Obesity
What is Obesity?
Obesity is a complex, chronic condition with several reasons that conduct to extreme body fat and occasionally, poor health. Body fat itself is not a condition, of course. But when your body has too greatly excess fat, it can alter the method of its functions. These changes are progressive, can aggravate over time, and they can conduct in adverse health outcomes.
The good information is that you can enhance your health risks by losing some of your extra body fat. Even small weight changes can have a big effect on your health. Not every fat loss plan works for everyone. Most patients have attempted to lose weight more than once. And maintaining the weight off is just as essential as losing it in the first place.
Is Obesity defined by your weight?
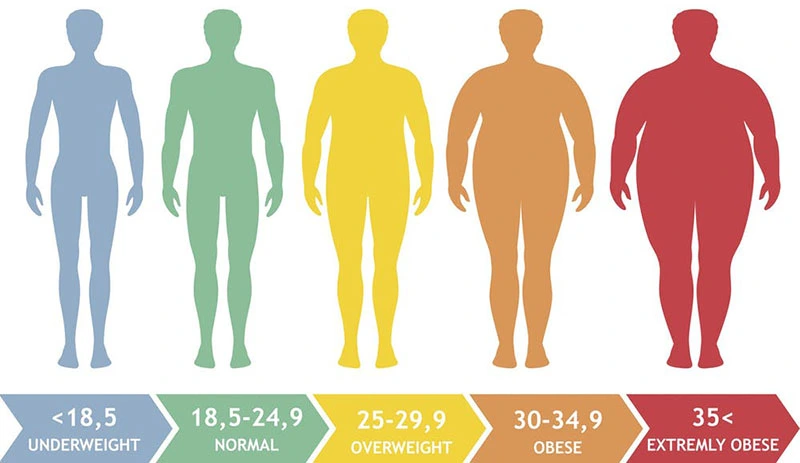
Healthcare providers or doctors generally use the Body Mass Index (BMI) to determine obesity in general people. The Body Mass Index (BMI) estimates average body weight against average body height. As a generality, healthcare providers or doctors associate a BMI of 30 or more increased with obesity. Although Body Mass Index (BMI) has its limits, its an easily measurable indicator and can assist to sign you of obesity-related health risks.
Measures of limitations contain bodybuilders and athletes, who have more muscle and may have more elevated Body Mass Index (BMI) scores even though their fat levels are low. It’s also likely to have obese at a normal weight. If your body weight is moderate but your body fat percentage is increased, you may have the exact health risks as a person with a more elevated BMI.
Healthcare providers or doctors have also marked ethnic dissimilarities in how much excess weight various people can bring before it involves their health. For instance, patients of Asian descent are more probable to have health risks at a lower BMI, and Black patients are more probable to have health risks at a more elevated BMI.
Another way of evaluating obesity is by calculating waist circumference. If you have more body fat near your waist, you are statistically more at risk of obesity-related conditions. The risk evolves effectively when your waist size is more than 35 inches for the patient assigned woman at birth or 40 inches for the patient assigned man at birth.
Types of Obesity
Healthcare providers or doctors categorize obesity into class types based on how extreme it is. They use BMI to accomplish it. If your BMI is between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m, they placed you in the overweight type. There are three general types of obesity that healthcare providers or doctors use to estimate what therapies may work best per person. They contain:
- Class I obesity: BMI 30 to <35 kg/m.
- Class II obesity: BMI 35 to <40 kg/m.
- Class III obesity: BMI 40+ kg/m.
- Underweight – Below 18.5 kg/m
- Normal – 18.5-24.9 kg/m
- Overweight – 25.0-29.9 kg/m
- Obesity – 30.0 kg/m and higher
Obesity affects the body
These health issues involve nearly every region of the body, involving:
- brain
- blood vessels
- heart
- liver
- gallbladder
- bones
- joints
Nervous system
Being overweight or obese vastly raises the risk of stroke, which occurs when blood stops flowing to your brain.
Respiratory system
Fat stored near the neck can produce airway too little, which can make breathing problematic at night. This disease is known as sleep apnea. Breathing may stop for brief periods in a patient with sleep apnea.
Digestive system
Obesity has been associated with a more increased risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD happens when stomach acid spreads into the esophagus.
In addition, obesity raises the risk of forming gallstones. This is when bile builds up and stiffens in the gallbladder. This may need surgery.
Fat can even build up near the liver and conduct to liver injury, scar tissue, and even liver collapse.
