Obliquus capitis superior muscle
Introduction
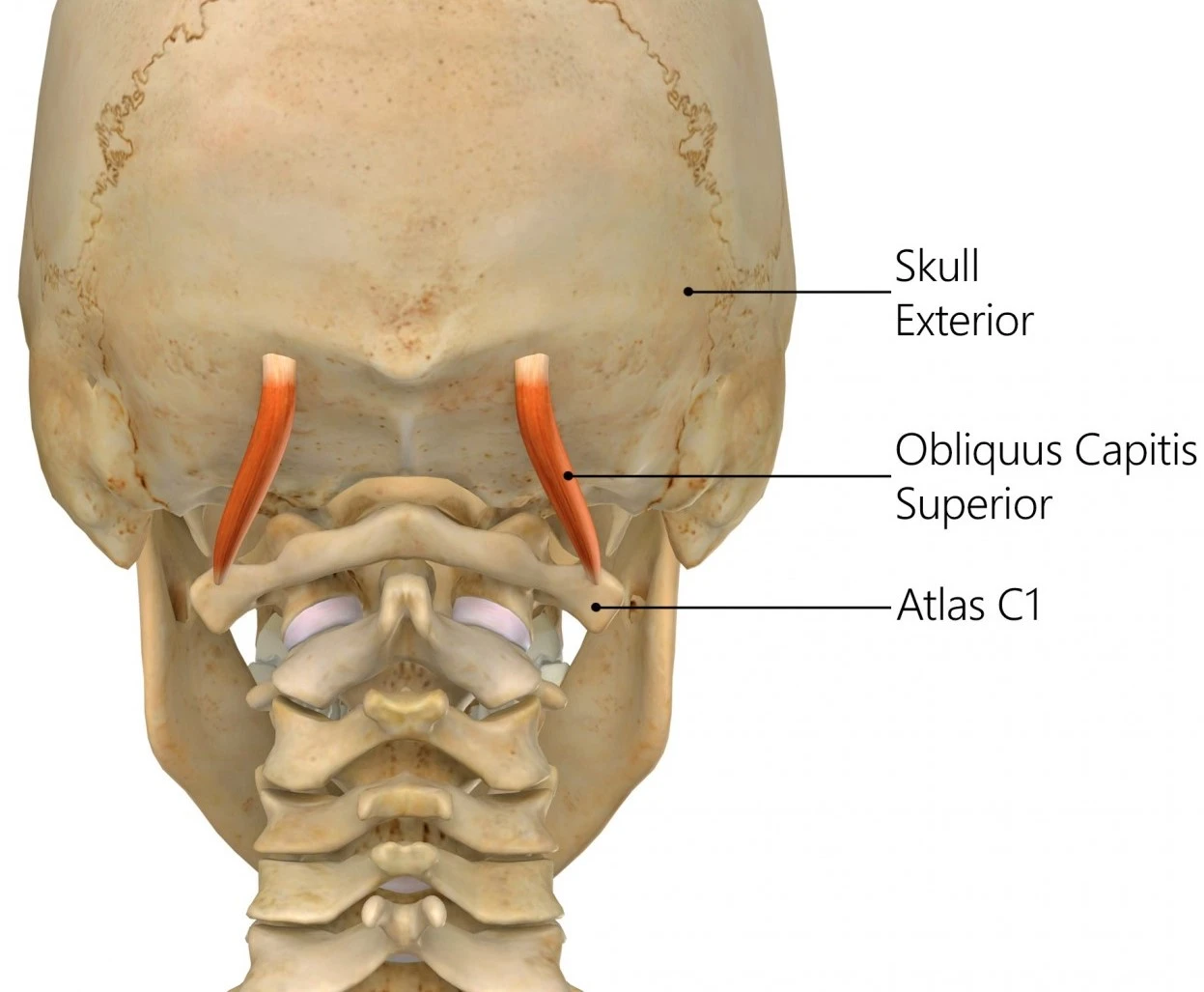
Obliquus capitis superior, or superior oblique muscle, is a small paired muscle found deep in the upper cervical region, at the base of the occipital bone. It is one of four muscles that incorporate the suboccipital muscles group along with rectus capitis posterior major, rectus capitis posterior minor and obliquus capitis inferior muscles.
