Nimesulide
Introduction
Nimesulide is a moderately COX-2 selective, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic belongings. Its approved indications are the remedies for acute pain, the symptomatic therapy of osteoarthritis, and/or primary dysmenorrhoea in adolescents and adults above 12 years old.
Nimesulide is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with ache medication and fever-reducing effects. Side effects may contain liver problems. It has a multifactorial method of action and is characterized by a fast onset of action. It operates by blocking the presentation of prostaglandins (a chemical associated with pain), thereby reducing pain and inflammation.
- CASE ID: 51803-78-2
- Boiling point: 442 °C
- Molar mass: 308.311 g/mol
- Formula: C13H12N2O5S
- ChEMBL Id: 56367
- ChemSpider ID: 4339
- IUPHAR ID: 7401
- Generic Name – Nimesulide
- Type – Small Molecule
- Groups – Approved, Investigational, Withdrawn
Synonyms
- Nimesulida
- Nimesulide
- Nimesulidum
Brand names
Nimesulide is known throughout the world as original product with the following trademarks: Sulide, Nimalox, Mesulid (Novartis, Brazil, Boehringer Ingelheim, Greece, Italy), Coxtal (Sanofi, China, Bulgaria), Sintalgin (Abbott, Brazil), Eskaflam (GSK, Brazil, Mexico), Octaprin, Nimside (Teva, Pakistan), and Nise (Russia, Venezuela, Vietnam, Ukraine), Nilsid (Egypt); Aulin (Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Italy, also Romania, Poland), Ainex, Drexel, Donulide, Edrigyl, Enetra, Heugan, Mesulid, Minapon, NeRelid, Nexen, Nidolon, Nilden (Mexico); Emsulide, Nimed, Nimedex, Nimesil (Czech Republic, Moldova, Latvia, Kazhakhstan, Georgia, Poland), Nimulid (Trinidad & Tobago), Nimutab, Nimdase, Nimopen-MP Nise, Nimuwin, Nisulid, Nodard Plus, Nicip, Nimcap, Nic-P, Nic-Spas, Nimupain (India); Mesulid, Novolid, Relmex (Ecuador); Remisid (Ukraine); Coxulid and Emulid, Frenag, Fuzo, Motival, Nimeksil, Nimelid, Nîmes, Nimesdin, Romasulid, Sulidin, Suljel, Thermo Sulidin (Turkey), Xilox (Hungary); Modact-IR (Pakistan); and/or ad Sulidene and/or Zolan for veterinary use. Many generic and copy-products also exist (Lusemin, Medicox, Nidol, Nimalox, Nimesil, Nimotas, Nimulid, Nizer, Sorini, Ventor, Vionim, Neolide, Willgo among others), new-aid, Nexulide (Syria), Nims, Nice, Nimulide (Nepal)
Background
Nimesulide is a somewhat COX-2 selective, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic belongings. Its approved indications are the remedies for acute pain, the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis, and primary dysmenorrhoea in adolescents and adults above 12 years old. Due to anxieties about the risk of hepatotoxicity, nimesulide has been withdrawn from the market by many governments. Nimesulide (ni mes’ sul ide) is a unique nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that has a basic sulfonanilide structure. Like additional NSAIDs, nimesulide inhibits the enzyme cyclo-oxygenase (COX), thereby stopping the formation of prostaglandins that are important in pain and inflammatory pathways.
Unlike most traditional NSAIDs, however, nimesulide has a relative specificity for COX-2 activity, the form that is most related to pain pathways as opposed to COX-1, which has major effects on gastric mucosa cell protection and platelet function. Nimesulide has analgesic as well as antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activities mediated by COX-2 activities but has a relatively scant effect on platelet function or loss of gastric cytoprotection which is associated with COX-1 activity. Nimesulide has an immediate onset of action and has other activities except for its effects of cyclo-oxygenases which may be important in its anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions. Nimesulide was never ended in the United States but has been widely used in many countries of the world since its introduction in the 1990s.
