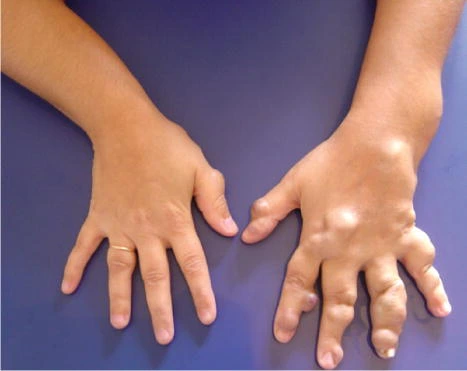
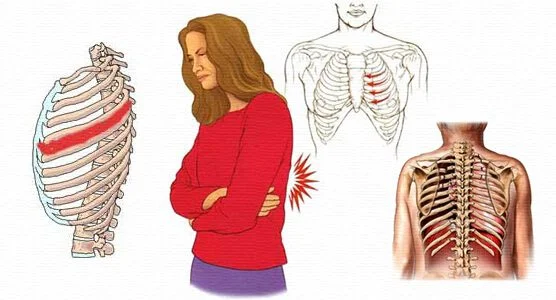
Polyneuritis
What is Polyneuritis?
Polyneuritis is neuritis of several peripheral nerves at the exact time (as that generated by a toxic substance, vitamin B deficiency, or an infectious condition).
Neuritis can involve one nerve (mononeuritis) or a plexus of nerves (plexitis). When several single nerves are involved simultaneously, the disease may be referred to as mononeuritis multiplex. When widely divided nerves are involved, it is called polyneuritis.
Types of Neuritis
- Polyneuritis or Multiple neuritides
- Brachial neuritis
- Optic neuritis
- Peripheral neuritis also called Peripheral neuropathy
- Vestibular neuritis
- Cranial neuritis, frequently represented as Bell’s Palsy
- Arsenic neuritis
Often, rather than a generalized disturbance of the nerves, only one nerve is involved. bell’s palsy, or facial paralysis, results when the facial nerve is involved. It generally stays only a few days or weeks. Occasionally, yet, the reason is a tumor depressing on the nerve, or injury to the nerve by a cut, blow, or bullet. On that occasion, healing relies on victory in managing the tumor or injury.
Sciatica is inflammation of or damage to the sciatic nerve, a big nerve running lowered from the spinal cord into the lower limb. The most familiar cause is likely a herniated disk. Back harm, irritation from arthritis of the spine, or stress on the nerve from specific kinds of work are further reasons. Specific conditions like diabetes mellitus or gout may also be initiating factors.
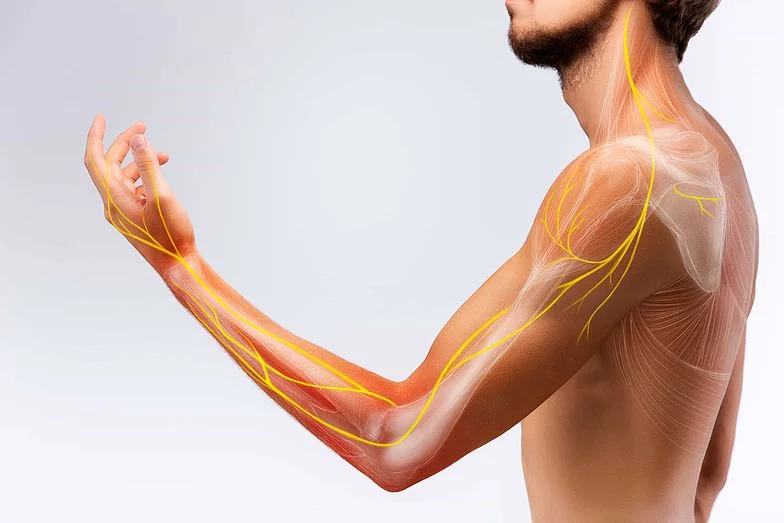
Neuritis of the Spinal Nerves. Injury or condition may involve any of the many nerves crossing out from the spine. For instance, inflammation of the nerves between the ribs induces pain in the chest that may correspond to pleurisy or actual coronary occlusion (heart attack). This is known as intercostal neuritis or intercostal neuralgia. Also, the nerves crossing down the neck to the arm may be subject to different injuries or conditions. For instance, too strong pulling on the nerves in the neck of a fetus, as in complex obstetrical deliveries, generates the disease called brachial paralysis.
