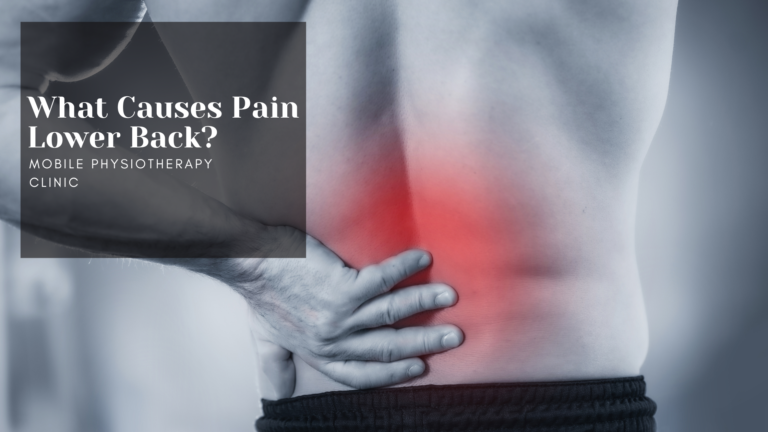
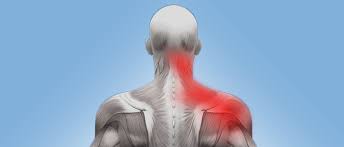
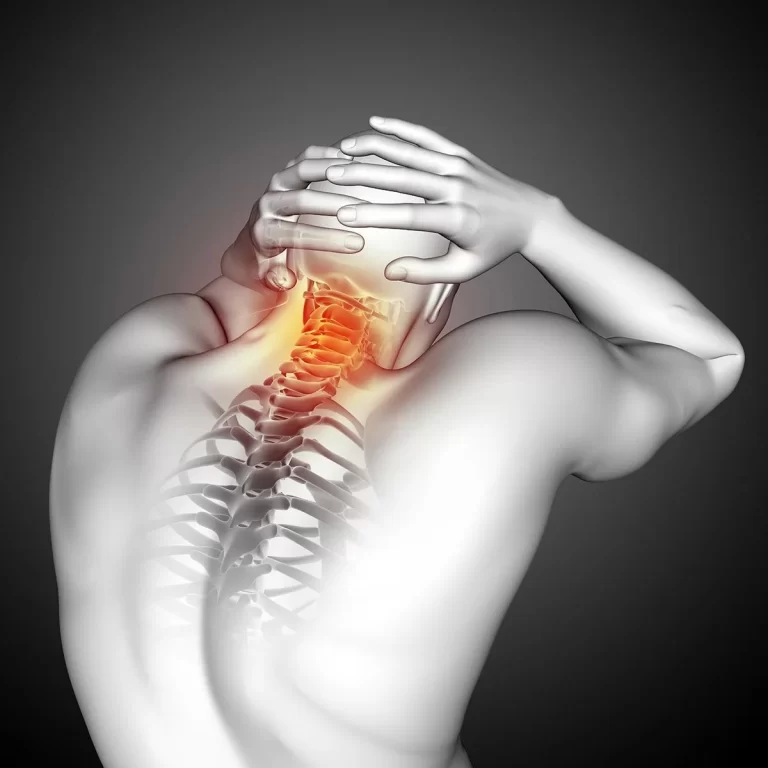
Triceps Muscle Pain
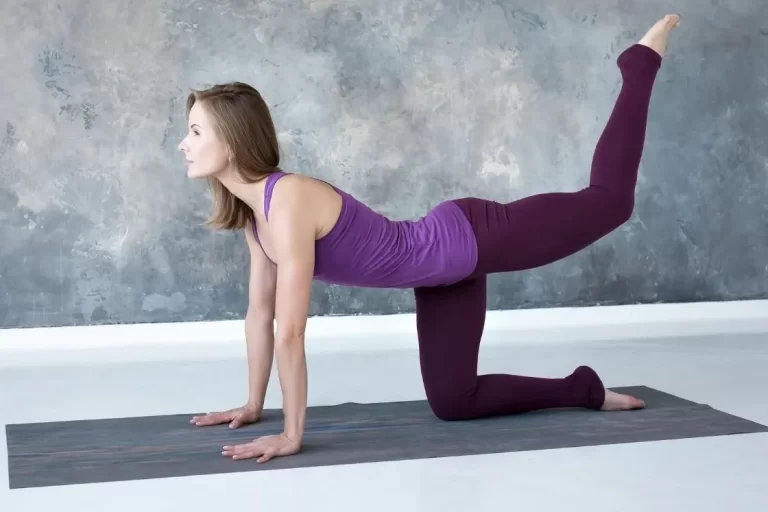
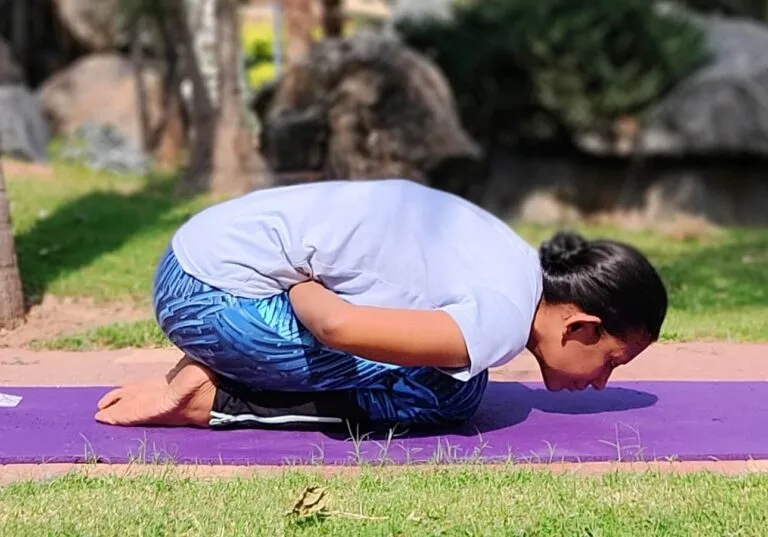
Introduction Triceps muscle pain, Soreness or irritation can be due to a variety of reasons. One of the most common of such is a muscle tear. It can either be micro tears leading to a painful range of motion or larger tears leading to limited mobility of the muscle. The triceps is a big and…