Contemporary symptoms vary by the government but are generally confined to mild-to-moderate acute pain for which the suggested dose in adults is 100 mg twice daily for no more than 15 days. Chronic medicine is not generally recommended, and/or nimesulide is considered contraindicated in youngsters. Nimesulide is obtainable by prescription in the form of capsules or granules for oral suspension of 100 mg and as suppositories of 200 mg in both generic and business formulations (Sulide, Nimside, and others). Nimesulide is commonly well tolerated, but side effects can also contain headache, dizziness, somnolence, gastrointestinal upset, nausea, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, peripheral edema, and hypersensitivity responses.
What is nimesulide?
Nimesulide is a non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat:
- acute (short-term) pain,
- painful osteoarthritis (swelling in the joints),
- primary dysmenorrhoea (period pains).
Medicines containing nimesulide have been available since 1985 and are authorized in several Member States. They are only obtainable with medication. Systemic nimesulide treatments are available in the following Member States: Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Cyprus, France, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia. Nimesulide-containing prescriptions are authorized but not marketed in Austria and Ireland.
Nimesulide is a painkiller medicine. This medicine is used in the therapy of pain. It provides relief from mild to moderate pain due to menstrual cramps and osteoarthritis (which occurs when flexible tissue at the ends of your bones wears down). Nimesulide diminishes the intensity of pain signals to the brain and also controls the release of substances called prostaglandins in the brain that cause pain and fever. Nimesulide has some side effects like nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stomach pain, loss of appetite, skin rash, pain at the site of injection, and diarrhea. Confer your doctor if these side effects persist. Do not utilize this medicine if you are allergic to it. Nimesulide is not suggested for use in children below 12 years of age as safety is not established.
Nimesulide is available in various dosage forms like tablet, tablet ER, syrup, capsule, tablet DT, tablet MD, injection, oral drops, suspension, and gel. Your doctor will decide on an appropriate dosage form and dose of the medicine based on your condition. Nimesulide injectables will also be given by your medic in the hospital setting. Nimesulide relieves pain and/or swelling due to arthritic conditions but does not cure them. Nimesulide should not be utilized for a long time due to the danger of severe liver damage. Preserve caution while taking this medicine if you have any kidney problems. This drug is not recommended to be used in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Nimesulide may sometimes cause dizziness. Avoid driving cars or operating machines after taking this medicine. Do not drink alcohol while using this medicine as it may worsen drowsiness.
General Instructions
Nimesulide is used to relieve fever and pain. Oral form: Take Nimesulide with food as suggested by your doctor. Ensure that the treatment course is completed. This medicine should not be employed for more than 15 days. Confer your doctor if you notice any undesirable effects after taking this medicine. Parenteral form: It should be administered by a skilled healthcare professional in a clinical or hospital setting. Do not self-administer. Your doctor will choose an appropriate dose of this injection based on your clinical condition. Report any unwanted side effects to your doctor promptly. Topical form: Nimesulide gel is suggested for external use only. Involve the gel in the affected areas of the skin as instructed by your doctor. Avoid physical activity after applying the gel and let it rest on the affected area for a few minutes. Advise your doctor if you have liver, kidney, or heart problems. Nimesulide is not suggested for use if you are pregnant or are breastfeeding a woman.
Medical uses
It may be utilized for pain, including period pains. Nimesulide is not suggested long-term, for chronic disorders such as arthritis. This is due to its association with an improved risk of liver toxicity, including liver failure. Despite its chance of hepatotoxicity, a 2012 evaluation by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) concluded that the overall benefit or risk profile of nimesulide is favorable and in line with that of the other NSAIDs such as diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen provided that the duration of service is limited to 15 days and the dose does not exceed 200 mg/day.
Children
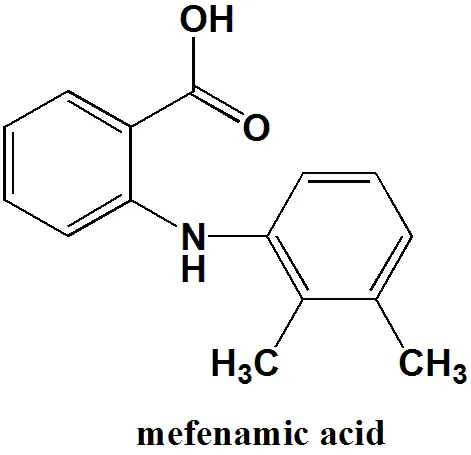
More diminutive than 10 days of nimesulide does not appear to increase the risk of hypothermia, gastrointestinal bleeding, epigastric pain, vomiting, diarrhea, or transient, asymptomatic elevation of liver enzymes compared to ketoprofen, paracetamol, mefenamic acid, aspirin, or ibuprofen in kids. Nevertheless, data does not speak to populations smaller than 6 months old.