Neuritis of the Cranial Nerves. Bell’s palsy outcomes from inflammation of the seventh cranial, or facial nerve. The fifth cranial, or trigeminal, nerve, even finishes in the face and jaws and may be the origin of a neuralgia that induces spasms of ache on one side of the face, known as tic douloureux or trigeminal neuralgia. It may be put off by a draft of cold air, by chewing, or by further factors. Drugs and, if required, surgery can reduce this aching malady.
Optic neuritis guides to any of the different states in the nerves leading to the retina of the eye; this is potentially harmful to vision and needs immediate therapy. Any of the further cranial nerves may be involved by tumors, infections, and toxins. The antibiotic streptomycin sometimes induces harm to the eighth cranial nerve, which assists to maintain the sense of balance in the inner ear. Any disruption of hearing, vision, balance, taste, swallowing, or speech may be a sign of a problem in the cranial nerves and should be instantly brought to the alert of a healthcare provider or doctor.
Cause of Polyneuritis
Infection:
- Herpes simplex
- Shingles
- Leprosy
Guillain-Barre syndrome
Chemical injury
Physical injury
Radiation
Drugs: Disulfiram, Pergolide, Vinblastine
Underlying illnesses causing localized neuritis (involving a single nerve):
- Diphtheria
- Localized injury
- Diabetes
Underlying diseases causing polyneuritis (involving multiple nerves)
- Beriberi
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Metabolic diseases
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Porphyria
- Infections, bacterial or viral
- An autoimmune condition, particularly Multiple Sclerosis
- Cancer
- Alcoholism
- Wartenberg migratory sensory neuropathy
Symptoms of polyneuritis
Symptoms of polyneuritis can differ depending on the reason, but the most familiar are:
Tingling or tingling sensations, numbness, “stinging” (called paresthesia) – paresthesia)
Loss of feeling in the legs, arms
Burning sensation in the feet or hands
Sudden onset of pain
severe sensitivity to touch (known as allodynia)
Weakness in the extremity, which may be due to muscle weakness or atrophy
Unable to walk straight, effortlessly tripping or falling
Problem in swallowing
Diagnosis
The correct diagnosis and description of neuritis start with a complete physical examination to describe and localize any symptoms to a detailed nerve or distribution of nerves.
An examination will consider the time course, distribution, severity, and nerve dysfunction as well as whether the conditioning process affects motor, sensory, or sensorimotor nerves.
After the lesion has been localized, a more attentive study may use precise methods suitable for the affected nerves.
Blood tests should be conducted to assess blood glucose and serum B12 levels with metabolites, and different measurements of precise vitamins or toxins may be conducted as shown if the record and physical examination are consistent. Medical examinations which are frequently useful contain MRI, nerve biopsy, nerve conduction examinations, fundoscopy, electromyography, and lumbar punctures. Yet, the diagnosis of many of the diseases associated with neuritis is a clinical one that does not depend upon any special diagnostic examination
Treatment of Polyneuritis
Treatment is directed toward the reason for the neuritis, analgesics may be defined for pain alleviation. Recovery is generally fast in less-severe issues.
Treatment choices for the disease are as follows:
Vitamin B supplementation – Used if the disease is induced by vitamin B deficiency.
Medical treatment
People may be defined with anti-seizure, painkillers, antidepressant medications, and topical therapies. This asset enhances the symptoms of the disease. They are utilized to control the involved nerves from sending ache signals to the brain. Steroids can also be utilized in some patients.
Surgery – Persons with a tumor that squeezes the involved nerve can undergo a surgical technique to have the abnormal growth extracted.
Physiotherapy treatment
While the general advantages of aerobic and flexibility activities are well-known, rising motion and heart rate are specifically essential for a patient suffering from polyneuritis. Physical exercise can enhance blood circulation, which boosts nerve tissues by raising the flow of oxygen.