Cardiovascular system
In a patient with obesity, the heart requires to work harder to pump blood near the body. This conducts to high blood pressure or hypertension. High blood pressure is the greatest cause of stroke.
High blood pressure can produce the blood vessels that bring blood to the heart to evolve stiff and narrow. Hardened arteries, also known as atherosclerosis, can raise the risk of heart attack and stroke. High blood pressure can also generate chronic kidney conditions.
Endocrine system
Obesity can also produce the body’s cells resistant to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that brings sugar from your blood to your cells, where it’s utilized for energy.
If you’re unsusceptible to insulin, the sugar cant be brought up by the cells, resulting in high blood sugar. This raises a patient’s risk of having type 2 diabetes, a disease where your blood sugar is too elevated. Type 2 diabetes is connected to a range of different health problems, involving kidney conditions, heart conditions, amputation, stroke, and blindness.
Reproductive system
Obesity can make it harder for a person to get pregnant. It has also been connected to reduced testosterone levels, which can produce it more difficult to conceive.
Additionally, obesity can raise the risk of severe difficulties during pregnancy.
Skeletal and muscular systems
Obesity can generate deteriorating bone density and muscle mass. This is guided to osteosarcopenic obesity. Osteosarcopenic obesity can conduct in a more increased risk of physical disability, fractures, insulin resistance, and poorer overall health results.
Excess weight can also place too much pressure on the joints, conducting to pain and stiffness.
Integumentary (skin) system
Rashes can happen where the skin of body fat folds. A disease called acanthosis nigricans can also happen.
Acanthosis nigricans is described by discoloration and thickening of the skin in the folds and wrinkles of your body. It has also been connected to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Mental health
Obesity has been associated with several various mental health diseases among various people. Patients with obesity may be more probable to have:
- less well-being
- negative emotions
- psychopathological symptoms
One way to address these problems is by concentrating on positive interventions, such as relaxation methods and self-strengthening skills to enhance mood and decrease anxiety, depression, restlessness, inner tension, and stress.
Obesity is also associated with a more increased risk of depression, inadequate self-esteem, and problems with body image.
Further effects on the body
Obesity has been connected to a raised risk of many various varieties of cancers, involving:
- endometrial
- liver
- kidney
- cervical
- colon
- esophageal
- pancreatic
As your body mass index (BMI) rises, so does your risk of evolving cancer.
Causes of Obesity
In the most basic class, obesity is generated by taking more calories than your body can use. Many aspects contribute to this. Some aspects are particular to you. Others are constructed into the structure of our society, either on a national, local, or family level. In some methods, controlling obesity needs consciously work against these numerous factors.
Factors that may raise calorie consumption to contain:
Fast and convenience foods. In communities and families where highly processed fast and comfort foods are dietary staples, it’s easy to take in a lot of calories. These foods are increased in sugar and fat and low in fiber and different nutrients, which can exit you hungrier. Their ingredients encourage addictive eating habits. In some communities, these may be the only varieties of foods readily available, due to both cost and access. The Centers for Disease Control calculate that 40% of households in America live more than a mile from healthy food traders.
Sugar is in everything or everyplace. The food company is not planning to control our health. it’s planned to sell products that we will evolve addicted to and want to purchase more of. High on that checklist of products are sweets and sugary drinks, which have no nutritional worth and a bunch of counted calories. But common foods have high levels of added sugar to create them more attractive and addictive. It’s so familiar that its altered our taste anticipations.
Marketing and advertising. Pervasive advertising makes sweets and sugary drinks, processed foods, the products that we require the least but that the industry requires us to purchase the most. Advertising creates these products seem such as a normal and essential aspect of everyday life. Advertising also plays a big role in selling alcohol, which adds a bunch of empty calories.
Psychological factors. Boredom, anxiety and depression, loneliness are all familiar in modern society, and can all conduct to overeating. They may particularly lead to eating specific varieties of foods that trigger pleasure centers in our brains, foods that manage to be higher in calories. Eating to sense more usefulness is a simple human instinct. We developed to see food, and evolution hasn’t noticed up to the variety or abundance of food that Western societies now enjoy.
Hormones. Hormones control our hunger and satiety signs. Many items can disrupt these regulatory functions, involving familiar items such as stress and lack of sleep and less familiar things such as genetic variations. Hormones can generate you to continue to hunger for more food even when you don’t require any more calories. They can make it difficult to speak when you’ve had it adequately.