Obliquus capitis superior muscle contributes to the extension of the head. Nevertheless, its role as a postural muscle is more important than its role as a prime mover. It is narrow below, wide and extended above, and is lateral to the semispinalis capitis muscle. It makes the superolateral border of the suboccipital triangle. The obliquus capitis superior is found laterally in the suboccipital compartment.
Origin of Obliquus capitis superior muscle
Obliquus capitis superior originates from the superior surface of the transverse process of the atlas vertebrae (Primary cervical vertebra). This happens when one of the levator scapulae muscles slips arises. The muscle evolves broader as it passes upward, traveling a short space to insert between the superior and inferior nuchal lines on the external surface of the occipital bone.
Insertion
The insertion is encountered lateral to the semispinalis capitis muscle and anterolateral to the rectus capitis posterior major muscle. Obliquus capitis superior muscles are the significant lateral of the suboccipital muscles, located superficially to the recti muscles and superiorly to the inferior obliquus muscle. It is even the smallest muscle of the suboccipital group.
Obliquus capitis superior muscle originates on the superolateral border of the suboccipital triangle where both the vertebral artery and the first cervical or suboccipital nerve are comprised. Both longissimus capitis and splenius capitis overlay these muscles.
Nerve supply
Equivalent to the other suboccipital muscles, the obliquus capitis superior muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve, this is the primary cervical posterior (dorsal) ramus.
Blood supply
The vertebral artery and deep descending branches of the occipital artery supply blood supply for the obliquus capitis superior muscle and the other suboccipital muscles. Obliquus capitis superior muscles are drained by the vertebral vein via the posterior external vertebral venous plexus.
Function of Obliquus capitis superior muscle
Functioning bilaterally, obliquus capitis superior muscles raise the head on the neck at the atlantooccipital joint. Its action laterally flexes the head to the ipsilateral side when performing unilaterally. The muscles’ considerable prominent role is as a postural muscle, whereby it stabilizes the atlantooccipital during head motions. Is a postural muscle that observes the position of the head.
Clinical significance
Obliquus capitis superior muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck and the head that is liable for extension and also ipsilateral flexion of the head by performing motion at the atlantooccipital joint.
Headaches: The obliquus capitis superior muscle is the portion of a group of muscles called the suboccipital muscles. Overuse or faulty posture usually conducts in a strain or other injury of the muscles, resulting in neck pain, headaches, or also eyestrain. Exercises and stretches may help appease the symptoms. The usage of NSAIDs, like ibuprofen, will treat headaches.
Migraines: If migraines happen, it may be a sign to visit a doctor for the prescription of medication. These symptoms are improbable to go away without the improvement of posture.
Exercises of Obliquus capitis superior muscle
Suboccipital stretch
Sit or stand up straight, keeping good posture. Keep the mouth closed with the teeth concurrently and place two or three fingers on the front of the chin. While maintaining a straightforward neck, push on the chin towards the back of the head, until feeling a stretch in the back of the neck. Hold the position for ten seconds and replicate it four times. Execute this stretch five times a day.

Suboccipital stretch #2
Stand or sit with good posture. Tilt the chin down into the neck direction. Encounter both bumps on the back of the head and also touch them. Press upward toward the ceiling and maintain the pressure for twenty seconds. Perform this stretch five times a daytime.
FAQs
Where does the obliquus capitis superior originate?
It originates from the lateral mass of the atlas vertebrae. It gives superiorly and posteriorly to insert into the lateral half of the inferior nuchal line on the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscles are innervated by the suboccipital nerve, the dorsal ramus of the first spinal nerve.
What does the obliquus capitis superior do?
unctioning bilaterally, the obliquus capitis superior muscle raises the head on the neck at the atlantooccipital joint. It laterally flexes the head to the ipsilateral side when executing unilaterally. The muscles’ most prominent role is as a postural muscle, whereby it stabilizes the atlantooccipital during head movements.
What causes obliquus capitis superior pain?
The obliquus capitis superior muscle is the portion of a group of muscles called the suboccipital muscles. Overuse or incorrect posture often conducts in strain or another injury of the muscles, resulting in neck pain, headaches, or eyestrain. Exercises and stretches may assist alleviate the symptoms.
How do you treat obliquus capitis?
Exercises and stretches may assist alleviate the symptoms. The benefit of NSAIDs, like ibuprofen, will treat headaches. If migraines occur, it may be a sign to call a doctor for prescription medication. These symptoms are improbable to go away without the improvement of posture.


One Comment