Pregnancy and lactation
Women should use the drug with caution during lactation and nimesulide is contraindicated during pregnancy, and research suggests that it is also contraindicated in lactating women.
Available forms
100mg Nimesulide pills, Nimesulide is available in a variety of forms: tablets, powder for abolition in water, suppositories, mouth-dissolving tablets, and topical gel.
Directions for Use
Tablet and/or Capsule: Swallow it as a whole with water. Do not chew, crush, or break it. Mouth-dissolving tablet: Position the tablet on the tongue and let it dissolve or disintegrate in the mouth. The tablet must disintegrate completely within the mouth before you swallow it. Dispersible tablet: Check the label for directions before benefit. Distribute the tablet in the prescribed amount of water and swallow the contents. Drops or Syrup or Suspension: Bounce the bottle well before use. Take the prescribed dose by mouth utilizing the measuring cup or dosing syringe or dropper provided by the pack. Granules: Review the label for directions before use. Mix the granules in water, stir well, and drink instantly.
Storage – Store in a cool and dry place out from sunlight
Indication of nimesulide
For the therapy of acute pain, the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis and immediate dysmenorrhoea in adolescents and adults above 12 years old.
Associated Conditions
- Acute Pain
- Menstrual Distress (Dysmenorrhea)
- Pain
Pharmacology effects
Pharmacodynamics
Nimesulide is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), operating specifically as a relatively selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. yet, the pharmacological profile of nimesulide is peculiar, and additional, unknown, or yet-to-be-identified mechanisms appear to also be involved. One track that has been implicated in its actions is the ecto-5′-nucleotidase (e-5′NT/CD73)/adenosine A2A receptor pathway. Pharmacodynamics – Food, gender, and progressive age have negligible effects on nimesulide pharmacokinetics.
Pharmacokinetics
- Nimesulide is absorbed rapidly following oral administration.
- Nimesulide undergoes extensive biotransformation, mainly to 4-hydroxy nimesulide (which also appears to be biologically active).
- Food, gender, and developed age have negligible effects on nimesulide pharmacokinetics.
- Moderate chronic kidney disorder does not necessitate dosage adjustment, while in patients with severe chronic kidney disease or liver disease, nimesulide is contraindicated.
- Nimesulide has a fairly rapid onset of action, with meaningful decreases in pain and inflammation observed within 15 minutes of drug intake.
- The therapeutic effects of nimesulide are the result of its complex mode of action, which targets several key mediators of the inflammatory process such as COX-2-mediated prostaglandins, free radicals, proteolytic enzymes, and histamine. The clinical proof is available to support a particularly good profile in terms of gastrointestinal tolerability
Mechanism of action
The therapeutic effects of Nimesulide are the result of its complete mode of action which targets several key mediators of the inflammatory process such as COX-2-mediated prostaglandins, free radicals, proteolytic enzymes, and histamine.
- Absorption – Rapidly absorbed following oral administration.
- The volume of distribution – Not Available
- Protein binding = >97.5%
- Metabolism – Hepatic. Comprehensive biotransformation, mainly to 4-hydroxy nimesulide (which also appears to be biologically active).
- The course of elimination – Renal (50%), fecal (29%)
- Half-life = 1.8–4.7 hours
- Clearance – Not Available
- Toxicity – Oral TDLO (human): 1.429 mg/kg; Oral TDLO (woman): 2 mg/kg; Oral LD50 (rat): 200 mg/kg; Oral LD50 (mouse): 392 mg/kg
Side effects
Due to concerns about the risk of liver toxicity, nimesulide has been withdrawn from the market in several countries (Spain, Finland, Belgium, and Ireland). Liver concerns have resulted in both deaths and the need for transplantation. This may also occur in as small as three days after starting the medication. Continuous usage of nimesulide (more than 15 days) may cause the following side effects:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin rash
- Itchiness
- Dizziness
- Bitterness in mouth
- Acid or sour stomach
- Stomach discomfort and cramps
- Pain at the injection site
- Nervousness
- Loss of appetite
What is it prescribed for?