Certain medications. Drugs that you bring to manage further conditions may contribute to weight gain. Antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs, steroids, diabetes drugs, and beta-blockers are among them.
Factors that may reduce how many calories we spend contain:
Screen culture. As a shopping, work, and social life persist to move online, we increasingly consume more time in front of our phones and computers or social media. Streaming media and binge-watching create lengthy hours of inactive entertainment more likely.
Workforce changes. With industry modifications trending toward automation and computers, more patients now work at desks than on their feet. They also function more extended hours.
Fatigue. Sedentary lifestyles have snowball consequences. Analyses indicate that the ampler you sit still, the more tired and less motivated you evolve. Sitting creates your body rigid and contributes to aches and pains that discourage motion. It also generates general pressure, which adds to fatigue.
Neighborhood design. Many patients lack local areas to be busy, either due to permits or safety problems. More than half of Americans don’t live within half a mile of a garden. They may not live in walkable communities, and they may not notice others in their communities being involved in day-to-day life. When there is no general transportation choice, most people can only journey by car.
Childcare trends. Kids expend slightly more time playing outside than they used to. They expend more time in enclosed childcare settings, which may not have sufficient space or skills for physical activity. This is partially due to cultural trends that don’t find it safe for kids to play outside unattended. Its also due to insufficient access to public spaces and insufficient access to quality childcare. Numerous childcare environments replace TV for free play.
Disability. Grown-ups and kids with physical and learning disabilities are most in danger of obesity. Physical restrictions and lack of sufficient technical education and resources can contribute.
Risk factors
Obesity generally outcomes from a mixture of reasons and contributing factors:
Family inheritance and influences
The genes you inherit from your parents may involve the quantity of body fat you store, and where that fat is spread. Genetics may even play a role in how efficiently your body transforms food into energy, how your body controls your appetite, and how your body burns calories during activity.
Obesity manages to run in families. That’s not only because of the genes they transfer. Family members also manage to transfer equal eating and activity patterns.
Lifestyle choices
Unhealthy diet. A diet that’s elevated in calories, lacking in fruits and vegetables, a maximum of fast food, and loaded with high-calorie beverages and large parts contributes to weight gain.
Liquid calories. A patient can consume many calories without feeling full, particularly calories from alcohol. Further high-calorie beverages, like sugared soft drinks, can contribute to considerable weight gain.
Inactivity. If you have an inactive lifestyle, you can efficiently bring in more calories every day than you burn via activity and routine daily exercises. Looking at computer, tablet, and phone screens is an inactive exercise. The numeral of hours spent in front of a screen is favorably associated with weight gain.
Certain diseases and medications
In some people, obesity can be drafted to a medical reason, like Cushing syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, and further conditions. Medical issues, like arthritis, also can conduct to reduced activity, which may result in weight gain.
Some drugs can conduct to weight gain if you don’t compensate via diet or exercise. These drugs contain some antidepressants, diabetes drugs, antipsychotic drugs, anti-seizure drugs, steroids, and beta blockers.
Social and economic issues
Social and economic factors are connected to obesity. Avoiding obesity is hard if you don’t have secure locations to walk or exercise. Besides, you may not have been prepared with healthy ways of cooking, or you may not have access to more nutritious foods. In addition, the person you expend time with may influence your weight you’re more probable to produce obese if you have friends or relatives with obesity.
Age
Obesity can happen at any age, even in young kids. But as you age, hormonal modifications and a less busy lifestyle raise your risk of obesity. In extra, the quantity of muscle in your body tends to reduce with age. Normally, lower muscle mass conducts to a reduction in metabolism. These modifications also decrease calorie requirements and can make it more difficult to keep off extra weight. If you don’t intentionally control what you eat and evolve more physically active as you age, you’ll probably gain weight.
Other factors
Pregnancy. Weight gain is familiar during pregnancy. Some females find this weight hard to lose after the baby is born. This weight gain may contribute to the growth of obesity in females.
Quitting smoking. Quitting smoking is frequently associated with weight gain. And for some, it can lead to sufficient weight gain to allow for obesity. Usually, this occurs as a person uses food to manage smoking withdrawal. In the long run, yet, quitting smoking is still a greater advantage to your health than resuming to smoke. Your doctor can assist you to control weight gain after stopping smoking.
Lack of sleep. Not obtaining sufficient sleep or bringing too much sleep can generate changes in hormones that improve appetite. You may also hunger foods increased in calories and carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain.