Go for a Walk
The purpose is to walk 30 minutes a day five days a week 20 minutes earlier. If walking is hard at this time, start short by walking to the mailbox or near the home. Feel free to hold a friend and create a social occasion. A walk is solely the start.
Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises
If kickboxing is not your type, bring it comfortably with a likable afternoon of swimming or cycling. Both request low impact for muscles, bones, and joints. And the best item is, swimming and cycling enhance blood circulation.
Resistance Training
We’re not all bodybuilders and that’s alright Whether you’re raising five-pound weights, accomplishing sit-ups or pushups, adding resistance activity to your daily habit can improve flexibility and of course, blood flow.
Stretching Increases Flexibility
Bring a few minutes per day to stretch your neck, arms, legs, and feet. It doesn’t have to be extended or rigid. You can transfer your neck side to side and up and down or roll your legs in a bike movement while sitting or lying down.
Create your plan to attempt at least one of these movements. An activity of any type is better than none. Recall your body requires to heal and when you stay busy, blood persists to ventilate, and healing starts.
Carry some motivation from the tortoise and the hare, it’s not how quickly you go, but the decision to stay the route that you will get to the finish line.
Before beginning a new fitness habit, constantly confer with your physician.
Several treatments can also be used to enhance symptoms. These involve acupuncture, electrical nerve stimulation, and physical therapy. Doctors select the best therapy choice for particular persons based on the rigor of their state and their intentions.
Specific measures can be brought to control the disease from recurring after victorious therapy. These involve eating a well-balanced diet and managing any underlying reason. Regular input of vitamin B supplements and regular activity can also assist. Further steps that can be carried out are avoiding smoking, stress, and drinking too much alcohol. Doctors or physicians may also recommend people use relaxation methods.
Complications of polyneuritis
Because a patient with chronic polyneuritis frequently loses the capability to sense temperature and ache, they may burn themselves or generate an open injury to themselves without admitting it.
If the involved nerves are found in the internal organs, the person may feel diarrhea or constipation, as well as the defeat of bowel and bladder control. In extra, polyneuritis also shows sexual dysfunction and abnormally lower blood pressure.
One of the most severe difficulties of polyneuropathy is Guillain-Barre syndrome. This is a sudden, periodic, progressive disease in which the body’s immune system strikes nerves as soon as they exit the spinal cord. Symptoms manage to come on fast and worsen, occasionally leading to paralysis. The person will initially feel limb weakness and tingling, which then circulates throughout the arm. More extreme issues can generate troubles with heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing troubles. Although very severe, persons are more probable to heal if managed early.
Chronic polyneuritis is a chronic condition of Guillian-Barre syndrome. The symptoms then persist for months and even years. Approximately 30% of persons are at risk of living in a wheelchair, so early diagnosis and therapy are essential.
FAQ
What is an example of neuritis?
Some of the bacterial mechanisms most associated with neuritis are Lyme disease, leprosy, and diphtheria. Viral reasons for neuritis involve varicella-zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and HIV. Leprosy is often described by direct neural infection by the causative organism, mycobacterium leprae.
Is neuritis a serious disease?
In severe circumstances, it can generate paralysis. There are several types of the disease depending on the involved location. Generally, active nerves are those that conduct signals from the spinal cord to the arm, hand, and shoulder. The nerves of the eyes and ears can also be involved.
What is the best treatment for neuritis?
The main drugs suggested for neuropathic pain contain:
amitriptyline is also used for the therapy of headaches and depression.
duloxetine is also used for the therapy of bladder issues and depression.
pregabalin and gabapentin are also utilized to regale headaches, epilepsy, or anxiety.
Can neuritis be cured?
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
Generally, peripheral neuropathy can’t be healed, but you can accomplish a lot of items to control it from obtaining more harmful. If an underlying disease such as diabetes is at fault, your healthcare provider will manage that first and then manage the pain and further symptoms of neuropathy.
Is neuritis a damaged nerve?
Brachial neuritis is a condition of peripheral neuropathy that involves the shoulder, chest, arm, and hand. Peripheral neuropathy is a condition indicated by pain or loss of a role in the nerves that hold signals to and from the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system) to further regions of the body.