Uses of Nimesulide
- Pain due to osteoarthritis
- Nimesulide provides relief from acute pain due to osteoarthritis -a type of arthritis that occurs when cartilage breaks down, so joint bones begin to rub against one another; causing pain and stiffness.
- Fever
- Fever is usually not something to worry about unless the body temperature is very high or if it lasts for a long time. Nimesulide provides temporary relief from fever but does not treat the underlying cause.
- Primary dysmenorrhea
- Primary dysmenorrhea is the pain in your lower abdomen that occurs in 90% of women during the menstrual phase. Nimesulide is used as an over-the-counter medicine to reduce menstrual pain.
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Musculoskeletal pain is a widespread condition in adults and elderly people caused due to minor physical trauma or continuous physical activity. This pain is acute and is localized i.e., limited to a joint, bone, or tendon. Nimesulide is used to reduce pain in this condition.
When not to use it?
Allergy
Do not take or receive Nimesulide if you are allergic to it. If you notice any symptoms such as a skin rash, itching or swelling anywhere on your body, dizziness, problem breathing, etc., seek medical attention immediately.
Liver disease
Nimesulide is damaged down and absorbed in the liver. Thus, if you taking large amounts of this medicine, can damage your liver. The use of this medication is not recommended if you have extreme liver problems because it can further damage your liver.
Severe kidney disease
A long term usage with higher doses of some painkillers may harm normal kidney function. Nimesulide is not recommended for use if you have severe kidney problems as it may also cause serious side effects.
Warnings of nimesulide
Warnings for special populations:
Pregnancy
Nimesulide is not suggested for use in pregnancy especially during 1st trimester, as it has been reported to generate birth defects in the newborn baby. Confer your doctor before employing this medicine.
Breast-feeding
Nimesulide is not recommended for use in breastfeeding. An alternate medication may also be selected, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Confer your doctor before using this medicine.
General warnings
Gastro-intestinal bleeding
Long-term usage of Nimesulide can cause injury to the stomach and intestine. Serious disorders like bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestinal wall can occur. Any symptom indicating ulceration and bleeding like chronic indigestion, the appearance of coffee-colored dry blood in stools, or vomiting of blood should be reported to your doctor immediately.
Heart disease
Long-term use of Nimesulide may also increase the risk of a heart attack if you have pre-existing heart conditions or heart failure. It is not used for feasting pain after coronary bypass surgery.
External use only
Nimesulide gel is recommended for external use only. Avoid connection with the eyes, mucous membranes, or open wounds.
Use in Elderly
Nimesulide should be employed with caution in the elderly population due to an increase in the chance of undesired side effects. Monitoring of kidney, liver, and heart function as also symptoms of bleeding is necessary while receiving this medicine.
Driving or Operating machinery
Nimesulide may also cause dizziness or blurred vision. Do not conduct any activity such as driving a vehicle or operating a machine after taking this medicine
Use in children
The oral state of nimesulide is not recommended for use in children below 12 years of age as the safety and efficacy data is not available. Nimesulide injection is not recommended to be utilized in children below 18 years of age.
Other conditions
Nimesulide gel should be used with warning in conditions such as open wounds or skin with blisters as this medicine may slow the healing and instead may increase the pain.
Photosensitivity
The application of Nimesulide gel to inflamed skin can also make it photosensitive to direct sunlight and other light sources. Detour exposing the applied area to direct sunlight.
Concerns about drug
Onset of action
- The time of the beginning of action of Nimesulide may vary based on the dosage form. Parenteral form (injection): within 15 minutes of its intravenous administration. Oral form (tablet, tablet MD, capsule, tablet ER, syrup, oral drops, suspension): it takes 2-3 hours to show its action. Topical form (gel): unknown
Duration of effect
- The duration of movement for Nimesulide is not known.
Safe with alcohol?
- Consumption of liquor is not recommended while treatment with Nimesulide due to the chance of stomach bleeding, drowsiness, and lack of concentration.