Stress. Many external factors that involve mood and well-being may contribute to obesity. A person frequently seeks more high-calorie food when feeling stressful conditions.
Microbiome. Your gut bacteria are involved in what you eat and may contribute to weight gain or problems in losing weight.
If you have one or more of these risk factors, it doesn’t indicate that you’re destined to evolve into obesity. You can balance most risk factors via physical activity, diet, exercise, and behavior modifications.
Diagnosis
To analyze obesity, your doctor or provider will generally conduct a physical examination and suggest some examinations.
These examinations and tests normally contain:
Bringing your health record. Your doctor or provider may review your weight record, physical activity, weight-loss efforts, exercise patterns, eating habits, appetite management, what further conditions you’ve had, drugs, stress levels, and different problems with your health. Your doctor may also inspect your family’s health record to see if you may be predisposed to specific conditions.
A general physical examination. This contains estimating your height, inspecting vital signs, like blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature, hearing your heart and lungs, and analyzing your abdomen.
Calculating your BMI. Your doctor will inspect your body mass index (BMI). A BMI of 30 or more increased is believed obesity. Digits higher than 30 gain health risks even more. Your BMI should be inspected at least once a year because it can assist to define your overall health risks and what therapies may be proper.
Calculating your waist circumference. Fat stored near the waist, occasionally known as visceral fat or abdominal fat, may further raise the risk of a heart condition and diabetes. Females with a waist measurement (circumference) of more than 35 inches (89 centimeters) and males with a waist size of more than 40 inches (102 centimeters) may have more health risks than persons with fewer waist measurements. Like the BMI measure, waist girth should be inspected at least once a year.
Checking for different health issues. If you have understood health issues, your doctor will estimate them. Your doctor will also inspect for further possible health issues, like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, underactive thyroid, liver issues, and diabetes.
Treatment of Obesity
The purpose of obesity therapy is to reach and remain at a healthy weight. This enhances overall health and lowers the risk of developing difficulties connected to obesity.
You may require to work with a team of health professionals involving a dietitian, behavioral counselor, or an obesity specialist to assist you to understand and make modifications in your eating and activity patterns.
The initial treatment purpose is generally a modest weight loss of 5% to 10% of your total weight. That suggests that if you weigh 200 pounds (91 kilograms), you’d require to lose only approximately 10 to 20 pounds (4.5 to 9 kilograms) for your health to start to enhance. Yet, the more weight you lose, the greater the advantages.
All weight-loss programs need modifications in your eating patterns and raised physical activity. The therapy techniques that are right for you rely on your obesity severity, your general health, and your willingness to experience your weight-loss plan.
Dietary changes
Decreasing calories and practicing healthier eating patterns are vital to overwhelming obesity. Although you may lose weight fast at first, constant weight loss over the long term is believed the safest manner to lose weight and the best method to maintain it permanently.
There is no best weight-loss diet. Select one that contains healthy foods that you sense will work for you. Dietary modifications to manage obesity contain:
Cutting calories. The key to weight loss is decreasing how many calories you bring in. The first phase is to examine your typical eating and drinking patterns to see how many calories you generally take and where you can cut back. You and your doctor can choose how many calories you require to bring in per day to lose weight, but a specific quantity is 1,200 to 1,500 calories for females and 1,500 to 1,800 for males.
Feeling full on less. Some foods like candies, desserts, fats, and processed foods include a lot of calories for a little amount. In difference, fruits and vegetables deliver a bigger part size with fewer calories. By eating bigger amounts of foods that have rarer calories, you decrease starvation pangs, bring in fewer calories, and feel sufficiently regarding your meal, which contributes to how comfortable you sense overall.
Making healthier choices. To create your overall diet healthier, eat more plant-based foods, like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Also emphasize lean origins of protein like lentils, beans, and soy and lean meats. If you like to fish, attempt to contain fish twice a week. Restrict salt and added sugar. Eat little quantities of fats, and make certain they arrive from heart-healthy sources, like canola, olive, and nut oils.
Restricting specific foods. Specific diets limit the quantity of a certain food group, like high-carbohydrate or full-fat foods. Ask your doctor which diet programs are useful and which might be useful for you. Drinking sugar-sweetened drinks is a confident way to drink more calories than you planned. Restricting these drinks or stopping them altogether is the right position to begin cutting calories.
