lateral to the incisive fossa.
- Its fibers proceed upward and medialward, expanding into a thin aponeurosis which is continuous on the bridge of the nose with that of the muscle of the opposite side, and with the aponeurosis of the Procerus.
- The alar part is attached by one end to the greater alar cartilage, and by the other to the integument at the point of the nose.




One Comment