Is it habit forming?
- No habit-forming movement has been reported for Nimesulide.
Usage while breastfeeding?
- Nimesulide is not recommended for use in breastfeeding. An alternate medicine may also be preferred, particularly while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Confer your doctor before using this medicine.
Dosage of nimesulide
Missed Dose
Oral forms: Take the skipped dose of Nimesulide as soon as you remember. If it is nearly time for the next dose, forget the missed dose. Do not crease the dose to make up for the missed one. Injectable states: It is important to take your nimesulide injection at the designed time. If you missed taking the dose, notify your doctor, and get an appointment for further education. Topical forms: Involve the missed dose of nimesulide as soon as you recognize it. Do not apply in more quantities to reimburse for the missed dose.
Overdose
Oral forms: Never take more than the specified dose. Seek emergency medical restorative or contact your doctor in case you suspect an overdose of Nimesulide. Injectable form: Nimesulide injection is administered in a hospital environment by your doctor, so the likelihood of an overdose is rare. Reach your doctor if an overdose of Nimesulide is suspected. Topical forms: An overdose of nimesulide is not likely to induce severe symptoms unless it is applied for a long duration and in large amounts. Nevertheless, swallowing this medicine may cause harm and immediate medical intervention may also be required.
Interactions of drug
All drugs interact differently for person to person. You should check all the potential interchanges with your doctor before starting any medicine. Interaction with Alcohol
Description – N/A
Instructions – Consumption of liquor is not recommended while treatment with Nimesulide due to the chance of stomach bleeding, drowsiness, and lack of concentration.
Interaction with Medicine
- Ketoconazole
- Methotrexate
- Warfarin
- Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid
Disease interactions
Liver disease
Nimesulide has to be employed with caution if you have liver problems. Please confer with your doctor before taking the medicine. You will also be advised to experience liver function tests (LFT) while you are on treatment with Nimesulide.
Kidney diseases
The increased doses of some painkillers may harm normal kidney function. Hence maintain caution while taking Nimesulide if you control any kidney problems. Food interactions – Information not available. Lab interactions – Details are not available. This is not an exhaustive list of possible drug interactions. You should confer with your doctor about all the possible interactions of your drugs.
Safety Advice
Alcohol
- CAUTION
- Taking NIMESULIDE with spirits may cause dizziness or drowsiness. So, avoid or restrict the intake of alcoholic beverages with NIMESULIDE.
Pregnancy
- UNSAFE
- Usage of NIMESULIDE during pregnancy is not recommended, particularly during the last 3 months of pregnancy as it may harm the unborn baby.
Breastfeeding
- UNSAFE
- Use of NIMESULIDE during breastfeeding is not recommended as it may give through the milk and harm the baby.
Driving
- CAUTION
- NIMESULIDE may cause dizziness, sleepiness, and drowsiness. Drive only if you are alert.
Liver
- UNSAFE
- NIMESULIDE can cause hepatotoxicity (liver damage). So, it is not recommended in individuals with liver disease or impairment.
Kidney
- CAUTION
- NIMESULIDE is to be taken with caution, particularly if you have a history of kidney diseases or conditions. The quantity may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Children
- UNSAFE
- NIMESULIDE is contraindicated in youngsters below 12 years of age. It may also cause kidney problems in children and adolescents who are dehydrated.
Habit forming – No
Diet & Lifestyle Advice
- Get satisfactory sleep as resting the muscles can help in reducing inflammation and swelling.
- Acupuncture, massage, and physical restorative may also be helpful.
- Eat foods wealthy in antioxidants such as berries, spinach, kidney beans, dark chocolate, etc.
- Foods containing flavonoids such as soy, berries, broccoli, grapes, and green tea help in decreasing inflammation.
- Preserve a healthy weight by performing regular low-strain exercises and eating healthy food.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
Why was nimesulide reviewed?