Meal replacements. These programs recommend substituting one or two meals with their products like low-calorie shakes or meal bars and eating nutritious snacks and a healthy, balanced third dinner that’s lower in fat and calories. In the brief term, this variety of diets can assist you to lose weight. But these diets probably won’t teach you how to alter your general lifestyle. So you may have to remain on the diet if you want to maintain your weight off.
Be wary of fast fixes. You may be tempted by fad diets that vow fast and comfortable weight loss. The reality, yet, is that there are no magic foods or fast fixes. Fad diets may assist in the brief term, but the long-term outcomes don’t seem to be any better than further diets.
Also, you may lose weight on a crash diet, but you’re probably to recover it when you quit the diet. To lose weight and maintain it you must assume healthy-eating patterns that you can sustain over time.
Exercise and activity
Raised physical activity or exercise is an important component of obesity treatment:
Exercise. A person with obesity requires to obtain at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity physical activity to control different weight gain or to keep the loss of a modest quantity of weight. You likely will require to slowly raise the quantity you exercise as your endurance and fitness enhance.
Keep moving. Even though common aerobic exercise is the most efficient way to burn calories and shed extra weight, any additional motion assists burn calories. Park a distance from store doors and bring the stairs rather than the elevator. A pedometer can follow how many steps you bring over a day. Many people attempt to get 10,000 steps every day. Slowly raise the digit of steps you bring daily to achieve that goal.
Behavior modifications
A behavior change schedule can assist you to make lifestyle modifications and lose weight and maintain it. Steps to bring involve studying your current practices to find out what factors, stresses or conditions may have contributed to your obesity.
Counseling. Speaking with a mental health professional can assist address emotional and behavioral problems related to eating. Therapy can assist you to understand why you overeat and learning healthy habits to manage anxiety. You can also know how to observe your diet and exercise, understand eating stimuli, and manage food cravings. Counseling can be done one by one or in a group.
Support groups. You can see camaraderie and understanding in asset groups where others share equal challenges with obesity. Inspect your doctor or health care provider, local hospitals, or commercial weight-loss schedules for support groups in your place.
Weight-loss medication
Your healthcare provider may suggest drugs to use in conjunction with further therapies. Drugs aren’t the whole solution to weight loss, but they can assist to attack it from another grade. For instance, appetite suppressants can block some of the ways to your brain that involve your craving. For some people, this might be a little portion of the puzzle, but for others, it might be a larger one.
Familiar FDA-approved medications for treating obesity contain:
Orlistat (Xenical, Alli): Decreases absorption of fat from your gut.
Phentermine (Lomaira, Adipex-P, Suprenza): Reductions in your appetite. It’s authorized for use for three months at a time.
Benzphetamine (Regimex, Didrex): Declines your appetite.
Diethylpropion (Depletite # 2, Tenuate, Radtue): Reductions your appetite.
Phendimetrazine (Melfiat,Bontril): Reduce your appetite.
Bupropion-naltrexone (Contrave): May decrease cravings and food input.
Liraglutide (Saxenda): Decreases appetite and slows digestion.
Semaglutide (Wegovy): Stops appetite.
Cellulose and citric acid (Plenity): Makes you sense full.
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (Vyvanse): Helps controls symptoms of binge eating disease.
Phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia): Creates you less hungry.
Combination of SGLT2 inhibitors and glucagon-like-1 receptor agonists.
Surgery
These varieties of methods don’t need any incisions in the skin. After you are under anesthesia, flexible pipes and instruments are inserted via the mouth and down the throat into the stomach. Familiar methods contain:
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty. This method includes putting stitches in the stomach to decrease the quantity of food and liquid the stomach can hold at one time. Over time, eating and drinking less assists specific people to lose weight.
Intragastric balloon for weight loss. In this method, doctors or surgeons put a small balloon into the stomach. The balloon is then loaded with water to decrease the quantity of area in the stomach, so you’ll sense completely eating less food.
Weight-loss surgery
Also called bariatric surgery, weight-loss surgery restricts the quantity of food you’re capable of comfortably eating or reduces the absorption of food and calories. Yet, this can also result in healthy and vitamin deficiencies.
Familiar weight-loss surgeries contain:
Adjustable gastric banding. In this method, an inflatable band divides the stomach into two pouches. The surgeon drags the band tight, such as a belt, to make a small channel between the two pouches. The band maintains the opening from growing and is normally designed to remain in position permanently.
Gastric bypass surgery. In gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y), the surgeon or doctor makes a little pouch at the top of the stomach. The little intestine is then cut a brief distance below the main stomach and attached to the new pouch. Food and liquid flow straight from the pouch into this portion of the intestine, bypassing most of the stomach.
Gastric sleeve. In this method, the region of the stomach is extracted, making a less reservoir for food. It’s a less difficult surgery than gastric bypass.
Weight-loss victory after surgery relies on your commitment to creating lifelong modifications in your eating and exercise routines.
Schedules after surgery frequently begin with mild deep breathing and lower body (ankles, legs, feet) exercises. When it is secure, you will progress to strength and aerobic exercise. Your physical therapist will assist you after surgery to:
- Minimize pain.
- Regain movement and strength.
- Return to normal movements as soon as possible.
Additional treatments
Additional treatments for obesity contain:
Hydrogels. Available by prescription, these edible capsules include small particles that soak water and broaden in the stomach, to assist you to feel complete. The capsules are carried before meals and are passed via the intestines as a stool.
Vagal nerve blockade. This includes planting a machine under the skin of the abdomen that transmits intermittent electrical pulses to the abdominal vagus nerve, which informs the brain when the stomach senses empty or complete.
Gastric aspirate. In this method, a tube is put via the abdomen into the stomach. A part of the stomach contents is emptied per meal.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physical therapists utilize the latest proof to design therapy schedules for your precise requirements and purposes. Working with a physical therapist or physiotherapist can assist you:
Control your weight and control obesity.
Develop a schedule to address issues that may affect your capability to be active. Your physical therapist can guide you through fun, pain-free ways to exercise.
Safely advance your physical activity class. The right types and quantity of exercise are essential.
Your physical therapist will perform a complete evaluation. This will contain bringing your health record. They may ask you precise questions, like:
How much everyday physical activity do you do?
Do you have a problem doing any daily activities?
Do you have any joint aches?
Do you have any further medical diseases or issues that make physical activity hard?
Do you take any drugs for obesity or another disease?
Have you had any surgery connected to your obesity?
Are you under the supervision of a physician?
What are your purposes?
Your physical therapist will conduct examinations to inspect your overall fitness. These examinations will evaluate you:
- Movement.
- Strength.
- Coordination.
- Balance.
Your physical therapist also may conduct precise obesity examinations to:
Estimate your BMI (based on your height and weight).
Estimate your waist and skinfold thickness.
See your body fat percentage.
Your physical therapist also may function with your doctor or different health care providers or doctor. Your doctor may order different examinations to rule out different medical situations.
Your physical therapist will act with you to enhance your strength. They also can assist you to enhance your aerobic capacity (capability to convert oxygen to energy during activity). Both aerobic and strengthening activities assist with weight loss and weight control. Physical therapists make safe, adequate physical activity schedules to assist a person of all ages and capabilities. They can assist you to achieve the suggested quantity of physical activity. Beginning a fun exercise routine can assist you to make more suitable options regarding your diet.
Physical therapists also can manage the key causes of unhealthy behaviors. They can assist you:
- Recognize and overcome obstacles to physical activity.
- Develop healthy routines.
- Set personal purposes.
- Form healthy practices to assist you to stick to your schedule.
Your physical therapist therapy schedule will contain working with you to:
Reduce pain. Your physical therapist can instruct you on safe methods to do exercises with the least quantity of pain. Moving more can assist to reduce pain. Your physical therapist will create a schedule to assist you to move more.
Improve cardiovascular fitness. Your physical therapist will create a heart-healthy aerobic exercise schedule for you. This schedule will enhance your metabolism (the method of getting energy from food). It also will assist you to burn more calories. Physical therapists assist grown-ups, kids, and a person with disabilities do aerobic activities at their convenience level.
Improve strength. Your physical therapist will guide you through exercises to manage muscle weakness or enhance your strength. Building muscle strength benefits too:
- Burn calories.
- Make daily activities more comfortable.
- Reduce joint pain.
- Mild and low-impact resistance training (using elastic bands) can assist you to avoid joint stress.
Improve movement. Your physical therapist will choose precise activities and treatments to assist restore the normal motion of stiff joints. These might start with passive movements that your physical therapist functions for you. Then, you will advance to active activities that you do yourself.
Improve flexibility and posture. Your physical therapist will decide if any of your main muscles are tense. They will instruct you how to gently lengthen any tense muscles. Your physical therapist also will evaluate your posture. They will guide you through exercises to enhance your capability to maintain correct posture. Good posture can create doing difficult movements easier and less painful. It also can enhance your breathing.