Nimesulide was reviewed in 2007 because of concerns about liver injury. The review procedure was triggered by the decision of Ireland’s medicines regulatory authority in May 2007 to suspend the marketing authorization for systemic nimesulide-containing medicines, due to new information regarding cases of fulminant hepatic failure needing liver transplantation. The Committee supposed that the benefits of systemic formulations of nimesulide still outweigh their risks, supplied that the use of these medicines is restricted to ensure that the risk of patients developing liver concerns is kept to a minimum. To this effect, the Committee advised that therapy duration should be limited to a maximum of 15 days (packs were also limited to a two-week supply), that nimesulide should be restricted to second-line therapy, and that doctors should be informed of the risk. The CHMP also deduced that a fuller review of nimesulide was needed, that would look at all of the potential risks of the medicine, specifically the risk of side effects involving the stomach and the gut, which were outside the scope of the original review.
Accordingly, on 19 January 2010, the European Commission asked the CHMP to carry out a full assessment of the benefit-risk proportion of nimesulide and to issue an opinion on whether the marketing authorizations for systemic medicine containing nimesulide should be maintained, various, suspended, or withdrawn across the European Union.
Expert advice for nimesulide
- Nimesulide is prescribed to relieve pain, inflammation, and fever.
- Take it with food or milk to control an upset stomach.
- Take it as per the dose and duration specified by your doctor. Long-term help may lead to serious complications such as stomach bleeding and kidney problems.
- Notify your doctor if you have a history of heart disease or stroke.
- Avoid ingesting alcohol while taking Nimesulide as it can increase your risk of stomach problems.
- Your doctor may also regularly monitor your kidney function, liver function, and levels of blood components if you are taking this prescription for long-term treatment.
FAQ
Is Nimesulide an antibiotic?
Nimesulide is not an antibiotic, it belongs to the class of medicines known as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs; pain-relieving drug) which helps in relieving pain associated with various disease conditions.
Can I take Nimesulide with paracetamol?
Nimesulide and paracetamol belong to the identical type of medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; pain-relieving drugs). Taking the two medicines together is not advisable as it may improve the potential for gastric ulceration and bleeding. However, please confer with your doctor before using the two medicines together.
Can I take Nimesulide with ibuprofen?
Nimesulide can be taken with ibuprofen. No drug-drug interchanges have been reported between the two. Yet, taking the two medicines together is not advisable as it may increase the potential for gastric ulceration and bleeding. Please confer with your doctor before taking the two medicines together.
What is stronger diclofenac or nimesulide?
The consequences of this study indicate that nimesulide is as effective as diclofenac in the long-term treatment of osteoarthritis; nevertheless, nimesulide demonstrated a negligibly superior gastric safety profile. This finding may be especially beneficial to the elderly, who are most at risk for these side effects.
Can I take Nimesulide with aspirin?
Nimesulide can be taken with aspirin. However, No drug-drug interactions have been clinically examined between the two. Nevertheless, this does not mean that relations cannot occur. Please confer with your doctor before taking the two medicines concurrently.
Is Nimesulide safe during pregnancy?
No, Nimesulide is not safe to be used during pregnancy, especially in the last three months. There have been statements of kidney failure in newborn babies if the mother was taking Nimesulide in the late stage of pregnancy. Confer your doctor before taking any medicine during pregnancy. Nimesulide is not suggested for use in pregnancy especially during 1st trimester, as it has been reported to cause birth defects in the newborn baby. Confer your doctor before using this medicine.
Is Nimesulide safe for asthma?
Nimesulide is reported to be secure in patients with asthma if taken as advised by your doctor. However, always share your disease history with the doctor in case you have asthma and are advised to take other medicines.
Can I take nimesulide with an Antibiotic?
During the treatment, nimesulide plus antibiotics induced a significantly greater and more rapid improvement in the treated patients in comparison with antibiotics plus placebo, in case of prostate swelling, redness, edema, compulsion, pollakiuria, nycturia, and body temperature.
How Harmful is Nimesulide?
Nimesulide is typically well tolerated, but side effects can also include headache, dizziness, somnolence, gastrointestinal upset, nausea, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, peripheral edema, and hypersensitivity reactions.
When was Nimesulide banned?
The drug was banned in 2000 in various countries like Switzerland, Spain, the United States, etc, whereas in India it was banned in 2011 which was too late to be banned and still available in India for adult use despite its hepatotoxicity and possible drug interactions. Keywords: Adverse Drug Reaction. hepatotoxicity.