Increase activity levels. Your physical therapist will examine your activity purposes with you. They will design a safe therapy schedule to address your precise requirements to assist you to achieve your purposes in the fastest, most useful way likely.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Your struggle to overcome obesity is more probable to be victorious if you follow procedures at a house in addition to your formal therapy plan. These can contain:
Learning regarding your situation. Education regarding obesity can assist you to learn more about why you formed obesity and what you can do regarding it. You may sense more empowered to bring control and stick to your therapy plan. Read respected self-help books and believe in speaking regarding them with your doctor or therapist.
Setting realistic goals. When you keep losing a lot of weight, you may fix unrealistic plans, like attempting to lose too much too fast. Don’t put yourself up for failure. Fixed daily or weekly plans for activity and weight loss. Create small modifications in your diet rather than trying drastic modifications that you’re not probable to attach with for the long haul.
Sticking to your therapy plan. Altering a lifestyle you may have lived with for many years can be hard. Be frank with your doctor, therapist, or different health care professionals if you see your activity or eating plans slipping. You can work jointly to come up with new concepts or new methods.
Enlisting support. Obtain your family and friends on a panel with your weight-loss plans. Cover yourself with persons who will support you and assist you, not undermine your struggles. Make foolproof they understand how significant weight loss is to your health. You might also like to enter a weight-loss support group.
Keeping a record. Maintain a food and exercise log. This document can assist you to stay responsible for your eating and exercise routines. You can find behavior that may be maintaining your back and, conversely, what functions well for you. You can also use your diary to track further essential health parameters like blood pressure and cholesterol levels and general fitness.
Complications
Patients with obesity are more probable to develop several potentially severe health issues, involving:
Heart condition and strokes. Obesity makes you more probable to have high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for heart conditions and strokes.
Type 2 diabetes. Obesity can involve the way the body uses insulin to maintain blood sugar levels. This increases the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Certain cancers. Obesity may raise the chance of cancer of the uterus, endometrium, cervix, breast, ovary, rectum, colon, liver, esophagus, pancreas, kidney, gallbladder, and prostate.
Digestive issues. Obesity raises the likelihood of creating heartburn, gallbladder condition, and liver issues.
Sleep apnea. Patients with obesity are more probable to have sleep apnea, a potentially severe condition in which breathing frequently stops and begins during sleep.
Osteoarthritis. Obesity raises the stress put on weight-bearing joints, in extra to elevating inflammation within the body. These factors may conduct to difficulties like osteoarthritis.
Severe COVID-19 symptoms. Obesity raises the risk of developing extreme symptoms if you evolve infected with the virus that generates coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). A patient who has extreme cases of COVID-19 may need therapy in intensive care units or even mechanical assistance to breathe.
Prevention
Obesity prevention for kids
Obesity prevention starts in the young generation. It’s essential to assist a young patient to keep a healthy weight without concentrating on the scale.
Breastfeed infants, when possible
One 2014 study of 25 analyses found that breastfeeding was associated with a decreased risk of childhood obesity. Yet, analyses are combined when it arrives to the role of breastfeeding in obesity prevention, and more study is required.
Feed growing kids proper portion sizes
The American Academy of Pediatrics explains that toddlers don’t need huge quantities of food. From years 1 to 3, every inch of height should correlate to approximately 40 calories of food input.
Motivate more aged kids to learn what different part sizes look like.
Create early relationships with healthy foods
Motivate your kid to attempt a mixture of various vegetables, fruits, and proteins from an earlier age. As they develop more senior, they may be more probable to include these healthy foods in their diet.
Eat healthy foods as a family
Altering eating practices as a family permits kids to feel healthy eating early on. This will create it more comfortable for them to persist in following good eating patterns as they develop into grown-ups.
Motivate eating gradually and only when hungry
Overeating can occur if you eat when you’re not starving. This extra fuel finally evolves stored as body fat and can conduct to obesity. Motivate your kid to eat only when they sense starvation and to chew more gradually for adequate digestion.
Limit unhealthy foods in the household
If you get unhealthy foods into the household, your kid may be more probable to eat them. Attempt to stock the fridge and pantry with nutritious foods, and permit less-healthy snacks as a periodic manage rather.
Incorporate fun and exciting physical activity
The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that children and teens reach at least 60 minutes of physical activity every day. Fun physical exercises contain sports, gym classes, games, or even outdoor chores.
Limit your kid’s screen time
More time consumed sitting in front of a screen indicates less time for physical exercise and good sleep. Because activity and sleep play a part in a healthy weight, it’s essential to facilitate those movements over computer or TV time.
Make sure everyone is getting adequate sleep
Analysis indicates that both kids and grown-ups who don’t get adequate sleep may end up weighing more. Healthy sleep patterns from the National Sleep Foundation contain a sleep program, a bedtime routine, and a satisfactory pillow and mattress.
Know what your kid is eating outside of the home
Whether in school, with friends, or while being babysat, kids have plenty of options to eat harmful foods outside of the house. You can’t ever be there to watch what they eat, but asking questions can assist.
Obesity prevention for adults
Much of this obesity prevention information is the same for losing or keeping a healthy weight. The base is a line that eating a nutritious diet and bringing more physical activity can assist to control obesity.
Consume less bad fat and more good fat
Contrary to the idea behind the low-fat diet craze of the 90s, not all fat is bad. A 2017 analysis posted in the Nutrition Journal showed that the input of healthy dietary fats, like polyunsaturated fats, can enhance cholesterol levels and decrease obesity risk.
Consume less processed and sugary foods
According to a 2016 analysis posted in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, input of processed and ultra-processed foods is connected to a more increased risk of obesity. Many processed foods are increased in salt, fat, and sugar, which can promote overeating.
Eat more servings of vegetables and fruits
The daily suggestion for fruit and vegetable input is five to nine servings per day for grown-ups. Loading your plate with veggies and fruit can assist keep calories reasonable and decrease the risk of overeating.
Eat plenty of dietary fiber
Analyses continue to indicate that dietary fiber plays a part in weight care. One 2012 test found that patients who brought a fiber complex supplement three times every day for 12 weeks lost up to 5 % percent of their body weight.
Focus on eating low glycemic index foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale used to calculate how fast a food item will increase your blood sugar. Concentrating on low-GI foods can assist to maintain blood sugar levels more constant. Maintaining your blood glucose levels stable can assist with weight management.
Get the family interested in your journey
Social support isn’t only for kids and teens its essential for grown-ups to sense support too. Whether cooking with family or going on walks with friends, bringing a person interested can assist to promote a healthy lifestyle.
Engage in regular aerobic activity
Mixing regular physical activity into your program is essential for keeping or losing weight, among further benefits. The CDC suggests 150 minutes of mild aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise per week.
Incorporate a weight training regimen
Weight training is only as essential to weight keeping as an aerobic activity. In extra to weekly aerobic exercise, the WHO suggests weight exercise that affects all your major muscles at least two times per week.
Focus on decreasing daily stress
Stress can have many outcomes on the body and mind. A 2012 analysis indicates that stress may activate a brain reaction that alters eating habits and leads to cravings for high-calorie foods. Eating too considerably high-calorie foods can contribute to the growth of obesity.
Learn how to the food budget and meal prep
It’s much easier to the grocery store for nutritious foods when you have a schedule. Making a food budget and list for your shopping journeys can assist avoid attractions for unhealthy foods. In addition, preparing meals can permit you to have ready-to-go nutritious dinners.
FAQ
How to reduce obesity?
Selecting healthier foods (whole grains, healthy fats, protein sources, fruits, and vegetables,) and drinks. Restricting unhealthy foods (refined grains and potatoes, sweets, processed meat, red meat) and drinks (sugary drinks) Improves physical activity. Restricting screen time, television time, and further sit time
Which obesity is more harmful?
The collection of fat in the abdominal area, or central obesity, is more harmful than obesity in general and can conduct in a faster death
Who suffers from obesity?
Obesity involves some groups more than further
The obesity majority was 39.8% among grown-ups aged 20 to 39 years, 44.3% among grown-ups aged 40 to 59 years, and 41.5% among grown-ups aged 60 and more aged.
Is obesity cancerous?
Being overweight and obese can generate modifications in the body that assist to conduct cancer. These modifications can contain long-lasting inflammation and more elevated than normal levels of insulin, insulin-like growth factor, and sex hormones.
Does fasting reduce obesity?
Fasting for brief periods assists a person to eat fewer calories, which may result in weight loss over time. Yet, intermittent fasting may also assist to change risk factors for health diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular condition, like decreasing cholesterol and blood sugar levels.



21 Comments